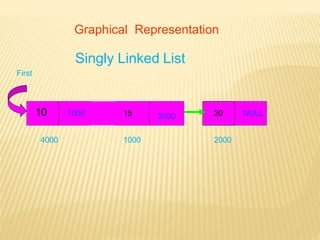
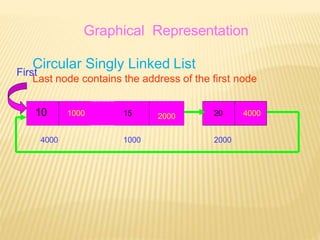
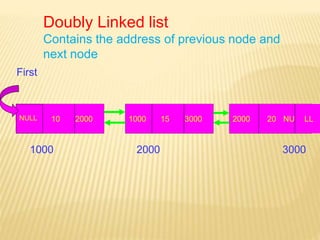
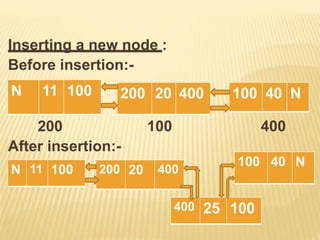
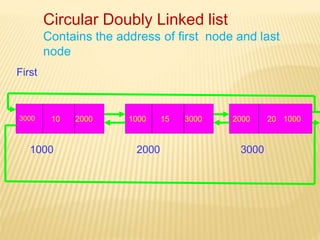
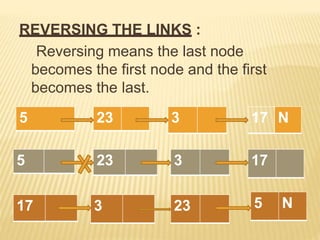
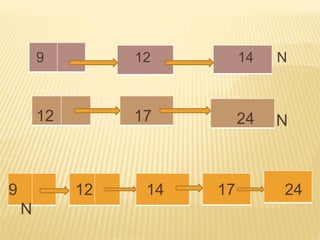
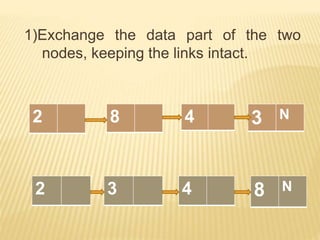
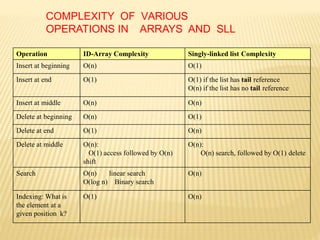
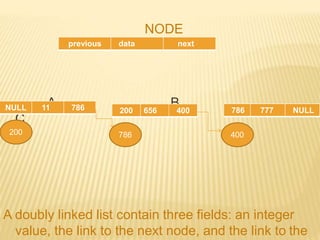
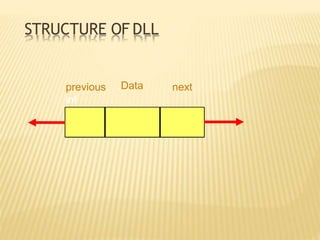
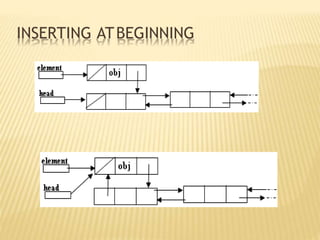
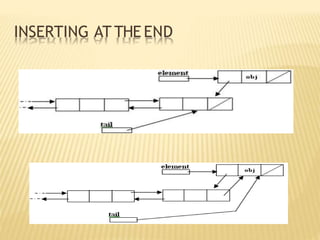
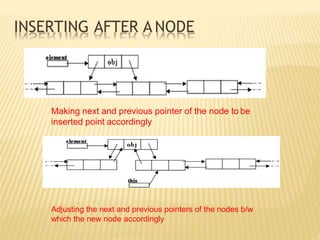
The document provides an overview of data structures, focusing on linked lists as a solution to the limitations of arrays, such as fixed size and inefficient insertions and deletions. It details the types of linked lists including singly, doubly, and circular linked lists, and explains operations like creation, insertion, deletion, searching, and more within these structures. Advantages of linked lists include dynamic memory allocation and simplified operations compared to arrays.






![ARRAYS VS LINKEDLISTS
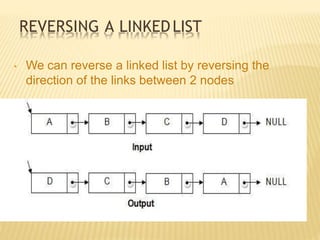
Arrays Linked list
Fixed size: Resizing is expensive Dynamic size
Insertions and Deletions are inefficient:
Elements are usually shifted
Insertions and Deletions are efficient: No
shifting
Random access i.e., efficient indexing No random access
Not suitable for operations requiring
accessing elements by index such as sorting
No memory waste if the array is full or almost
full; otherwise may result in much memory
waste.
Since memory is allocated dynamically(acc. to
our need) there is no waste of memory.
Sequential access is faster [Reason: Elements in
contiguous memory locations]
Sequential access is slow [Reason: Elements not
in contiguous memory locations]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linkedlist1-220922131834-4d30ec1d/85/Linked-list-1-pptx-10-320.jpg)