The document summarizes information about linked lists, including:
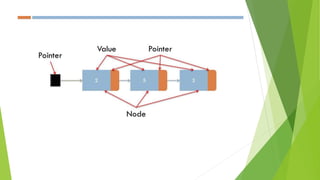
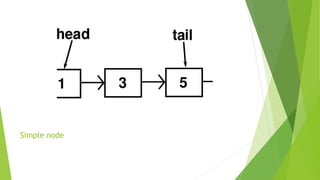
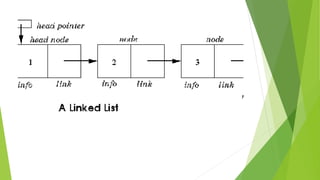
- Linked lists are linear collections of data elements called nodes connected by pointers.
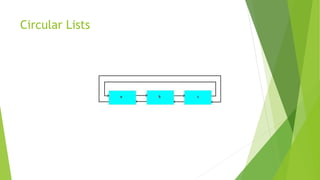
- There are single linked lists, double linked lists, and circular linked lists.
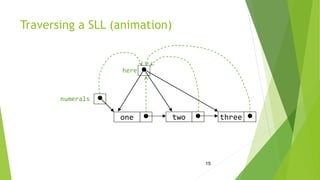
- Traversing a single linked list involves iterating through each node using the next pointer.
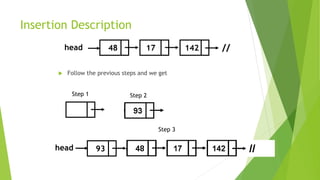
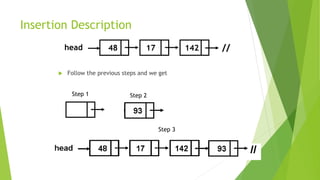
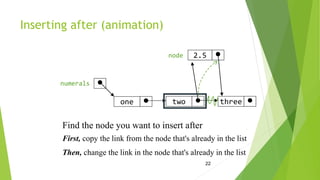
- Insertion can occur at the beginning, end, or middle of a list by creating a new node and adjusting pointers.
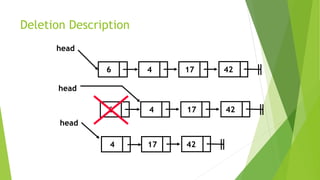
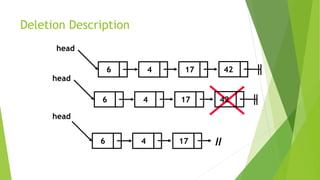
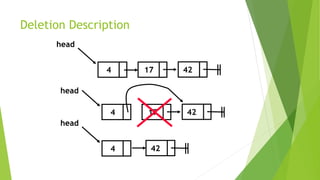
- Deletion involves removing a node by adjusting pointers of the previous and next nodes.
- A basic node implementation uses a struct with a data field and next pointer.