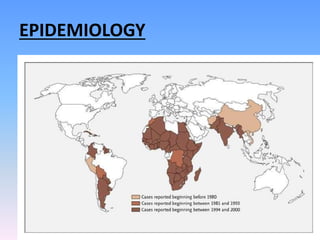
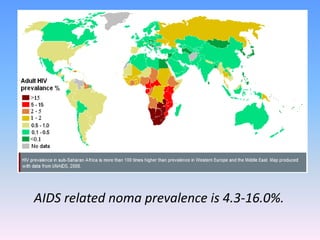
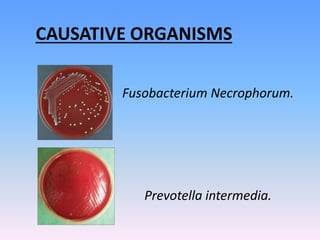
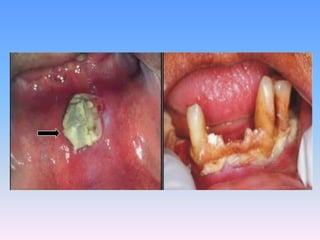
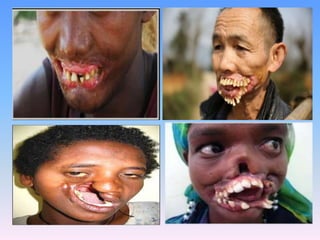
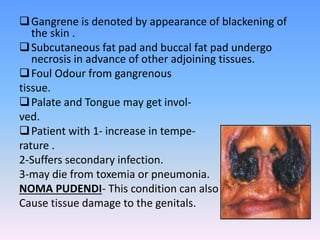
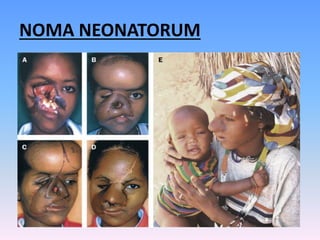
This document discusses Noma (bacterial infection of oral cavity). Noma is a rapidly progressive, polymicrobial infection caused by components of the normal oral flora that become pathogenic during periods of compromised immune status. It most commonly affects malnourished or immunocompromised children between 1-10 years of age or immunocompromised adults. Clinically, it begins as a small ulcer that rapidly spreads and causes gangrenous necrosis of the surrounding tissues of the jaw, lips, and cheeks. Treatment involves antibiotics like penicillin and metronidazole along with surgical excision of necrotic tissues. Even with treatment, mortality rates are high, around 75% prior to availability of antibiotics.