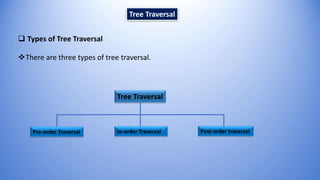
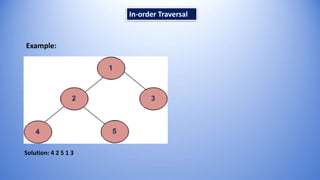
The document discusses tree traversal in the context of discrete mathematics, detailing its definition and types: pre-order, in-order, and post-order traversal. It provides the sequence of node visits for each traversal type and includes algorithms for implementation. Examples are given for each traversal method to illustrate the concepts.