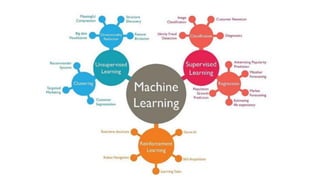
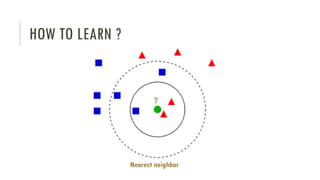
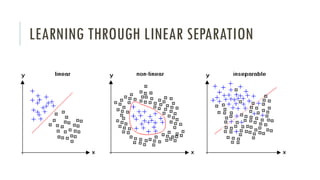
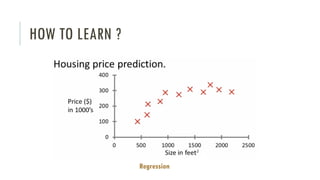
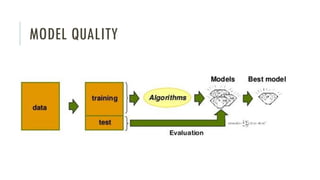
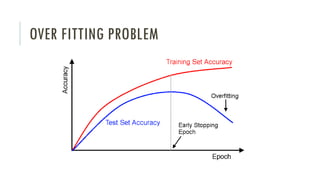
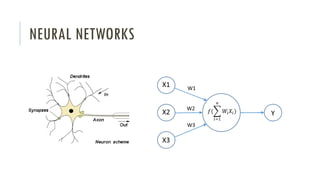
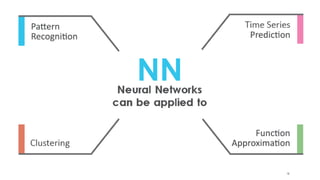
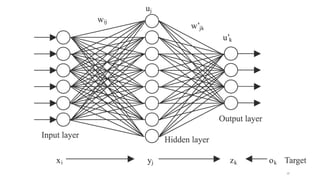
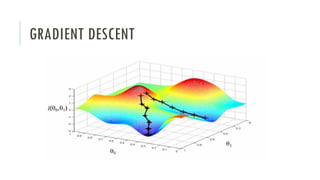
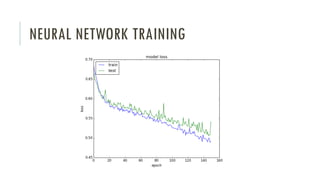
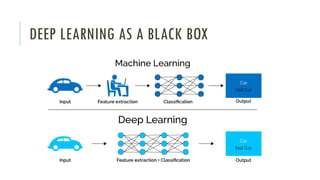
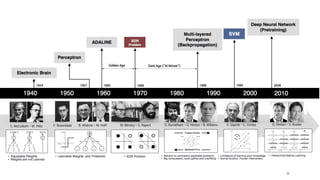
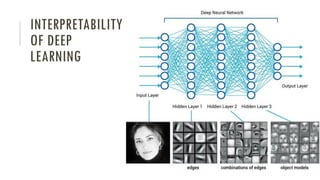
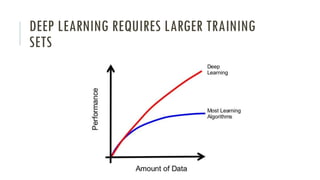
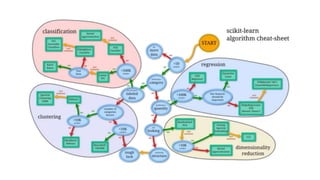
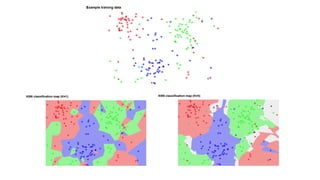
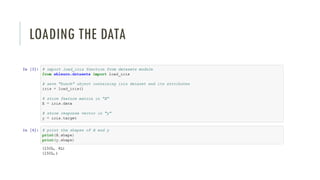
The document outlines an introductory agenda for a machine learning presentation, covering tools such as scikit-learn, case study applications, and key learning resources. It emphasizes hands-on learning through examples like the iris dataset and discusses machine learning concepts like classification, regression, and model evaluation techniques. The presentation also advises next steps for participants, including completing specific courses and engaging in Kaggle competitions.