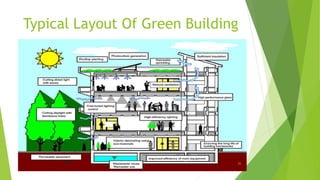
Green building materials aim to reduce environmental impact and promote sustainability. Some key green building materials include wool bricks, sustainable concrete containing recycled materials, and paper insulation made from recycled paper. Selection criteria for green building materials include factors like durability, embodied energy, and toxicity. Fundamental green building principles center around efficient structure design, energy/water use, materials selection, and waste reduction. Several notable green building projects in India employ strategies like natural ventilation, greywater systems, and solar power to lessen environmental impact.