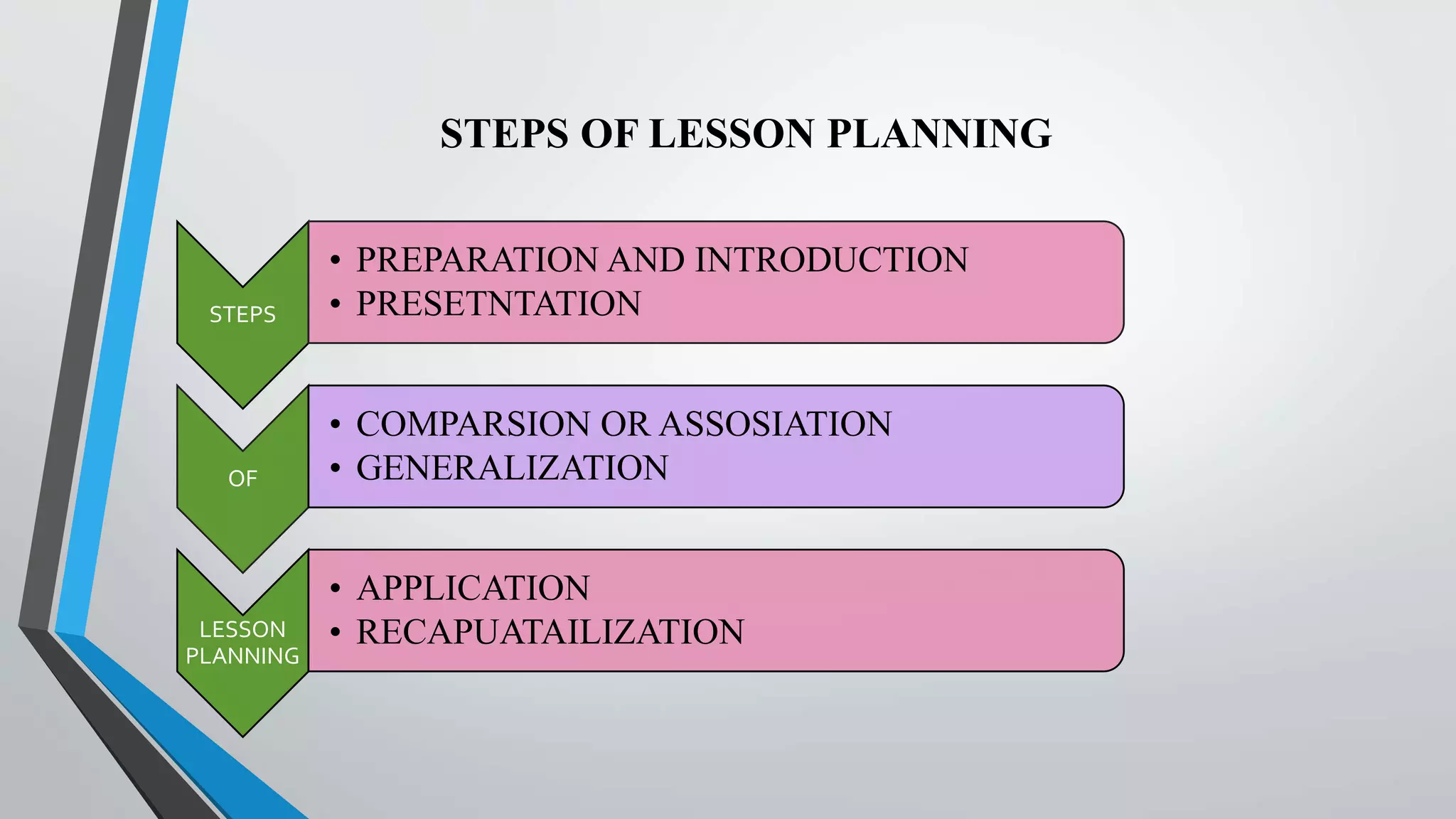
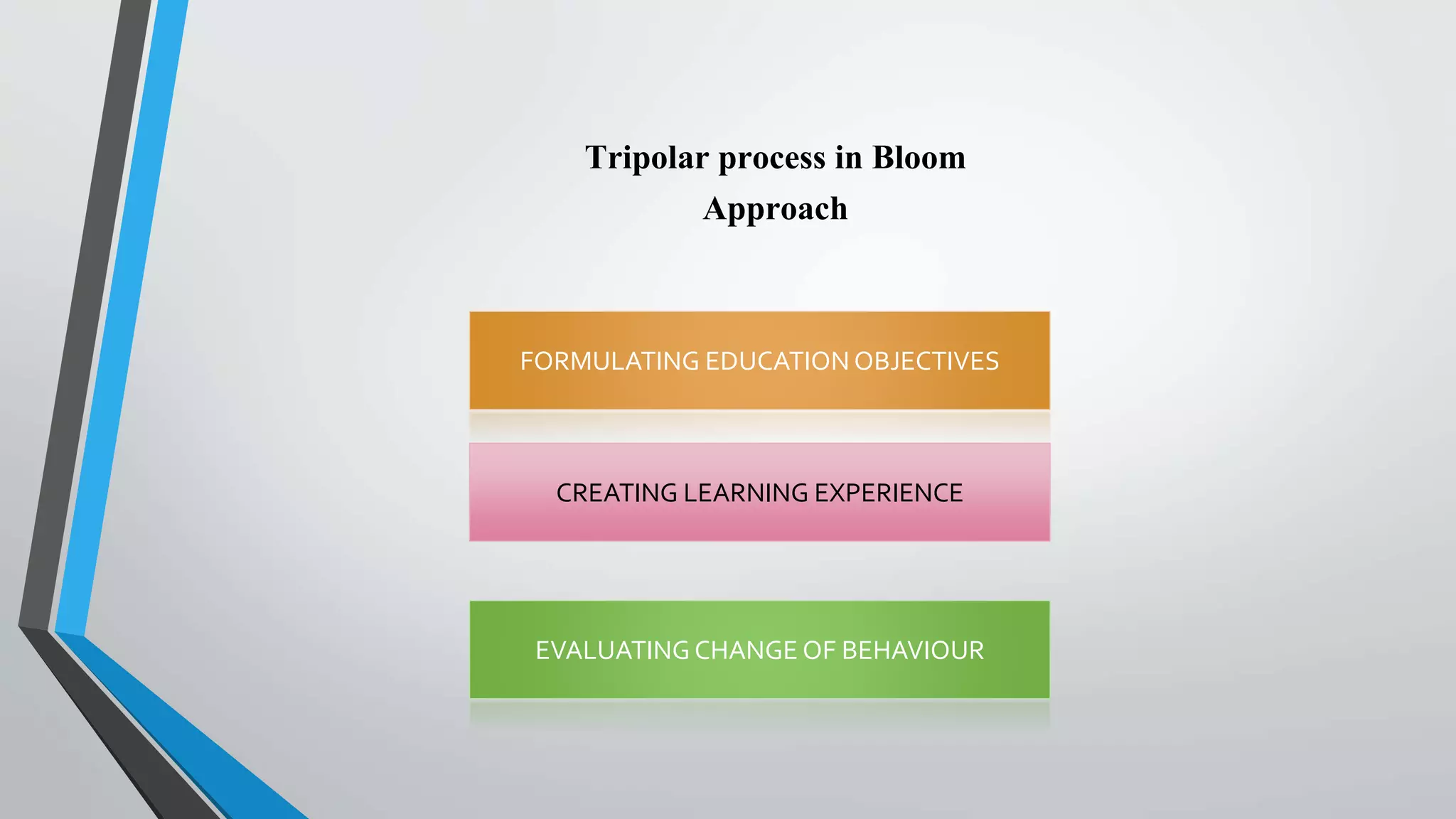
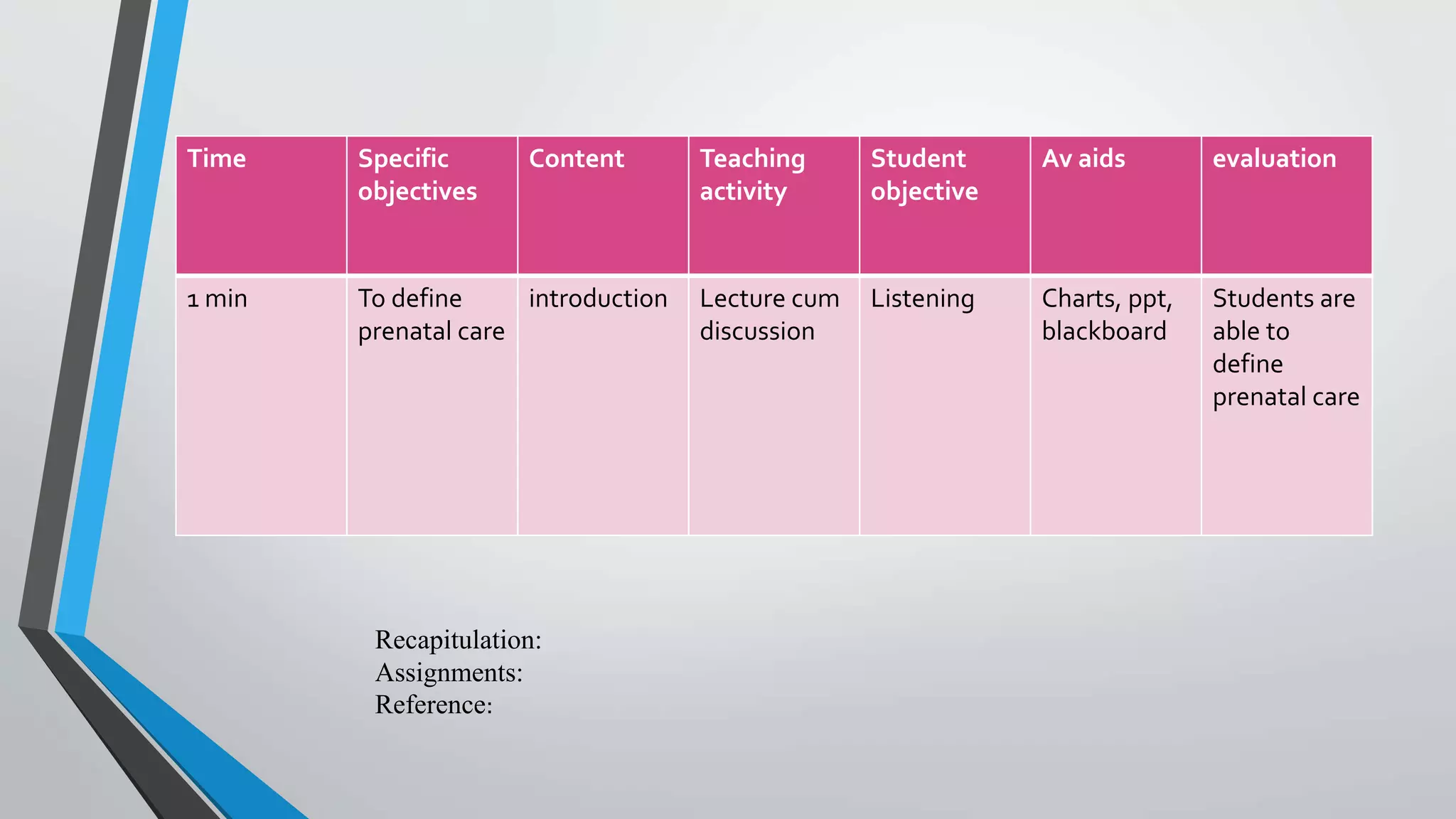
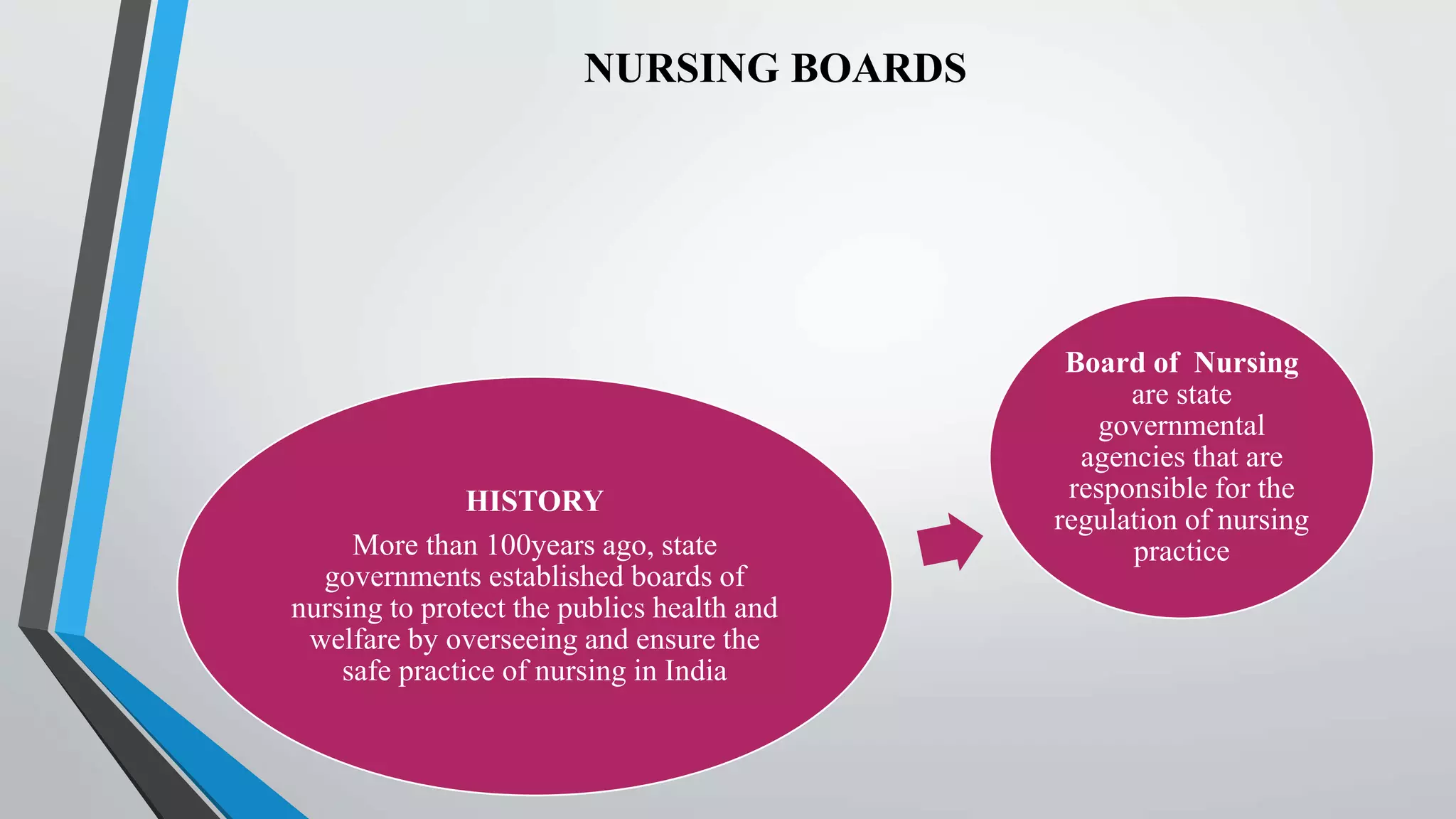
The document provides a comprehensive overview of lesson planning in nursing education, detailing its definition, purpose, characteristics, principles, and importance. It discusses various methods and approaches to lesson planning, including the Herbartian, Bloom's, and RCEM approaches, along with their merits and demerits. Additionally, it outlines the roles and functions of nursing councils and universities in regulating nursing education and ensuring quality training.