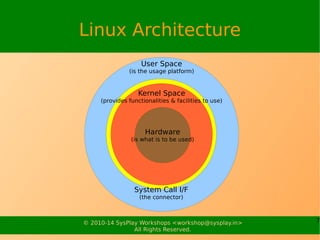
The document provides an overview of the Linux kernel, including its architecture, startup process, functionality, configuration, and compilation. It discusses the differences between micro and monolithic kernels. It also explains the Linux kernel architecture with user space and kernel space separated by a system call interface. Key aspects covered include process management, memory management, device management, and the kernel build system.