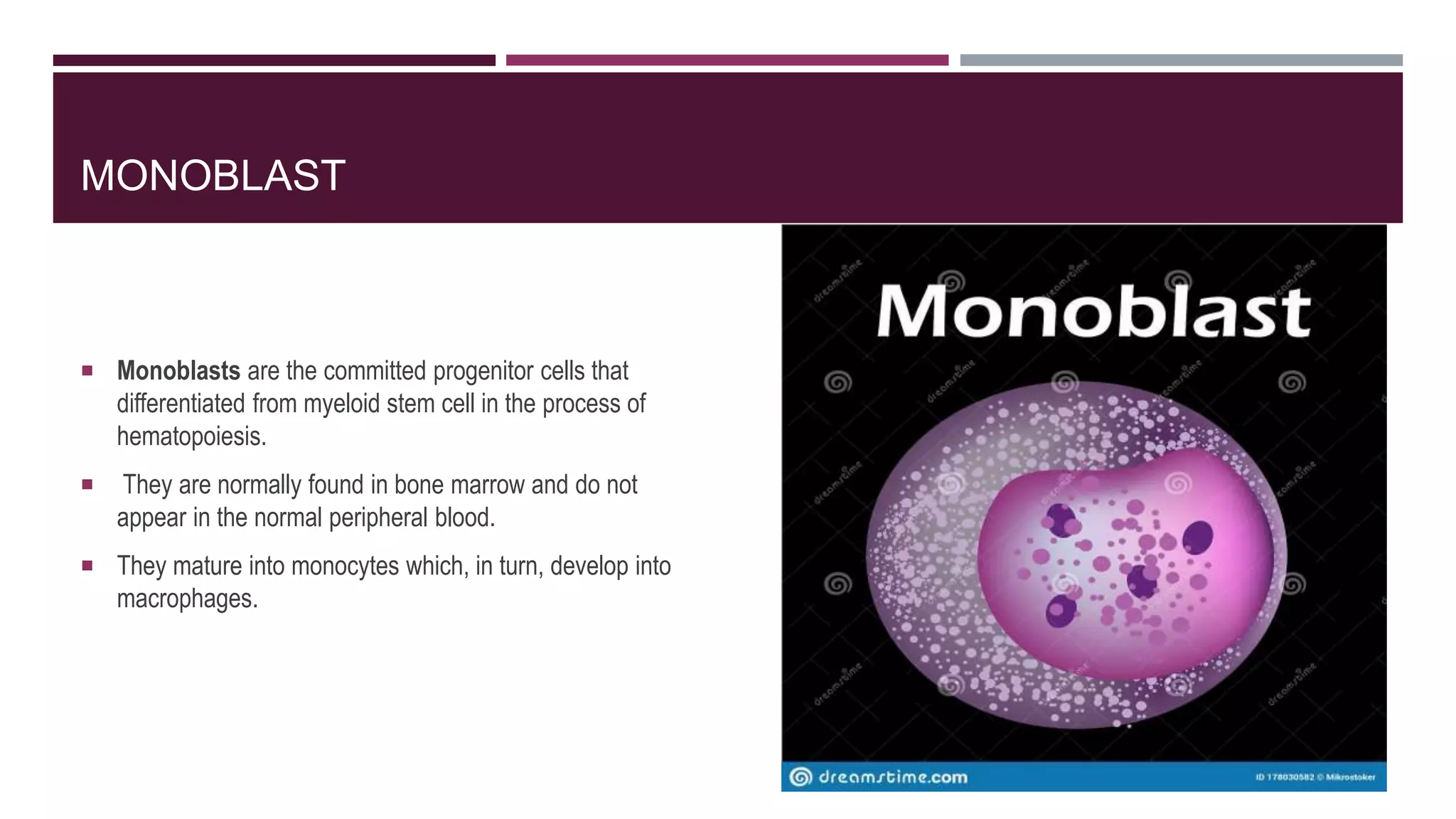
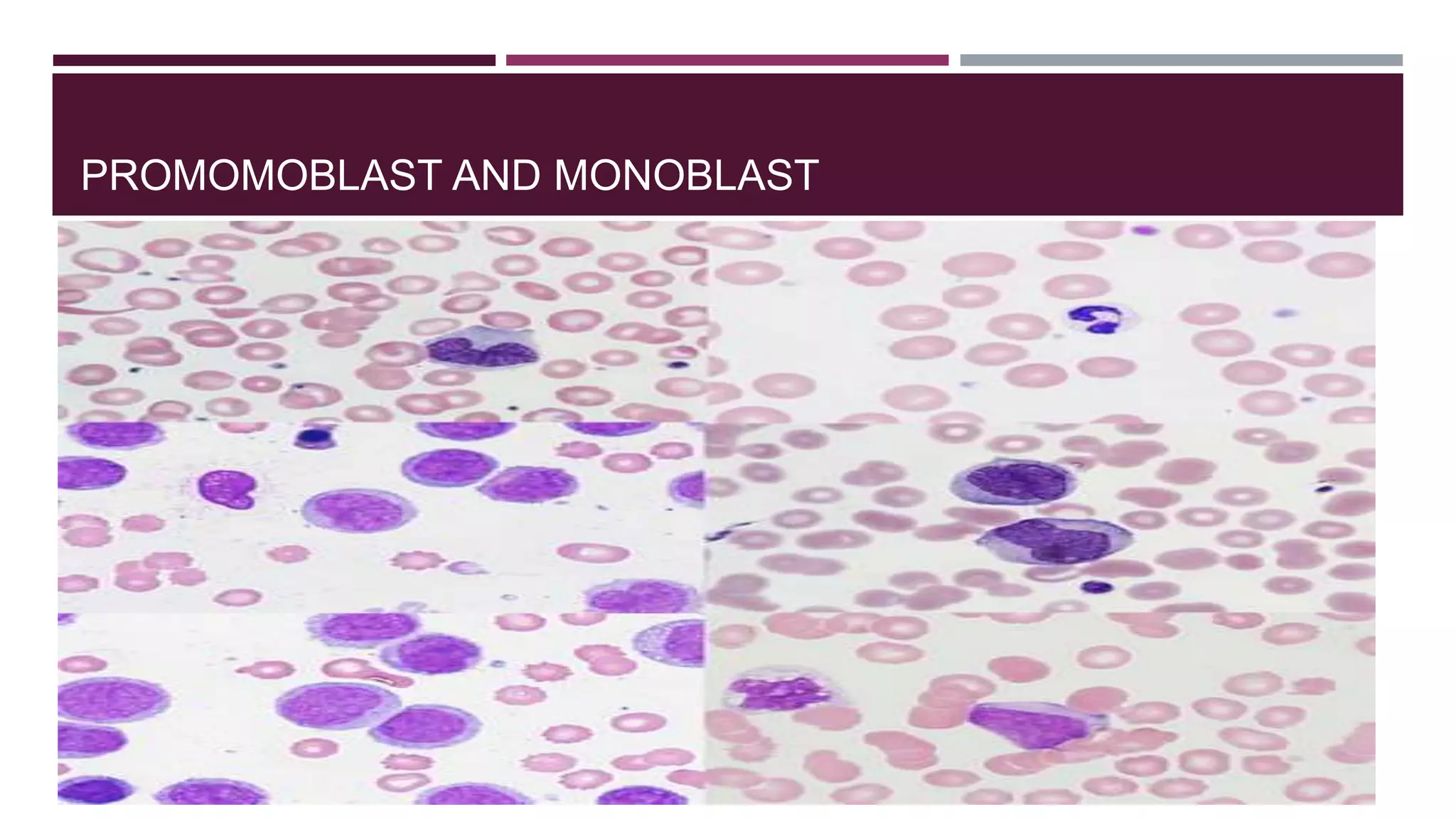
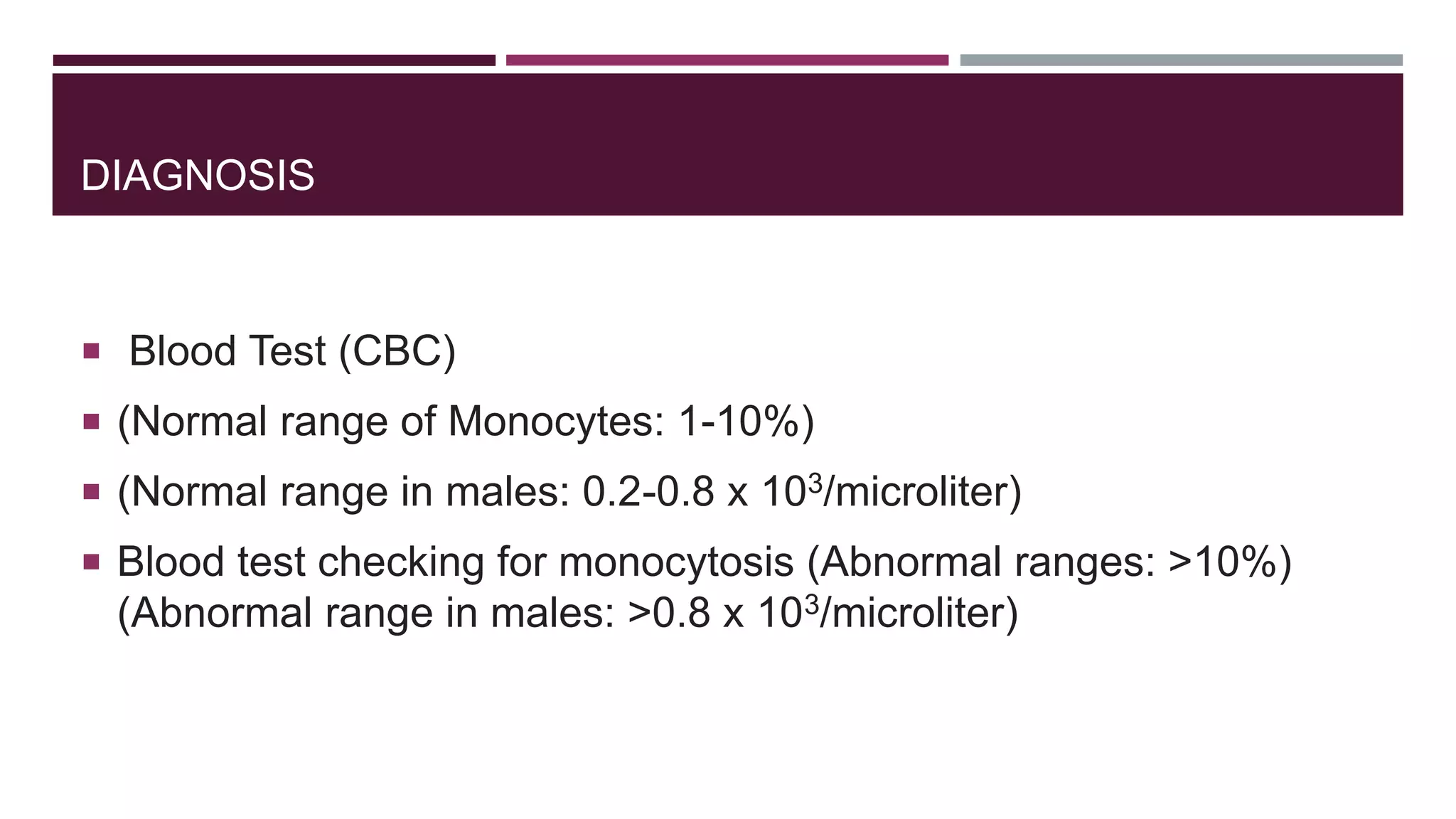
This document discusses monocytosis, which is an increased number of monocytes in the blood. Monocytes are a type of white blood cell that develop from bone marrow precursors and help fight infection and promote healing. The document defines monocytosis and describes monoblasts and promonocytes, the precursors to monocytes. Potential causes of monocytosis include chronic infections, inflammatory diseases, cancers, and heart attacks. Symptoms may include spleen or liver enlargement. Monocytosis is diagnosed via a blood test and treated by addressing its underlying cause.