This document provides an introduction to Linux, including:
- An overview of what Linux is, its history originating from UNIX, and popular Linux distributions like Red Hat, Debian, and SuSE.
- A comparison of Linux and Windows in terms of cost, open source vs proprietary software, and operating system stability.
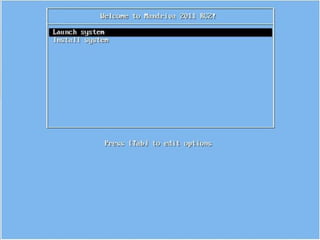
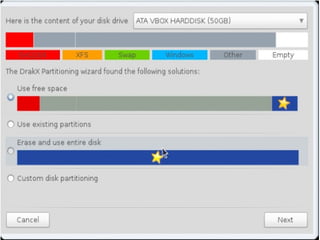
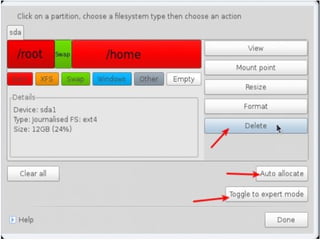
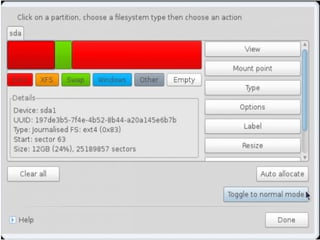
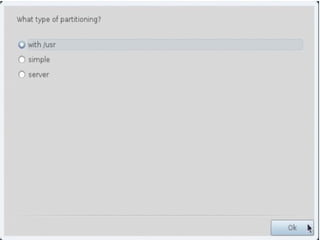
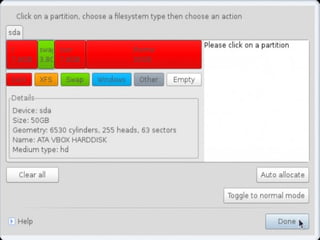
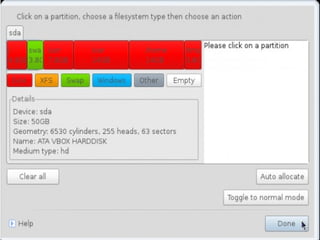
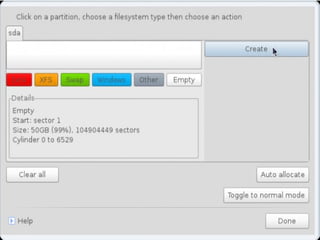
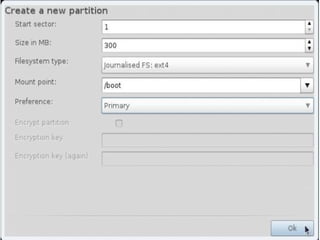
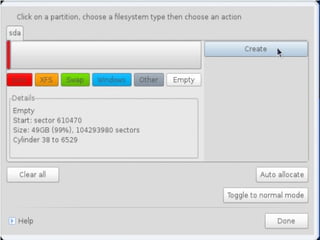
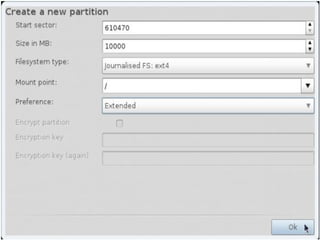
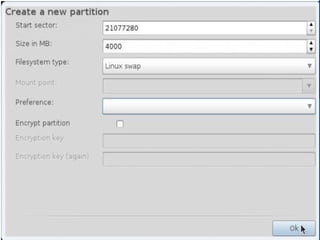
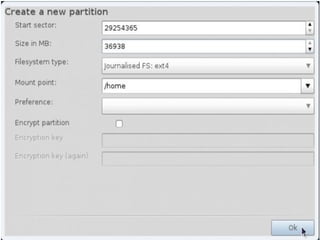
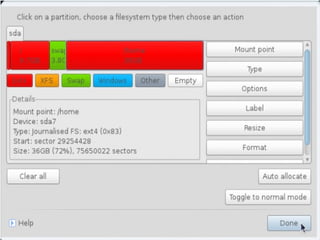
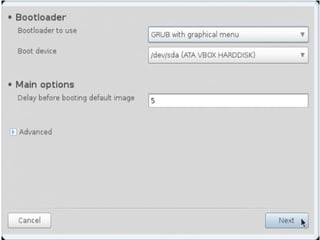
- Details about installing Linux, including partitioning schemes, file system types, and methods of installation like using DVD/CD or a USB drive.
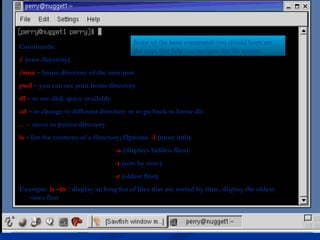
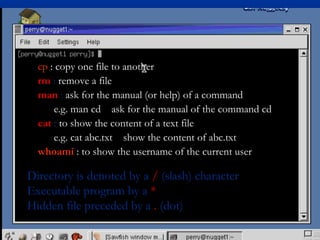
- An overview of basic Linux commands for navigating the file system, like cd, ls, pwd, and man, as well as copying, removing, and viewing files.
- A working example of using Backtrack Linux for phishing