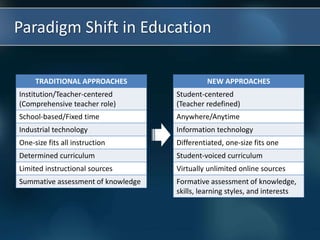
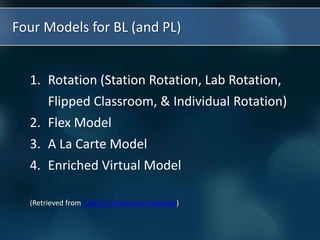
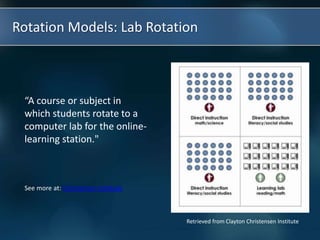
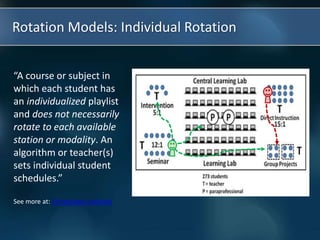
The document discusses the paradigm shift occurring in education from traditional teacher-centered models to new student-centered approaches enabled by technology and personalized learning. It defines blended learning as a formal education program that combines online and in-person learning, with students having some control over time, place, path and pace. Personalized learning tailors instruction to individual student needs, interests and preferences. The document then describes four models for blended and personalized learning: rotation models, flex model, a la carte model, and enriched virtual model.