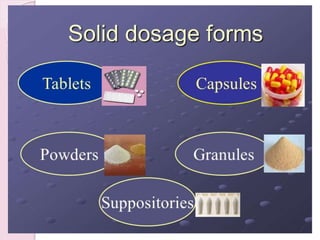
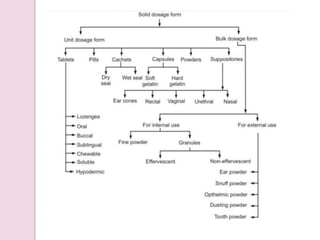
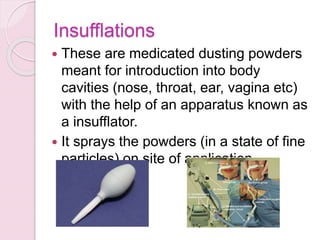
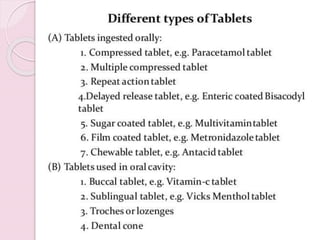
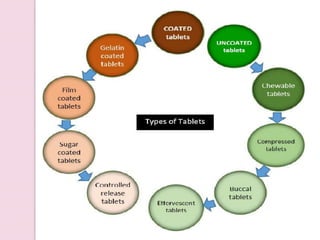
The document provides an overview of solid dosage forms, classifying them into various categories based on their intended use, such as powders, tablets, granules, and capsules. It details the preparation, advantages, and disadvantages of these dosage forms, emphasizing benefits like precise dosing and ease of formulation, while also noting challenges such as difficulty in swallowing for certain populations. Key types of solid dosage forms include effervescent granules, coated granules, and various powder applications, with specific mentions of their uses in medical and surgical contexts.