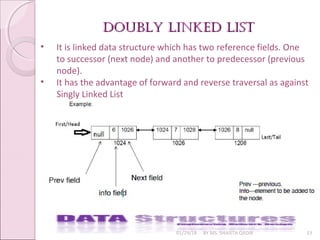
The document presents an overview of linked lists, including singly linked lists, doubly linked lists, and circular linked lists, detailing their structure and functions. It outlines algorithms for insertion, deletion, and searching within these lists, illustrated with class definitions and operations for singly and doubly linked lists. Additionally, specific methods for adding and removing nodes are provided, alongside descriptions of how these structures can be utilized in programming.









![01/29/18 BY MS. SHAISTA QADIR 14
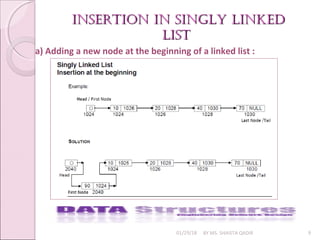
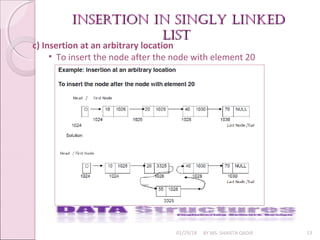
c) Insertion at an arbitrary location
• To insert the node after the node with element 20
If (START == NULL) Then
2. Print: Linked-List is empty. It must have at least one node
3. Else
4. Set PTR = START, NEW = START
5. Repeat While (PTR != NULL)
6. If (PTR->INFO == N) Then
7. NEW = New Node
8. NEW->INFO = ITEM
9. NEW->LINK = PTR->LINK
10. PTR->LINK = NEW
11. Print: ITEM inserted
12. ELSE
13. PTR = PTR->LINK
[End of Step 6 If]
[End of While Loop]
[End of Step 1 If]
14. Exit .
Here START is a pointer variable
which contains the address of first
node.
NEW is a pointer variable which will
contain address of new node.
N is the value after which new node
is to be inserted and ITEM is the
value to be inserted.
INFO is data in the node and LINK is
address of next node.
insertion in singly linkedinsertion in singly linked
listlist](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture3-180129180102/85/linked-list-14-320.jpg)



![01/29/18 BY MS. SHAISTA QADIR 21
deletion from singlydeletion from singly
linked listlinked list
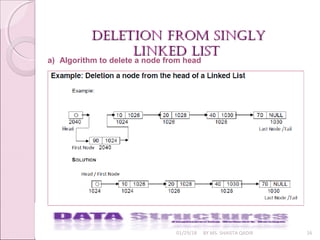
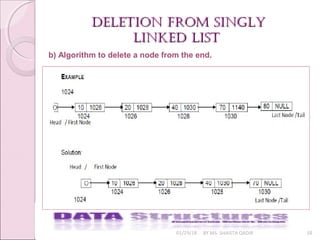
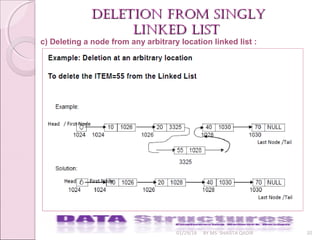
c) Deleting a node from any arbitrary location linked list :
1. If (START == NULL) Then
2. Print: Linked-List is empty. It must have at least one node
3. Else If (START->INFO == ITEM) Then
4. PTR = START
5. START = START->LINK
6. Delete PTR
7. Else
8. PTR = START, PREV = START
9. Repeat While (PTR != NULL)
10. If (PTR->INFO == ITEM) Then
11. PREV->LINK = PTR->LINK
12. Delete PTR
13. Else
14. PREV = PTR
15. PTR = PTR->LINK
[End of Step 10 If]
[End of While Loop]
16. Print: ITEM deleted
[End of Step 1 If]
17. Exit
•Here START is a pointer
variable which contains the
address of first node.PTR is a
pointer
•variable which will contain
address of node to be deleted.
PREV is the pointer variable
which
•contains the address of
previous node. ITEM is the
value to be deleted.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture3-180129180102/85/linked-list-21-320.jpg)
![01/29/18 BY MS. SHAISTA QADIR 22
searching a singly linkedsearching a singly linked
listlist
Searching an element from any arbitrary location linked list :
1. Set PTR = START, LOC = 1
2. Repeat While (PTR != NULL)
3. If (ITEM == PTR->INFO) Then
4. Print: ITEM is present at location LOC
5. Return
6. Else
7. PTR = PTR->LINK
8. LOC = LOC + 1
9. [End of If]
10. [End of While Loop]
11. Print: ITEM is not present in the list
12. Exit
• The search operation
explained is to find if a data
is present in the
Linked List or not.
• START is the pointer
variable which corresponds
to the address of
first node.
• ITEM is the value to be
searched. LOC is used to
give node no.
which contains ITEM.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture3-180129180102/85/linked-list-22-320.jpg)





![01/29/18 BY MS. SHAISTA QADIR 29
Searching an element from any arbitrary location of doubly linked list :
1. Set PTR = START, LOC = 1
2. Repeat While (PTR != NULL)
3. If (ITEM == PTR->INFO) Then
4. Print: ITEM is present at location LOC
5. Return
6. Else
7. PTR = PTR->NEXT
8. LOC = LOC + 1
9. [End of If]
10. [End of While Loop]
11. Print: ITEM is not present in the list
12. Exit
searching a Doubly linkeDsearching a Doubly linkeD
listlist
• The search operation explained
is to find if a data is present in
the Linked List or not.
• START is the pointer variable
which corresponds to the
address of first node.
• ITEM is the value to be
searched.
• NEXT corresponds to the next
field of a node in Doubly Linked
List
• LOC corresponds to the node
number in which ITEM is
present](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture3-180129180102/85/linked-list-29-320.jpg)