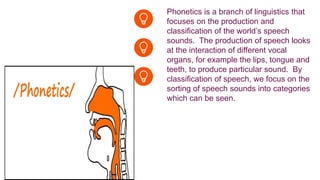
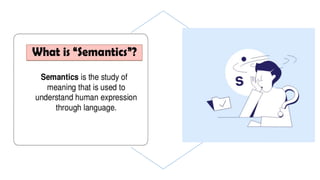
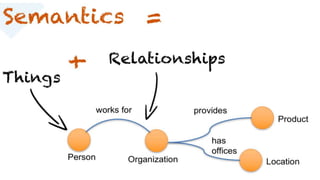
This document provides an overview of the major and minor branches of linguistics. The major branches discussed are phonology, morphology, syntax, and semantics. Phonology is the study of sound structure in language. Morphology studies word formation. Syntax deals with the arrangement of words. Semantics is the study of meaning. The minor branches covered are phonetics, sociolinguistics, psycholinguistics, and pragmatics. Phonetics focuses on speech sounds. Sociolinguistics examines the relationship between language and society. Psycholinguistics studies language processing in the brain. Pragmatics relates to practical language use. Examples are provided for some branches.