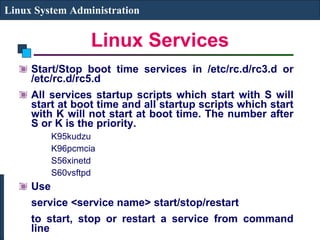
The document discusses various system administration tasks in Linux including setting the run level, managing users and services, monitoring the system, and configuring networking. It provides details on default runlevels, common Linux services, managing user accounts through commands like useradd and managing service startup scripts located in /etc/rc.d directories.