This document discusses different types of powders used in pharmaceuticals. It describes powders as mixtures of finely divided drugs or chemicals in dry form that can be used internally or externally. The key types discussed are:
- Bulk powders for internal or external use which contain multiple doses and are less accurate.
- Simple and compound powders for internal use which contain a single ingredient or multiple ingredients divided into individual doses wrapped in paper.
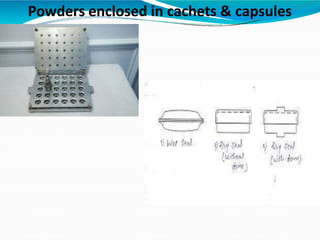
- Powders enclosed in capsules or cachets to allow ingestion of unpleasant tasting powders.
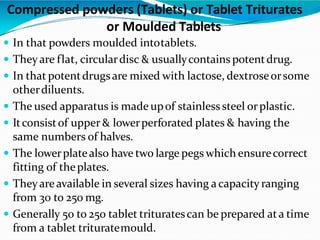
- Compressed powders which are potent drugs mixed with diluents and compressed into tablet form using moulds.