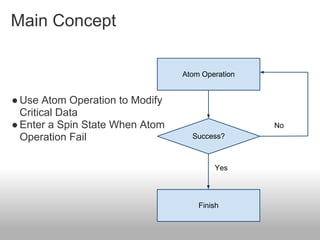
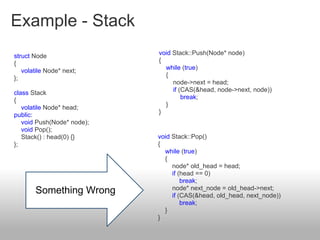
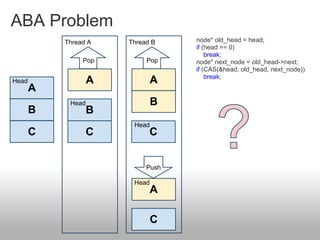
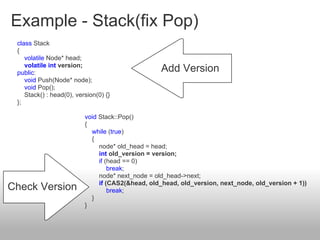
Lock-free algorithms use atomic operations instead of locks to allow for thread-safe concurrent access to shared data structures. This avoids issues like deadlocks but makes implementation more complex. Common atomic operations include compare-and-swap (CAS) and load-linked/store-conditional (LL/SC). A key challenge is avoiding the ABA problem where a value is changed back to its original. Solutions involve adding version numbers or using more advanced operations like CAS2. Overall, lock-free approaches can improve performance over locking but require careful design to ensure correctness and avoid data corruption between threads.




![What is Lock-Free?
A lock-free data structure is one that doesn't
use any mutex locks. The implication is that
multiple threads can access the data structure
concurrently without race conditions or data
corruption, even though there are no locks —
people would give you funny looks if you
suggested that std::list was a lock-free data
structure, even though it is unlikely that there
are any locks used in the implementation. [1]
Non-Blocking
Obstruction-Free
Lock-Free
Wait-Free
[1] http://www.justsoftwaresolutions.co.uk/threading/non_blocking_lock_free_and_wait_free.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lock-freealgorithms-130724010300-phpapp02/85/Lock-free-algorithms-5-320.jpg)