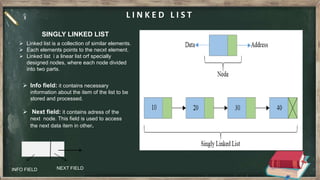
This document provides summaries of different data structures: arrays, stacks, queues, and linked lists. Arrays allow storing multiple values in a single variable using indexes. Stacks follow LIFO order using push and pop operations. Queues follow FIFO order using enqueue and dequeue operations. Linked lists contain nodes with a data and pointer to the next node, allowing dynamic size lists.



![01 02 03
A R R AY
INTRODUCTION
TO ARRAY
Array is vital part of
programming. It
allows user to stored
multiple value in
single variable.
For example an
array may contains
all integer or
character elements,
but not both. Each
array can be
accesed by using
array index and its
is must be poitive
integer value
This is starts from
the numerical
value 0 and ends
at 1 less thanof the
array index value.
For example an
array[n] containing
n number of
elements are
denoted by 0’s and
1’s is called array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructure-210824095803/85/Data-structure-4-320.jpg)





}[())]) is not a simple counting is
not enough to check balance.
You can do it with a stack: going left
to right,
• If you see a (, [, or {, push it on the
stack.
• If you see a ), ], or }, pop the stack
and check wheather you got the
corresponding (, [, or {
Checking For Balanced
Braces](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructure-210824095803/85/Data-structure-10-320.jpg)