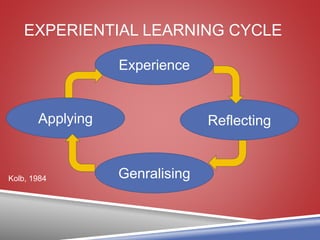
This document discusses experiential learning and Kolb's experiential learning cycle. It defines experiential learning as engaging in an activity, reflecting critically on it, deriving useful insights, and incorporating what was learned through changed understanding or behavior. The experiential learning cycle involves four steps: having an experience, reflecting on that experience, thinking about how to apply what was learned, and using those lessons to inform future experiences. Experiential learning involves actively engaging intellectually, physically, emotionally, and socially through experiences that can involve success, failure, risk-taking, and uncertainty.