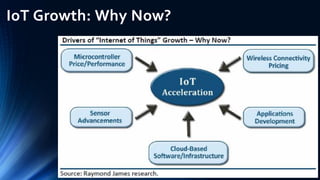
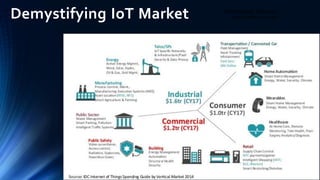
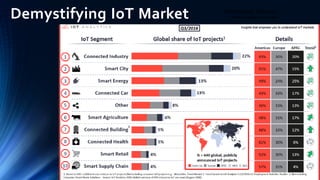
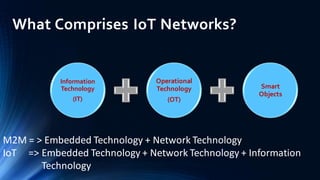
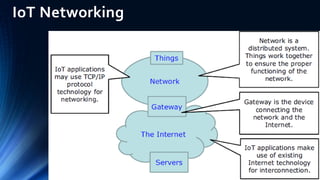
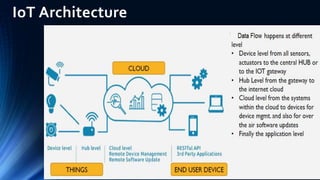
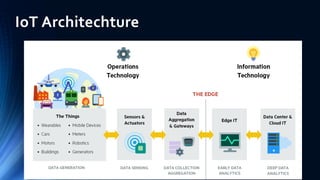
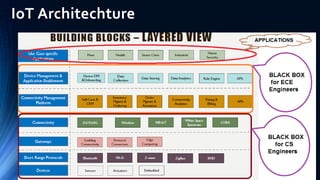
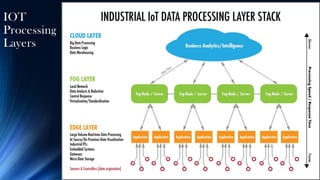
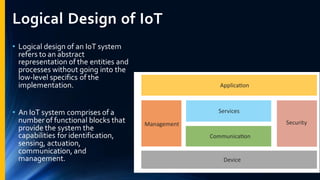
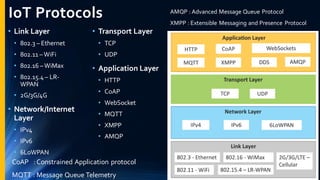
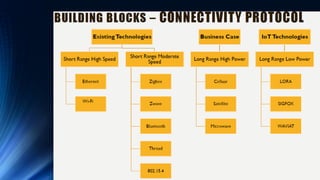
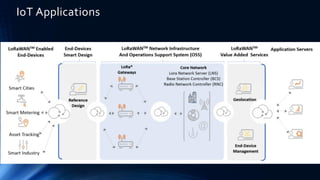
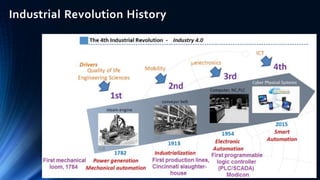
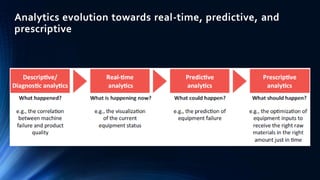
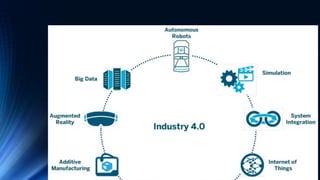
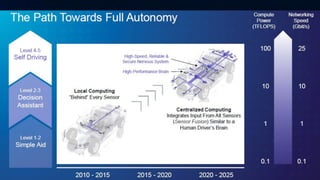
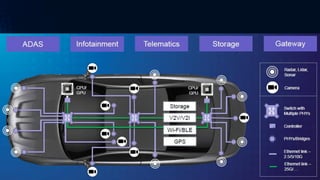
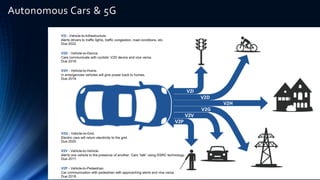
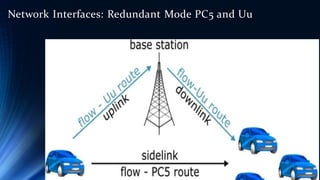
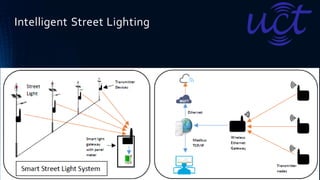
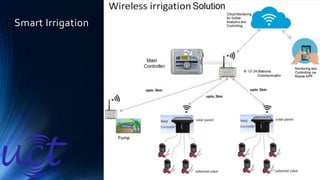
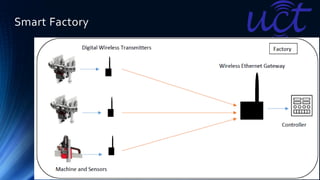
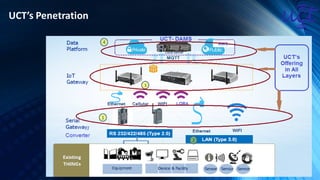
The document provides an overview of the Internet of Things (IoT). It discusses IoT architecture including components like sensors, gateways, cloud platforms and applications. It outlines various IoT applications in different domains like manufacturing, healthcare, transportation etc. The document also discusses challenges in IoT deployment related to interoperability, security and skills. It highlights the importance of skills like embedded systems, cloud computing, data analytics for jobs in IoT domain. Finally, it gives examples of how a company called UCT is applying IoT in products like street lighting, irrigation and building automation.