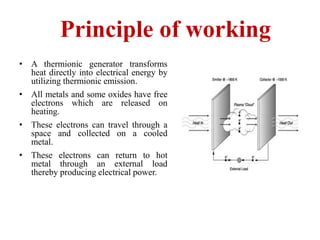
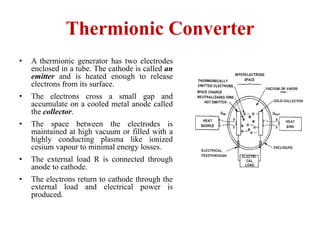
Thermionic conversion directly converts heat into electrical energy using thermionic emission. A thermionic generator has two electrodes in a vacuum tube - a heated cathode that emits electrons and a cooled anode that collects them. As electrons travel through an external load, electrical power is produced. Thermal efficiencies of 10-20% have been achieved, with higher efficiencies possible in the future. Thermionic generators can utilize various heat sources and have applications for remote power generation on Earth and in space.



![Performance of Thermionic Generator
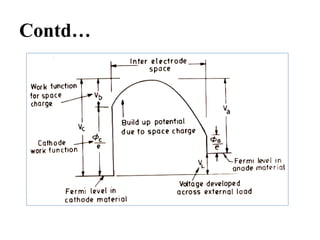
Thermal Efficiency of thermionic generator,
η = {(γc - θ γa)[1 – θ2 e(γc
- γa
)]}/{(γc + 2) – θ2 (γa + 2θ) e(γc
- γa
)}
Where, θ = Ta/Tc
γc = Vc/KTc, γa = Va/KTa,
Where K = Boltzmann’s constant
= 1.38 x 10-23
V = Work function for space charge
If γc = γa, and neglecting the smaller terms
ηmax = (1 – θ) . γ/(γ + 2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thermionicconversion-220123052452/85/Thermionic-conversion-6-320.jpg)