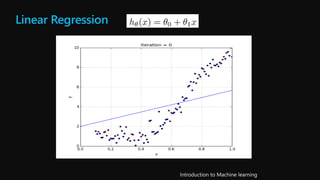
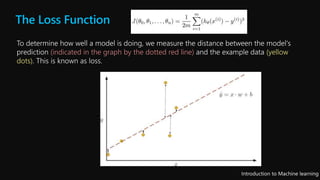
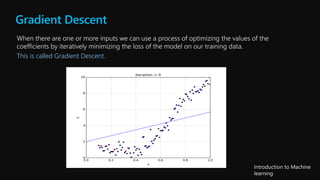
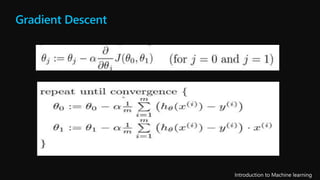
This document serves as an introductory overview of machine learning, detailing its principles, types, and applications. It explains the differences between supervised, unsupervised, deep learning, and reinforcement learning, along with concepts such as features and regression models. The course emphasizes hands-on experience and the importance of relevant data in training machine learning algorithms to make predictions.













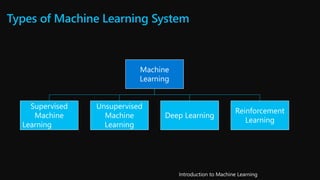
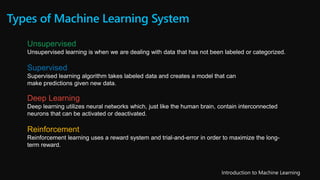
![Types of Machine Learning System
[NOC]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoml-200616172757/85/MachineLlearning-introduction-20-320.jpg)