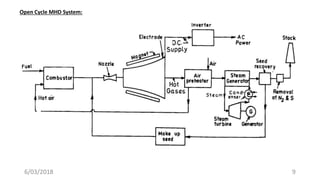
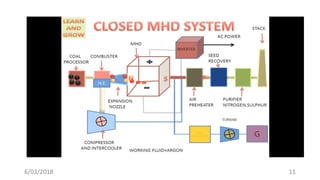
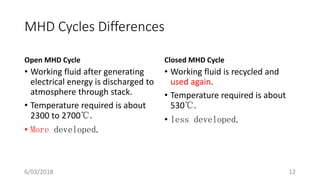
The document discusses magneto hydrodynamic (MHD) power generation as a direct energy conversion system that transforms thermal energy into electrical energy without mechanical energy conversion, promoting fuel economy. It outlines the principles, types (open and closed cycle MHD), advantages, and disadvantages, as well as applications in various fields. Additionally, it highlights the need for further research to address challenges related to materials that can withstand high temperatures and corrosive environments.