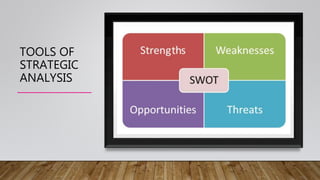
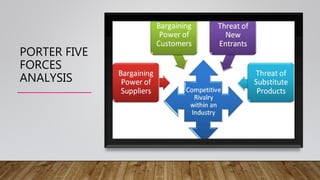
This document discusses strategic analysis and intuitive thinking. It defines strategic analysis as researching a business's environment and itself to formulate strategy. It explains tools for strategic analysis like PEST analysis, SWOT analysis, Porter's Five Forces, and value chain analysis. PEST analysis examines political, economic, social, and technological factors. SWOT analyzes strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Intuitive thinking is decision making based on feelings and past experience rather than facts. Characteristics of intuitive leaders include seeing patterns, using analysis as support, sizing people up, and lifelong learning. Intuition can be improved by developing leader characteristics and practicing intuitive decision making.