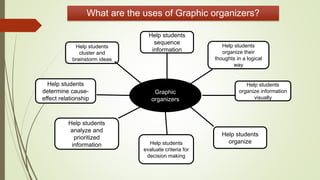
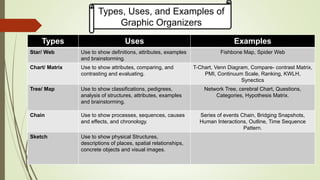
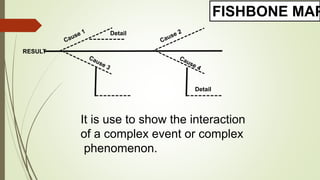
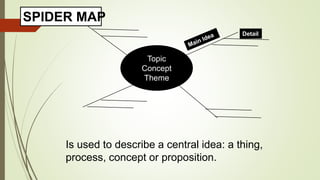
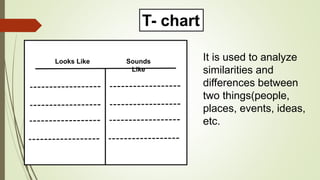
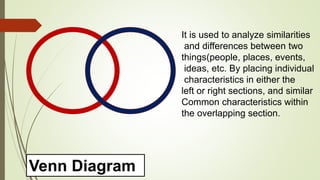
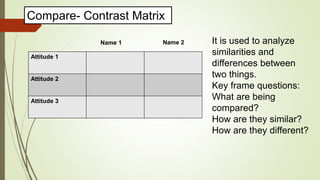
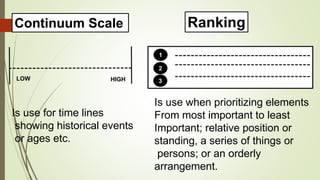
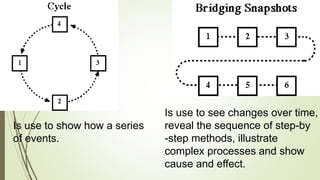
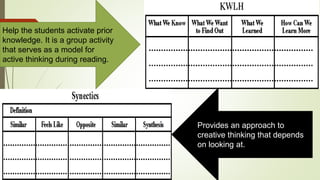
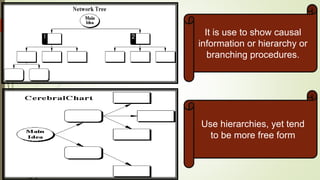
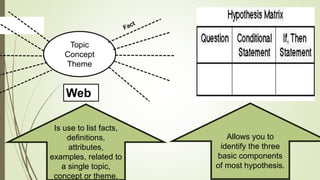
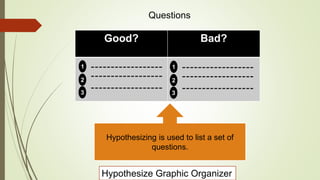
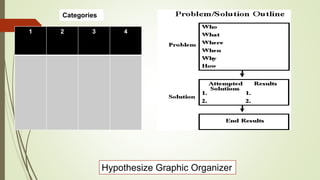
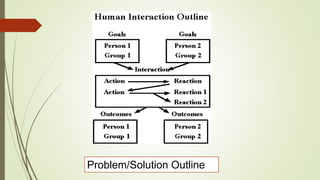
Graphic organizers are visual tools that help students actively organize and structure information. They can be used to sequence events, compare and contrast ideas, classify information, and show relationships. Common types include webs, charts, trees, and chains. Graphic organizers compress information, focus learning, and make complex ideas easier to understand. They guide students' research by focusing their purpose and showing what information has been collected and what is still missing. Overall, graphic organizers promote higher-order thinking by engaging students in active representation of key concepts and skills.