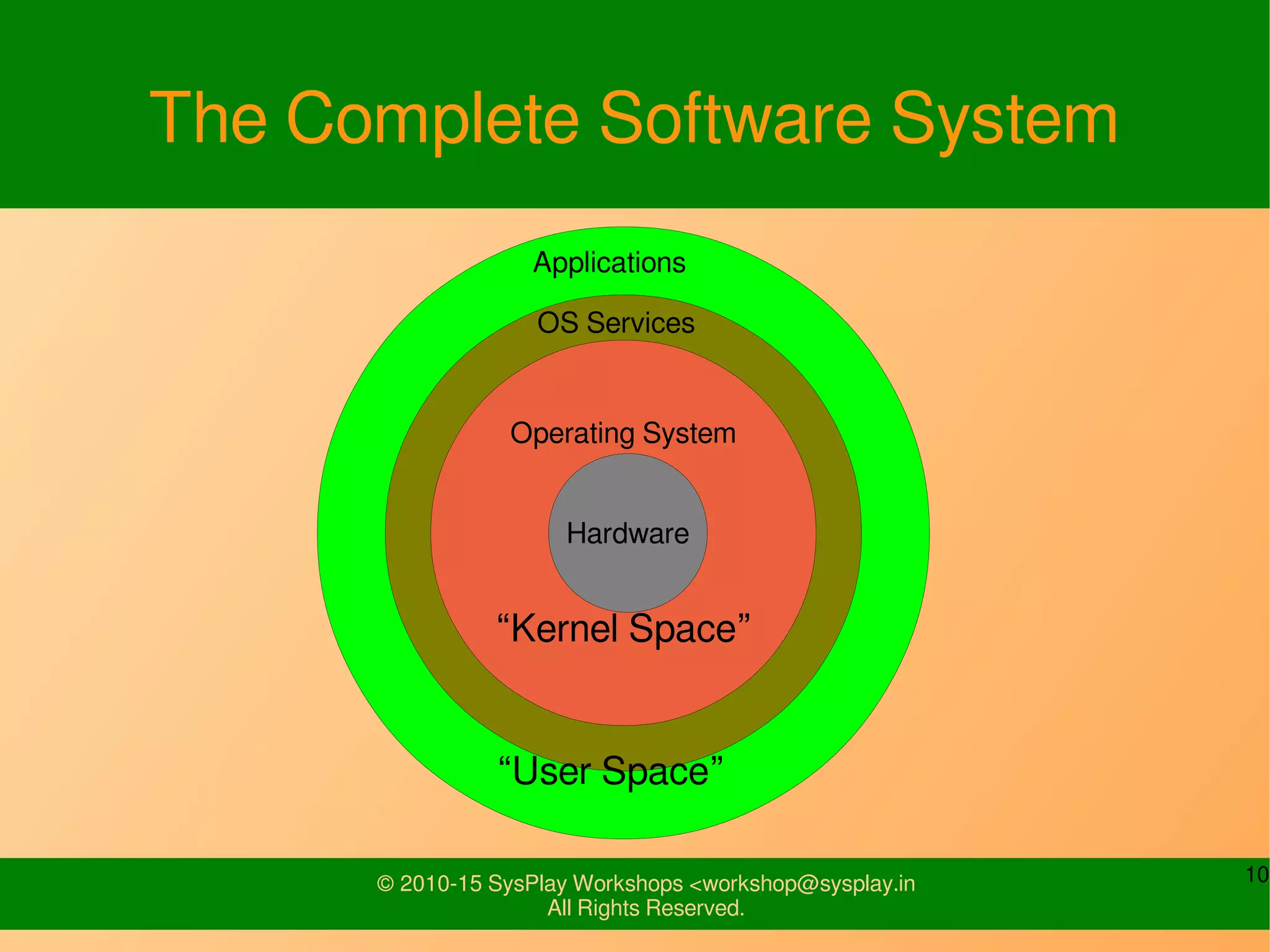
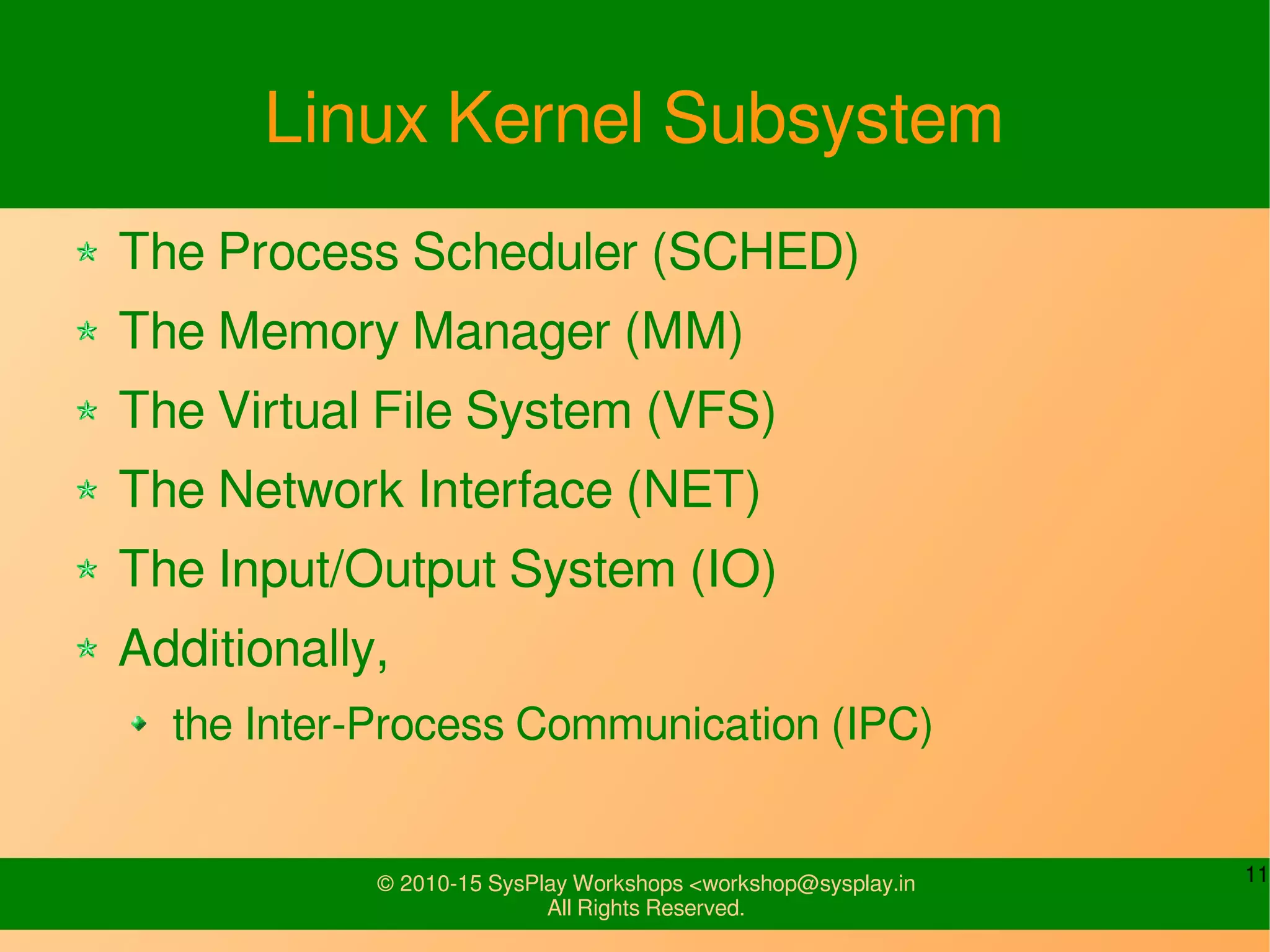
This document provides an introduction to Linux, including definitions of open source software and its advantages. It discusses the Linux system overview consisting of the kernel, OS services, and applications. It also covers Linux usage basics such as directories, shells, files, users, permissions, and input/output redirection. The document is intended to explain what topics will be covered in an introduction to Linux workshop.















![19© 2010-15 SysPlay Workshops <workshop@sysplay.in
All Rights Reserved.
Bourne Again SHell
env - shell environment variables
export [var_name] - export a shell variable
HOME - path to user’s home directory
PATH - executable search path
PWD - present user directory
PS1 - command prompt
which - shows executable path
history - command recall](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontolinux-101003193742-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Linux-19-2048.jpg)