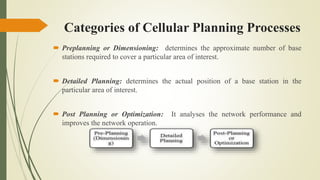
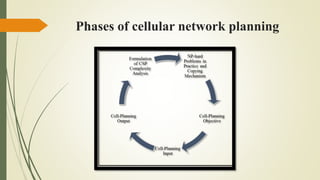
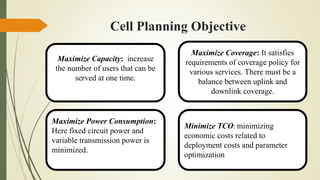
The document discusses capacity planning in cellular networks, highlighting its crucial role in optimizing coverage and minimizing the number of base stations. It covers components such as traffic modeling, planning phases, recent trends like energy-efficient strategies, and the challenges posed by new technologies like 5G, IoT, and M2M communications. The conclusion emphasizes the necessity of adapting to new technologies to improve network efficiency and support increasing traffic demands.