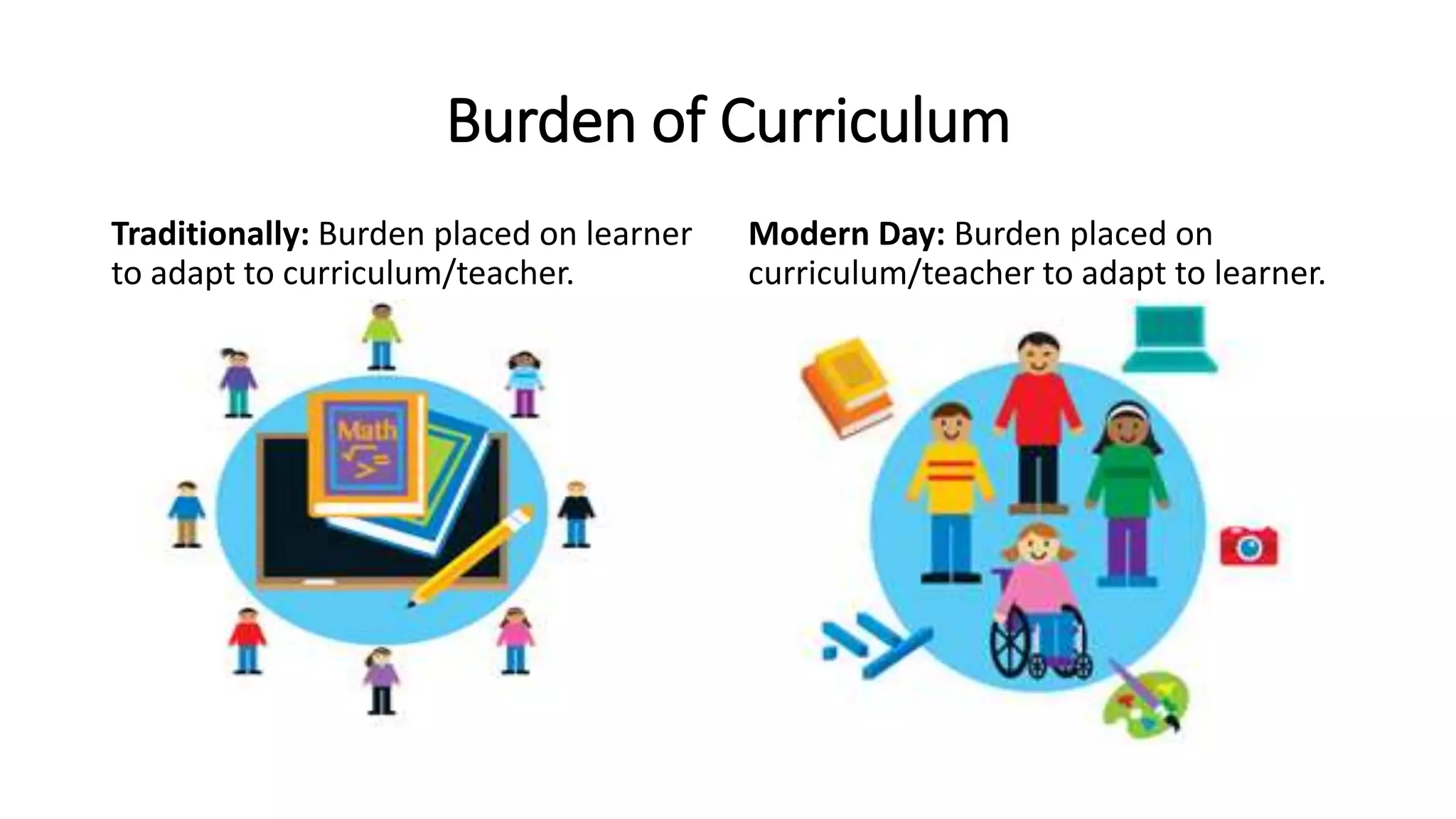
The document outlines the concept of blended learning as a personalized approach to education, emphasizing the need for a shift from traditional curriculum burdens to student-centered learning. It details various blended learning models, including the rotation model, which incorporates different instructional strategies to support individual learning paths. Additionally, it highlights essential components of personalization, equitable access, and the use of technology to enhance student engagement and achievement.