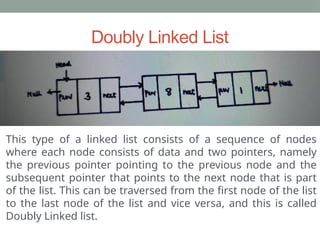
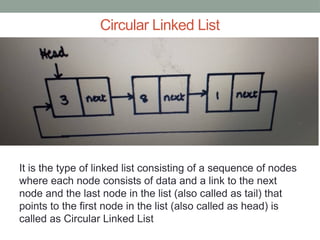
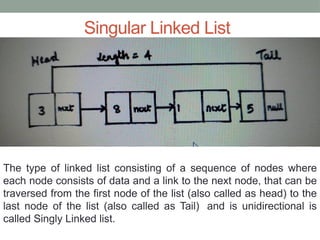
A linked list is a linear data structure where elements (nodes) are linked in sequence, with the first element as 'head' and the last as 'tail'. Java's LinkedList class provides various methods for adding, accessing, changing, and removing elements, as well as supporting different types of linked lists such as singly, doubly, and circular linked lists. Each type of linked list has distinct characteristics and traversal mechanisms, with specific examples provided for each implementation.


![Example
import java.util.LinkedList;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
// create linkedlist
LinkedList<String> animals = new LinkedList<>();
// Add elements to LinkedList
animals.add("Dog");
animals.add("Cat");
animals.add("Cow");
System.out.println("LinkedList: " + animals);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter4linkedlist-250125145518-227ce4f3/85/Chapter-4-Linked-List-introduction-lessons-pptx-4-320.jpg)

![Example
// Import the LinkedList class
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<String> StudentName = new LinkedList<String>();
StudentName.add(“Hassan");
StudentName.add(“Mohamed");
StudentName.add(“Ali");
StudentName.add(“Sucad");
System.out.println(StudentName);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter4linkedlist-250125145518-227ce4f3/85/Chapter-4-Linked-List-introduction-lessons-pptx-6-320.jpg)








![Creating Single Nodes List
public class IntNode {
//create an int that holds the data
public int data;
// create a pointer to the next node
public IntNode next;
// build a constructor to accept the values and points to next
public IntNode(int data, IntNode next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
// add one method to return the data
public String toString() {
return data + " ";
}
//create the main method to run the program
public static void main(String[] args) {
IntNode front = new IntNode(25,null);
System.out.println(front);
} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter4linkedlist-250125145518-227ce4f3/85/Chapter-4-Linked-List-introduction-lessons-pptx-17-320.jpg)
![Another Example
public class IntNode {
//create an int that holds the data
int data;
// create a pointer to the next node
IntNode next;
// build a constructor to accept the values and points to next
public IntNode(int data, IntNode next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
// add one method to return the data
public String toString() {
return data + " ";
}
//create the main method to run the program
public static void main(String[] args) {
IntNode LastNode = new IntNode(25,null);
IntNode MiddNode = new IntNode(21,LastNode);
IntNode FirstNode = new IntNode(15,MiddNode);
System.out.print(FirstNode);
System.out.print(MiddNode);
System.out.print(LastNode);
} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter4linkedlist-250125145518-227ce4f3/85/Chapter-4-Linked-List-introduction-lessons-pptx-18-320.jpg)
![Singly linked list to store and display string
public class
SinglyLinkedList {
ListNode head;
public static class
ListNode {
String data;
ListNode next;
// constructor
public ListNode(String
data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}}
public void display() {
ListNode current = head;
while(current != null) {
System.out.println(current.
data + "-->");
current = current.next;
}
System.out.print("null");
public static void
main(String[] args) {
SinglyLinkedList sll = new
SinglyLinkedList();
sll.head = new
ListNode(“Ahmed");
ListNode second = new
ListNode(“Mohamed");
ListNode third = new
ListNode(“Ali");
ListNode fourth = new
ListNode(“Gedi");
sll.head.next = second;
second.next = third;
third.next = fourth;
sll.display();
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter4linkedlist-250125145518-227ce4f3/85/Chapter-4-Linked-List-introduction-lessons-pptx-19-320.jpg)