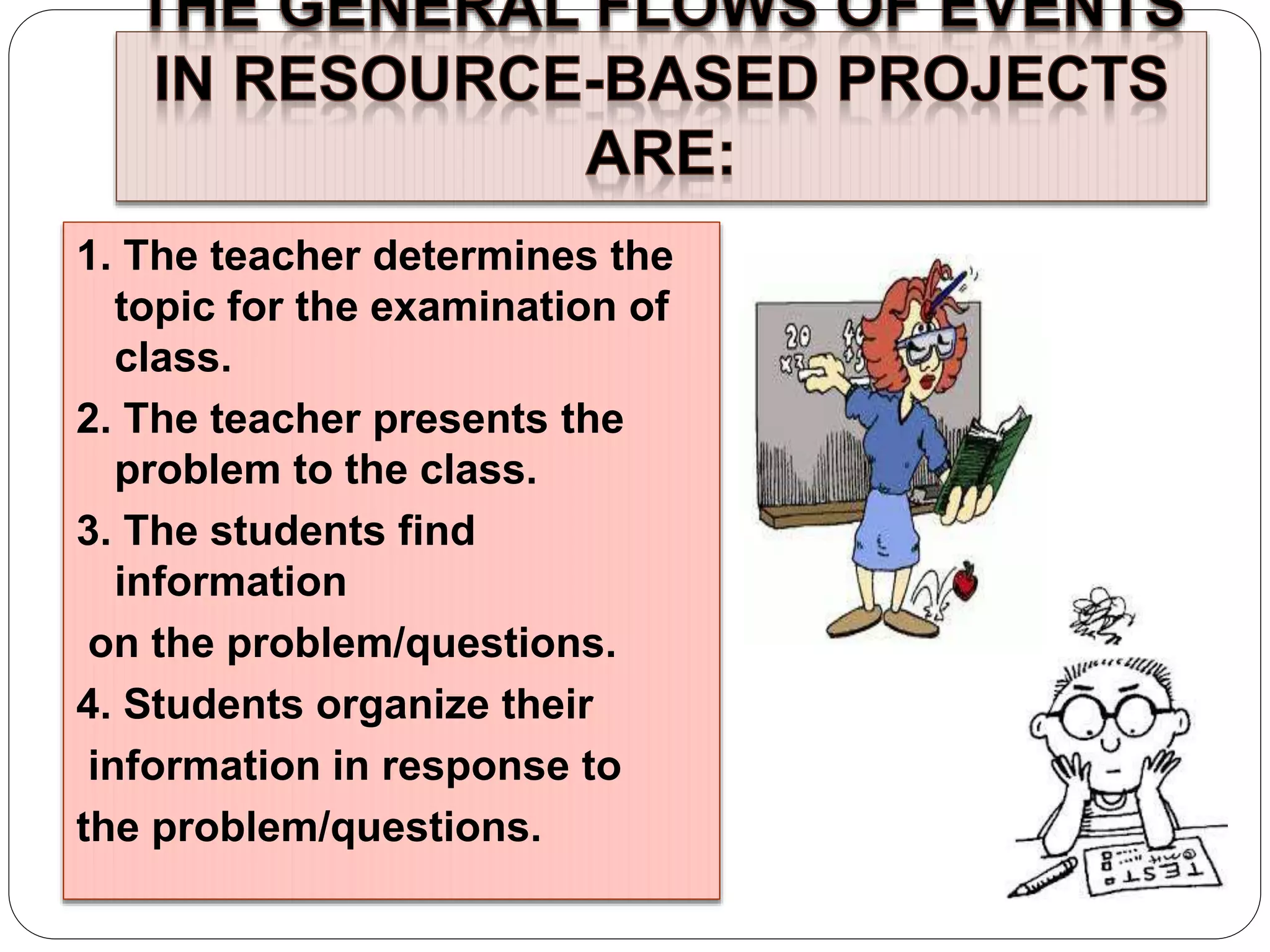
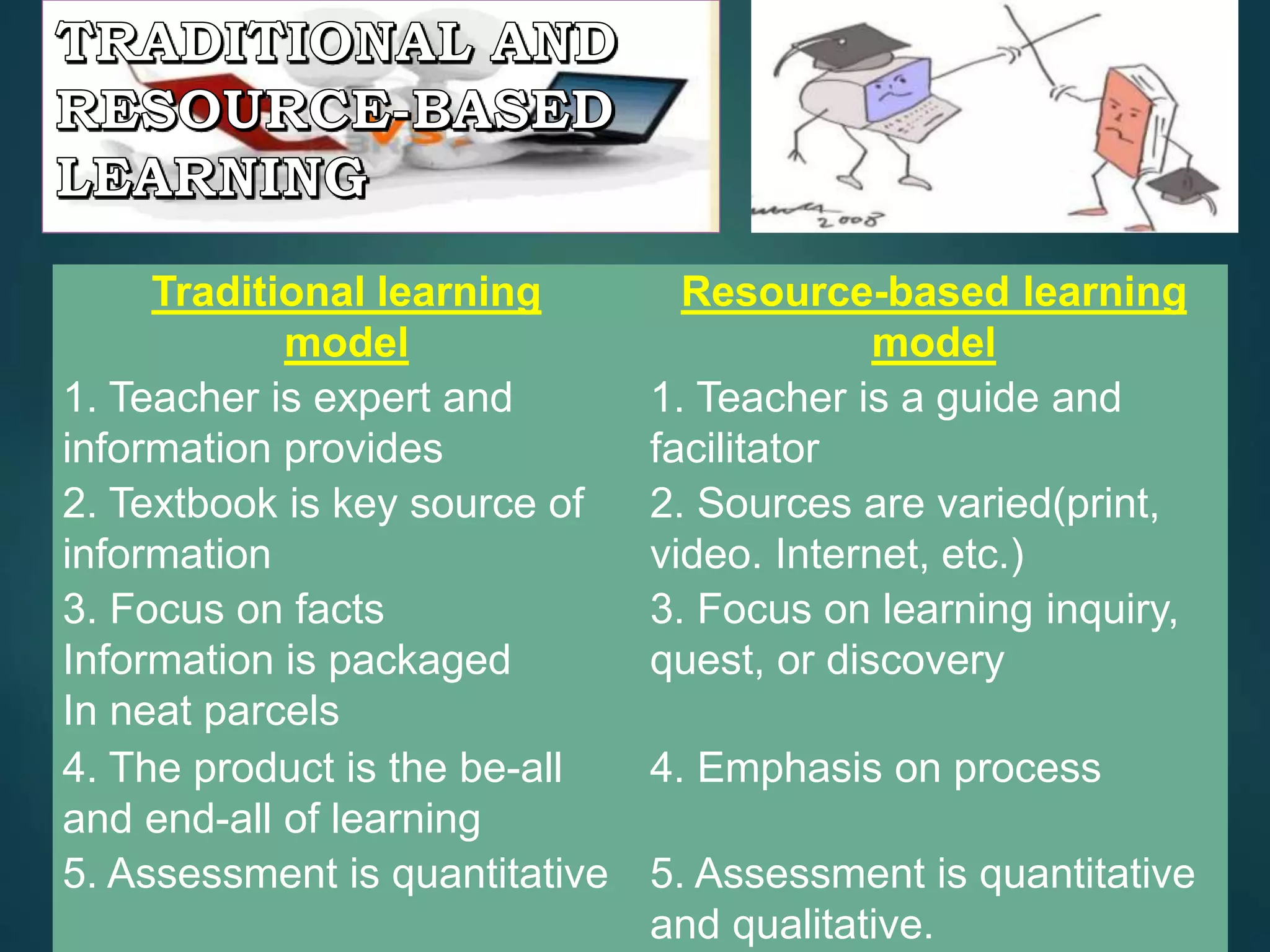
The document discusses various educational frameworks focusing on constructivist and resource-based learning models, highlighting the teacher's role as a facilitator rather than a traditional information provider. It emphasizes the importance of process over product, encouraging students to engage in inquiry, collaboration, and flexibility while working on projects. Additionally, it mentions guided hypermedia and web-based projects as tools for enhancing creativity and learning, although acknowledges challenges with implementation due to sophistication and time constraints.