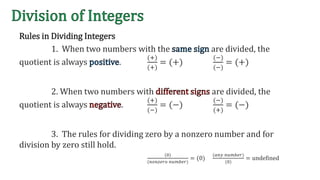
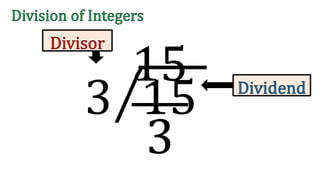
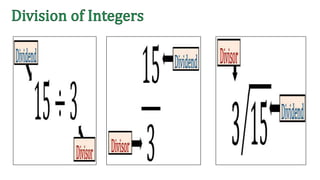
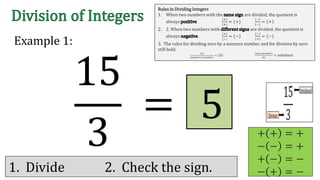
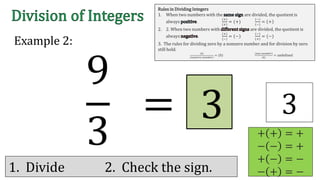
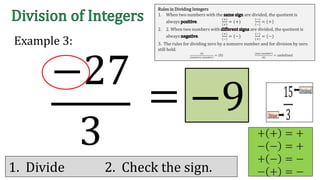
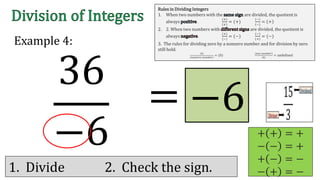
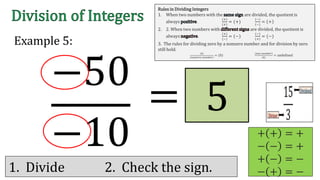
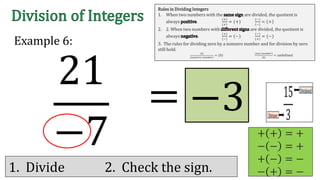
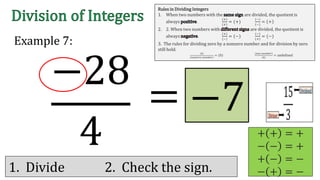
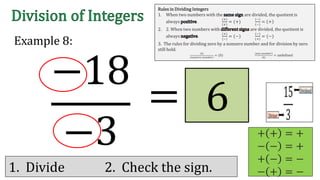
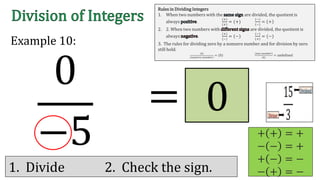
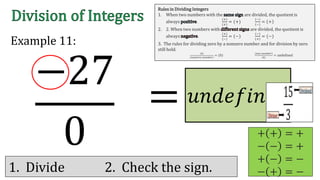
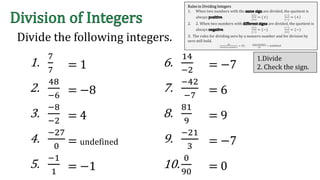
The document discusses the rules for dividing integers. It states that when two numbers with the same sign are divided, the quotient is positive, and when the numbers have different signs, the quotient is negative. It also notes that dividing zero by a non-zero number equals zero, and dividing any number by zero is undefined. The document provides examples of dividing integers with step-by-step workings and checks the sign of the answer according to the rules.