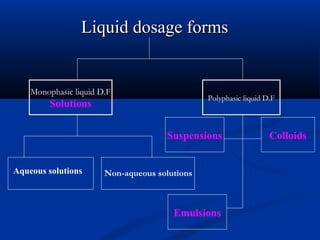
This document discusses different types of liquid dosage forms including solutions, suspensions, emulsions, and colloids. It defines each type and provides examples. Solutions are homogeneous mixtures where one substance is dissolved in another. Factors that affect solubility include temperature, nature of the solute and solvent, and pH. The document focuses on solutions, classifying them based on route of administration, composition, vehicle, and concentration. It also discusses saturated, unsaturated, and solubility of solutions.