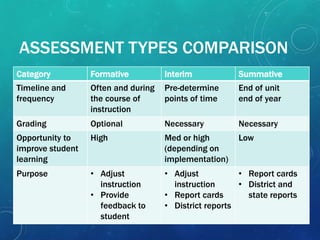
The document discusses different types of assessment including formative, interim/benchmark, and summative assessment. It defines formative assessment as a process of gathering evidence of student learning through feedback and adjusting instruction to enhance achievement. Formative assessment includes informal observations and formal activities like quizzes. Summative assessment evaluates student learning at the end of a period of instruction, while interim assessments evaluate periodically. The document emphasizes that the purpose of assessment is to improve student learning and instructional practices.