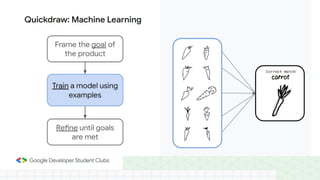
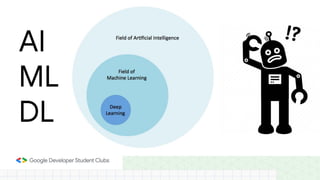
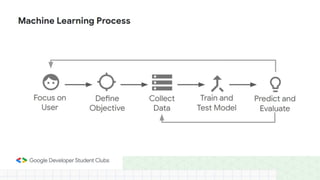
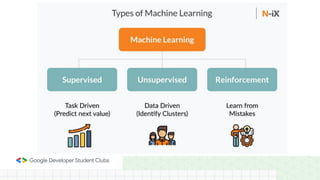
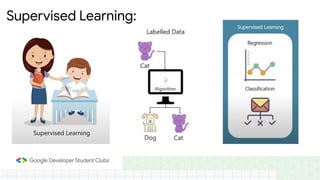
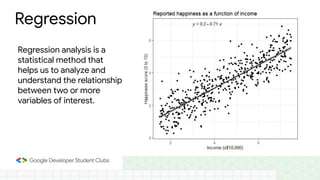
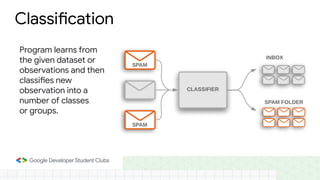
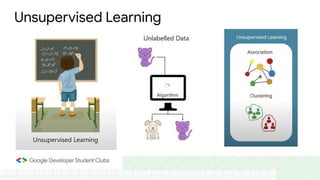
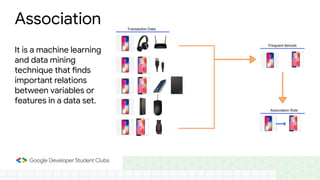
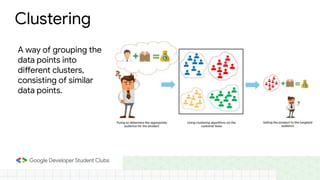
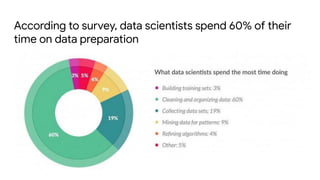
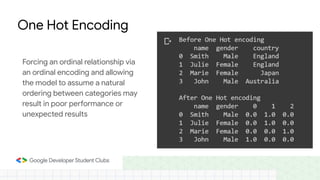
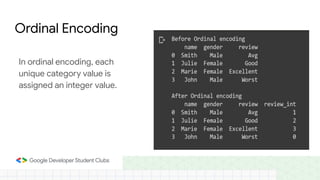
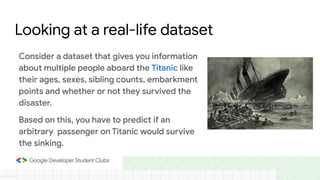
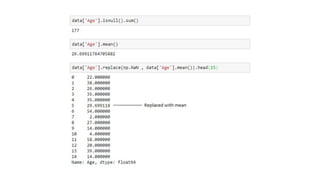
This document provides an introduction to machine learning concepts including supervised learning techniques like regression, classification, unsupervised learning techniques like clustering and anomaly detection, and reinforcement learning. It discusses common machine learning tasks like feature handling, preparing data by addressing issues like categorical variables, missing values which can be handled using mean, median or mode imputation methods. Real-life machine learning problems often involve analyzing datasets to make predictions, which requires data cleaning and feature engineering steps before applying machine learning algorithms.