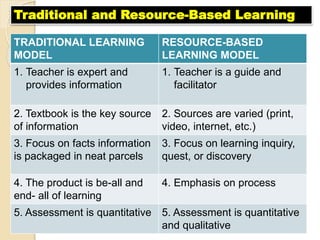
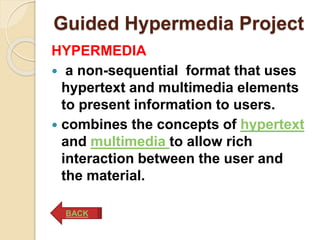
The document discusses four IT-based projects to develop higher-order thinking skills: 1) Resource-based projects engage students in finding and organizing information from multiple sources to answer teacher-provided problems or questions. 2) Simple creations allow students to create their own software or multimedia materials. 3) Guided hypermedia projects involve students producing instructional or communicative multimedia presentations using tools like PowerPoint. 4) Web-based projects have students create and post webpages on given topics.