The document discusses physical and cognitive development in early adulthood. It covers several topics:
- Emerging adulthood is characterized by identity exploration, instability, self-focus, feeling in-between, and possibilities for transformation.
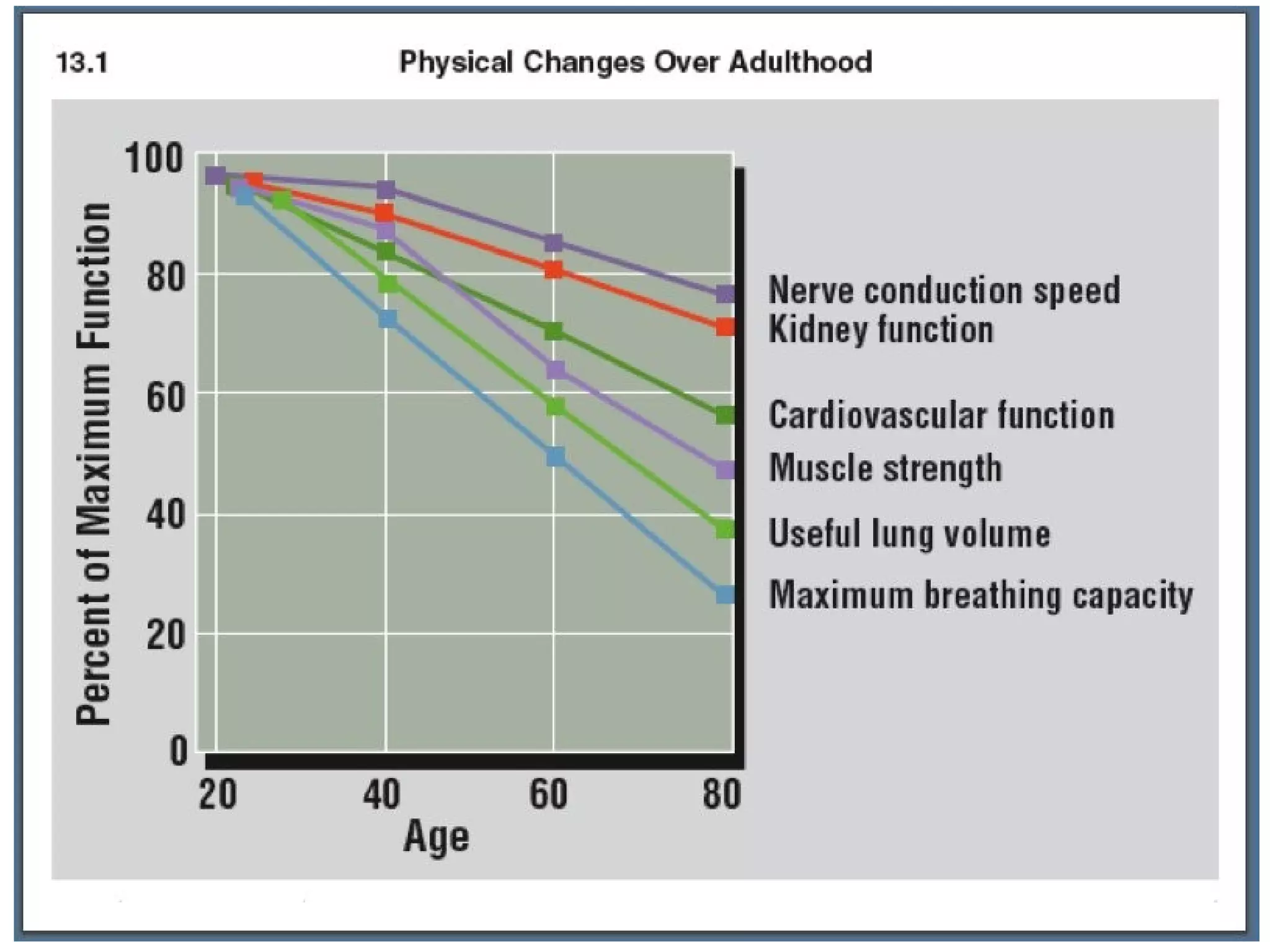
- Physical performance peaks before age 30 then declines, while sensory systems change little. Exercise in young adulthood boosts health in later life.
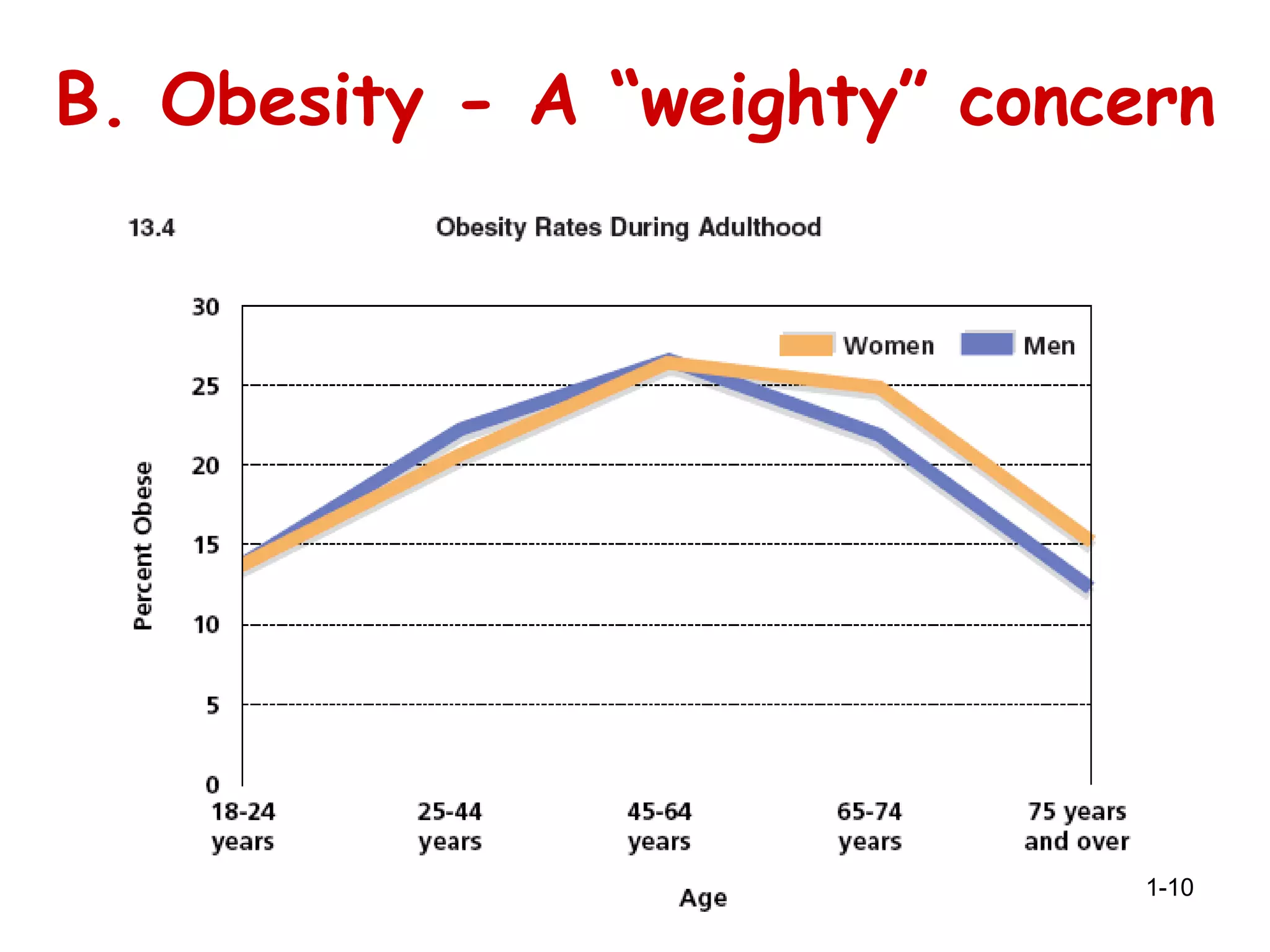
- Lifestyle choices can hasten aging effects, but few young adults consider this. Violence is a major cause of death for some groups. Obesity risks increase without attention to nutrition.
- Sternberg's triarchic theory of intelligence includes componential, experiential, and contextual aspects of thinking. Creat



![A. Physical Development and the Senses Maturation mostly complete. Senescence [next]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lifespan-chapter-11online-stud-1209230317881218-8/75/Lifespan-Chapter-11-Online-Stud-4-2048.jpg)


![Health Few chronic health problems, but still significant deaths by: Accidents, suicide, homicide [p.311] Lifestyle choices (drugs, alcohol, smoking, unprotected sex) can hasten secondary aging, but few think about it. 5 years after stopping smoking, health risk is significantly lower](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lifespan-chapter-11online-stud-1209230317881218-8/75/Lifespan-Chapter-11-Online-Stud-8-2048.jpg)











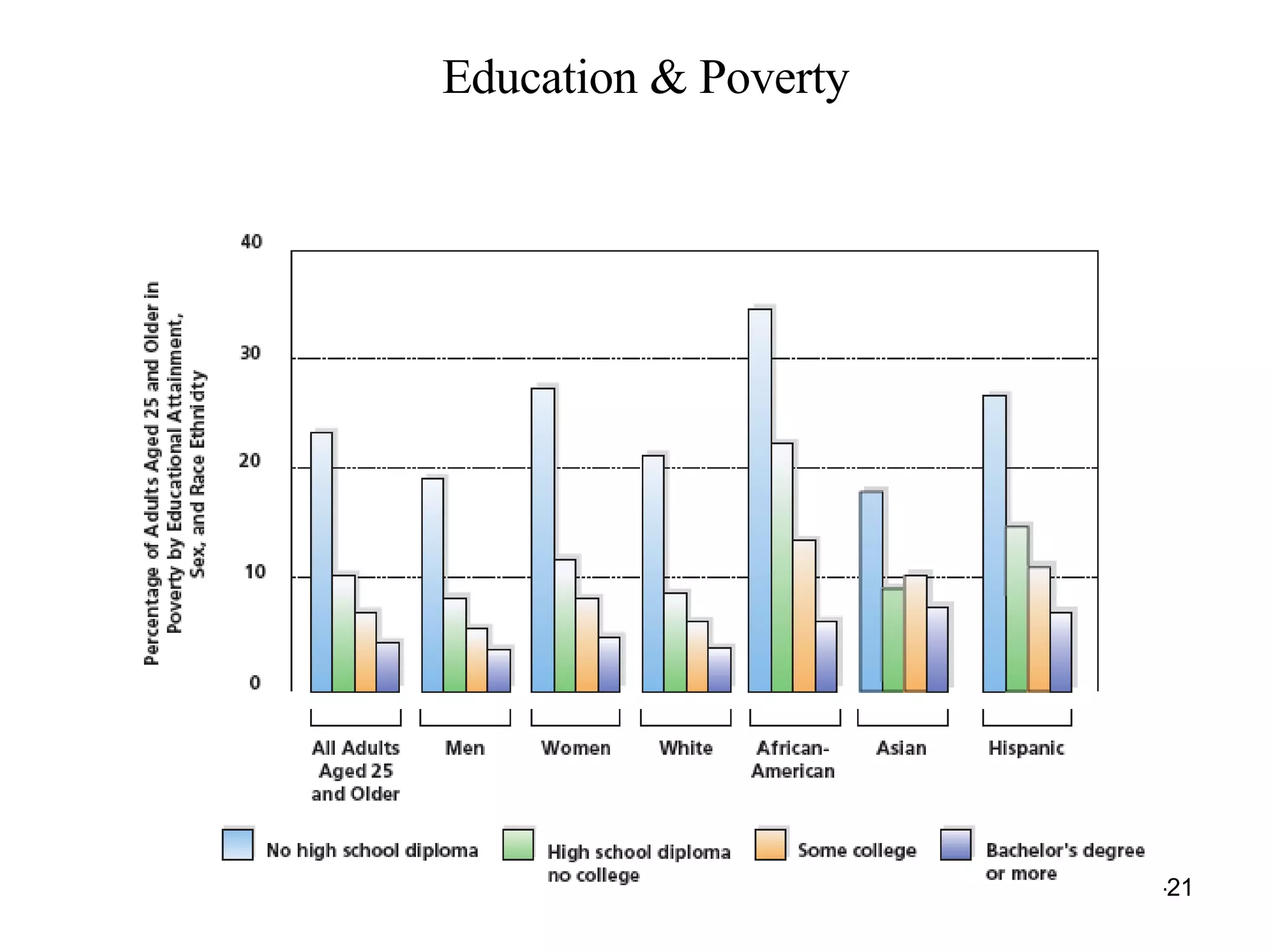

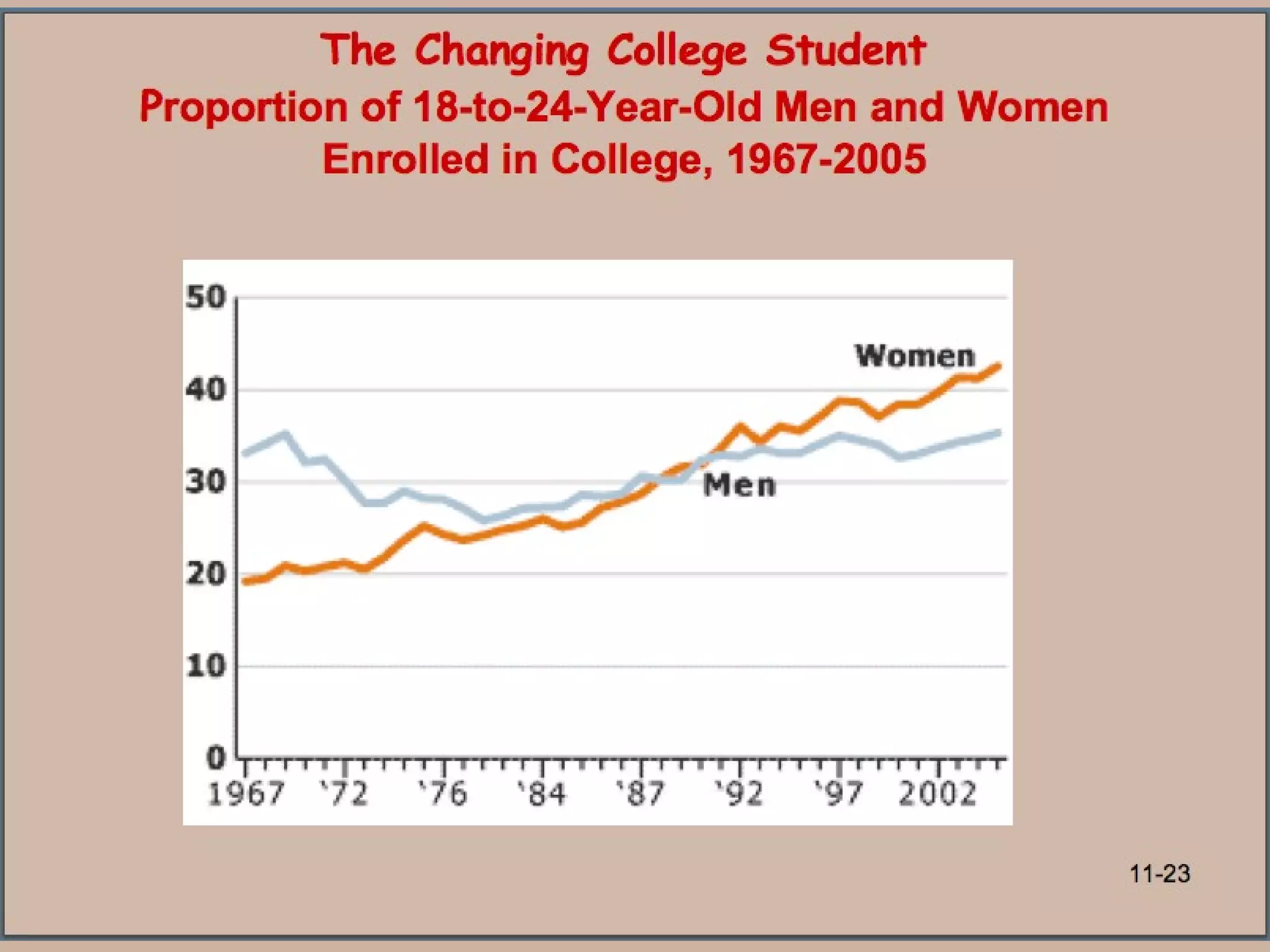
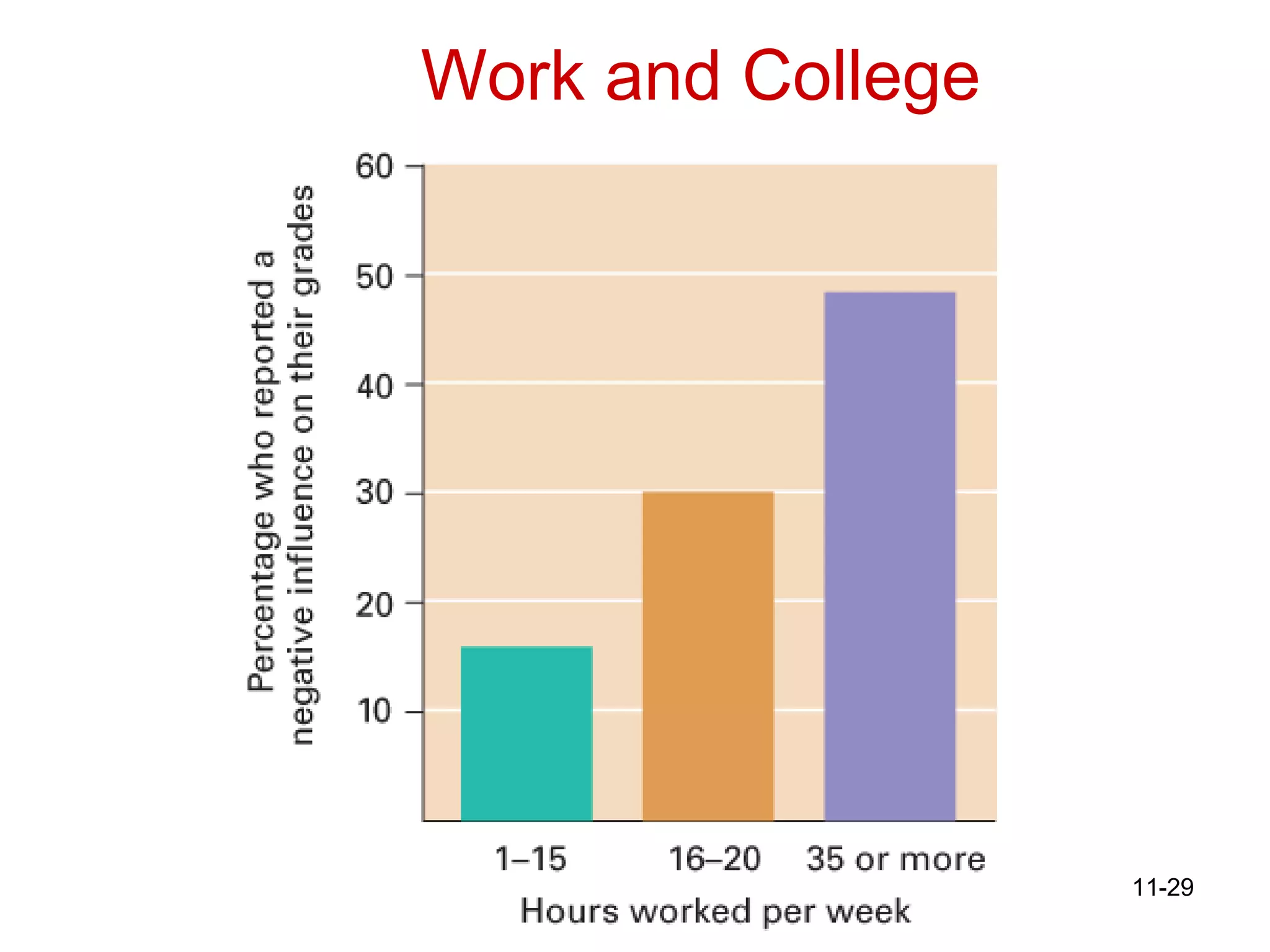
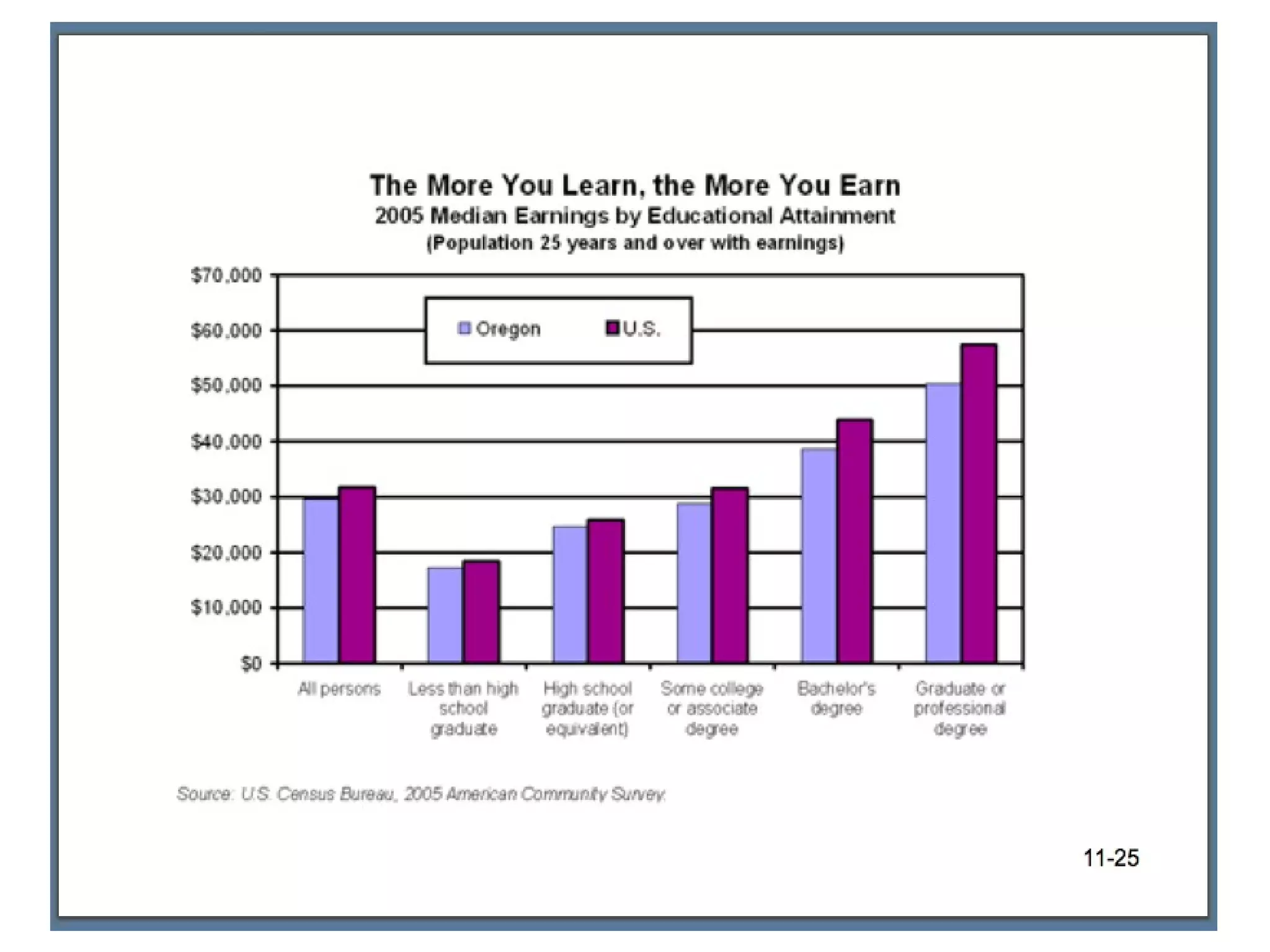
![The Changing College Student 1/3 of college students today are 25 years of age or older. Average age at CC is 31. “ A college degree is becoming increasingly important in obtaining a job.” RM: Essential to a good job [next]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lifespan-chapter-11online-stud-1209230317881218-8/75/Lifespan-Chapter-11-Online-Stud-24-2048.jpg)
![College Adjustment Surveys: almost half have a least one significant psychological issue. [next] Relationship changes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lifespan-chapter-11online-stud-1209230317881218-8/75/Lifespan-Chapter-11-Online-Stud-26-2048.jpg)