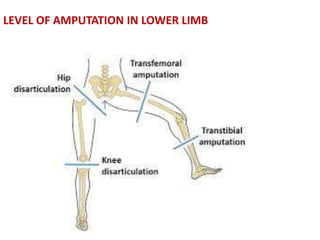
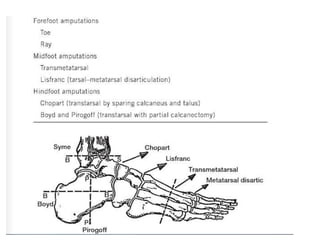
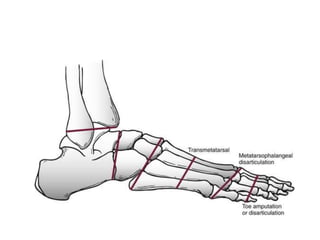
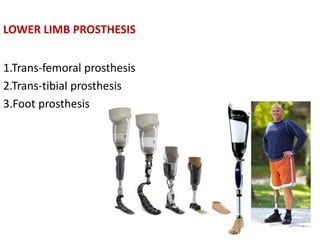
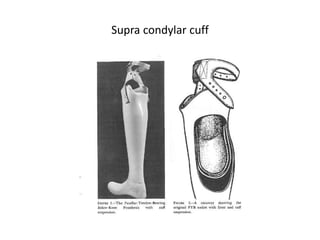
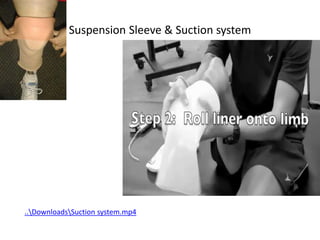
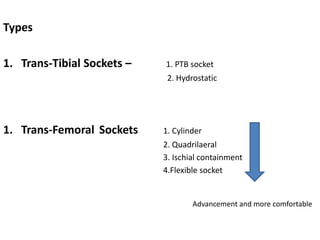
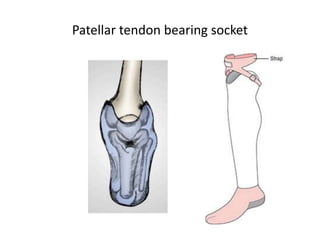
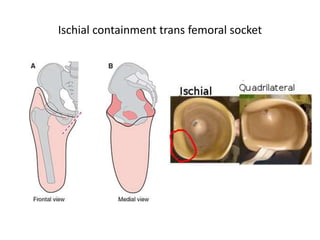
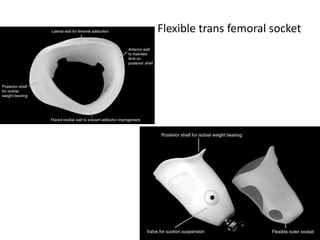
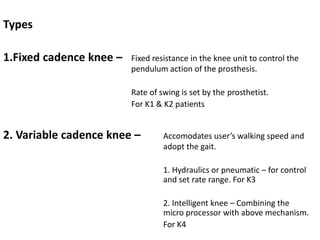
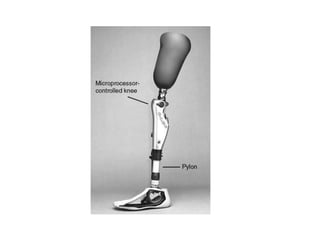
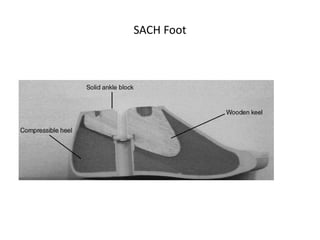
This document discusses lower limb prosthetics. It defines key terms like prosthesis, residual limb, and orthosis. It then describes the ideal characteristics of a prosthesis and factors considered in prescribing one, like amputation level and activity level. The major components of a lower limb prosthesis are also outlined, including the suspension system, socket, knee joint (for transfemoral prosthetics), pylon, and terminal device. Different types of each component are explained. Complications from prosthetics are noted.