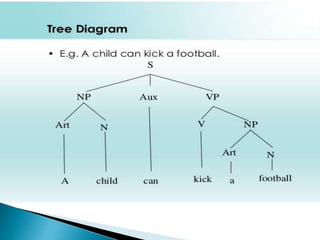
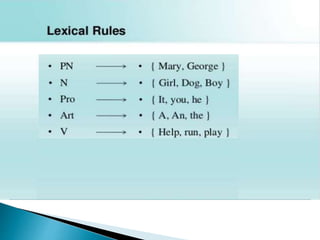
Linguistics is the scientific study of language, including analysis of language form, meaning, and context, as well as social, cultural, and political factors that influence language. Noam Chomsky argued that language acquisition is innate and proposed the existence of a language acquisition device in the brain. His theory of generative grammar and universal grammar posited that humans are biologically programmed with innate principles and parameters that facilitate language learning.