Embed presentation
Download as PPSX, PPTX

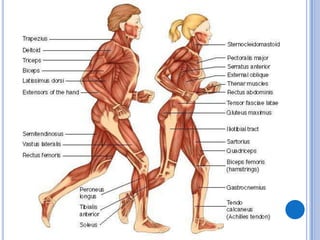

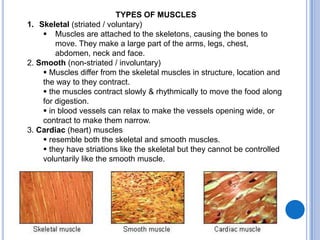
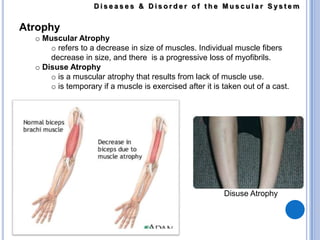



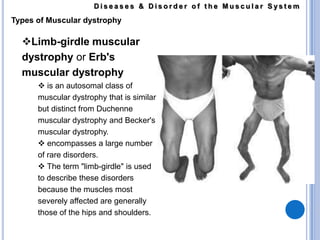



The muscular system allows for movement through muscles that are connected to the skeleton and controlled by the nervous system. There are three main types of muscles: skeletal muscles that move bones, smooth muscles that control internal organs, and cardiac muscles that form the heart. Muscular dystrophy is a genetic disease characterized by the progressive weakening and loss of skeletal muscles. Some common forms include Duchenne muscular dystrophy which affects boys and leads to wheelchair dependence in the early teens, and facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy which initially affects muscles in the face, shoulders, and arms. Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy affects muscles in the hips and shoulders. Myotonic muscular dystrophy affects multiple body systems and causes muscle wasting










