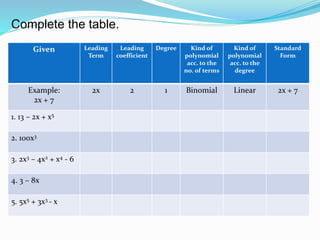
The document defines terms related to polynomials such as numerical coefficient, literal coefficient, degree, similar terms, monomial, binomial, trinomial, multinomial. It also defines the different kinds of polynomials according to the number of terms and degree such as constant, linear, quadratic, cubic, quartic, quintic polynomials. It provides examples of determining the degree, kind according to number of terms, leading term, leading coefficient of a polynomial and writing it in standard form.