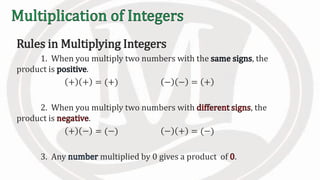
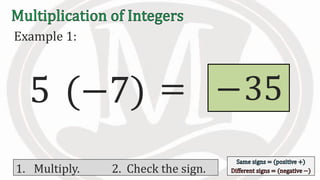
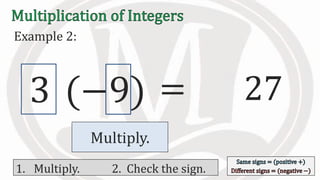
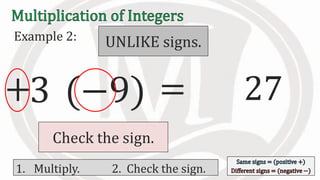
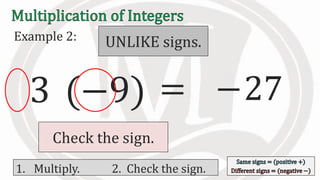
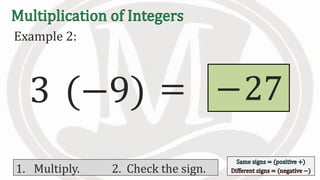
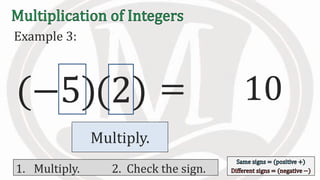
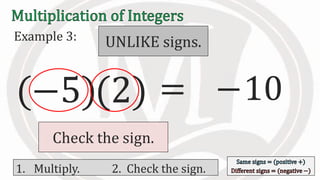
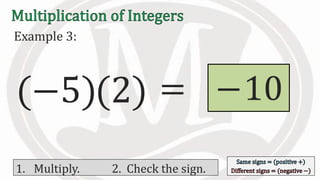
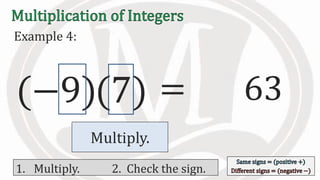
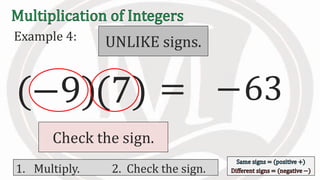
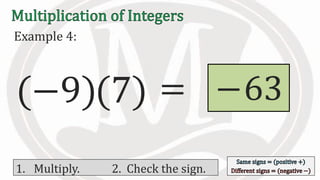
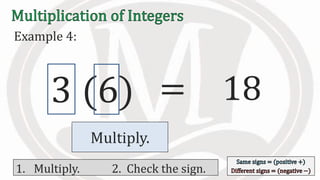
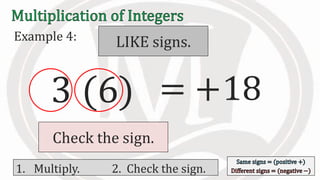
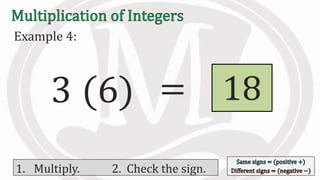
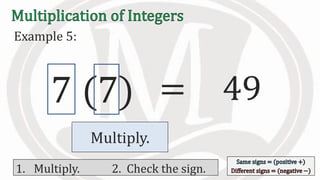
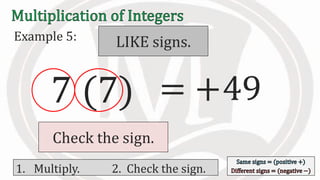
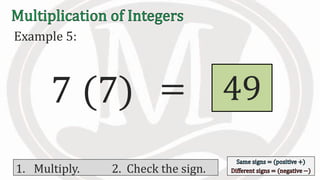
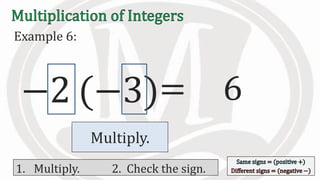
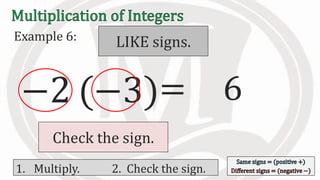
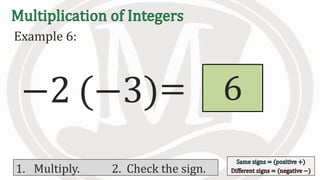
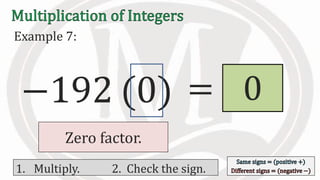
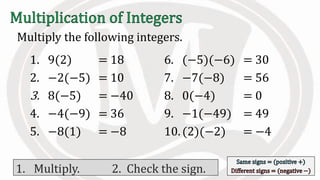
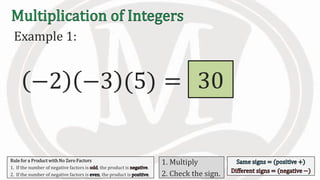
1. The document discusses rules for multiplying integers, including: multiplying two numbers with the same sign results in a positive product, and multiplying two numbers with different signs results in a negative product.
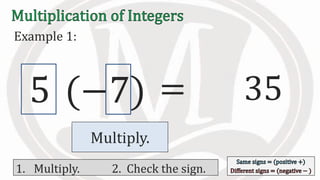
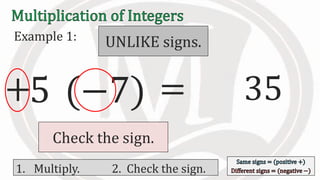
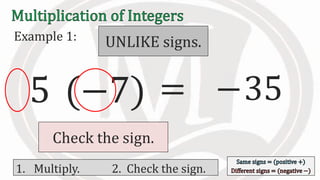
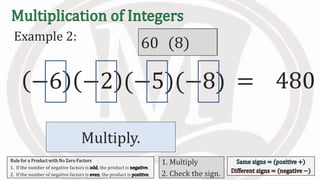
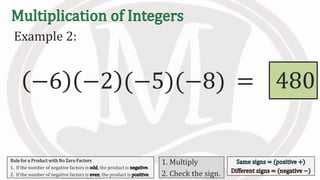
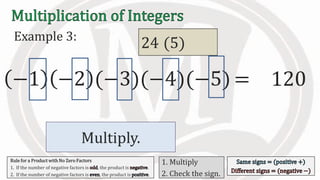
2. Examples are provided to illustrate multiplying integers and checking the sign of the product based on the signs of the factors.
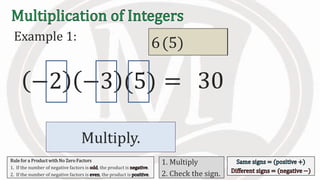
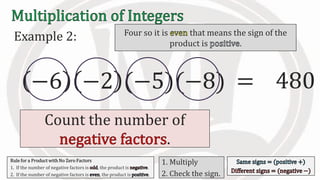
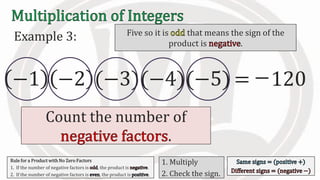
3. An additional rule is introduced - if the number of negative factors in a product is odd, the product is negative, and if it is even, the product is positive.













(10)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1-181113234231/85/Lesson-1-7-multiplying-integers-52-320.jpg)

(10) = 240](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1-181113234231/85/Lesson-1-7-multiplying-integers-54-320.jpg)

