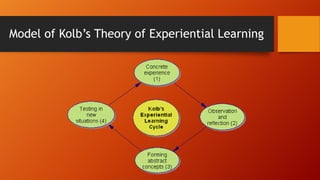
Kolb's theory of experiential learning posits that learning is a process that involves creating knowledge through the transformation of experiences. It involves four stages: concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation. Experience plays a central role in learning as knowledge is continuously created and recreated through transforming experiences. Kolb's theory aligns with adult development as experience is the source of both learning and development for adults. Experiential learning can be applied to teaching by incorporating experiences that engage students personally and allow for reflection and discussion to optimize the learning process.