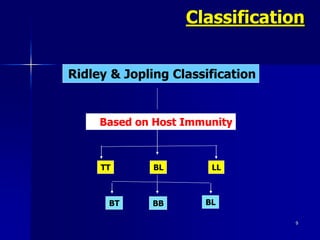
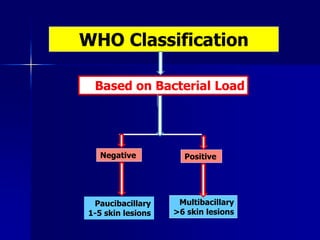
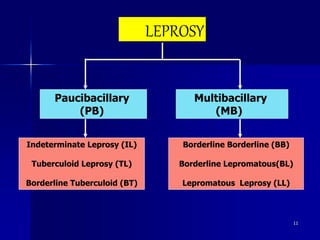
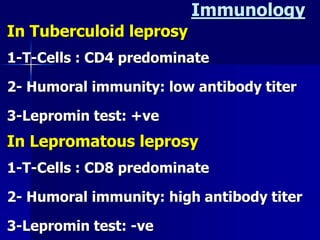
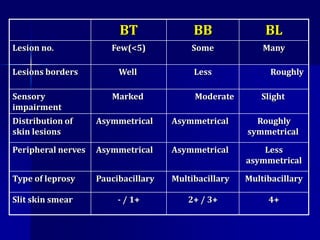
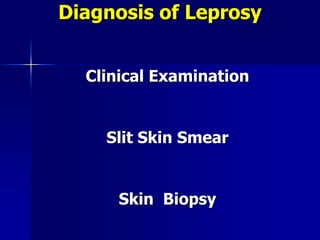
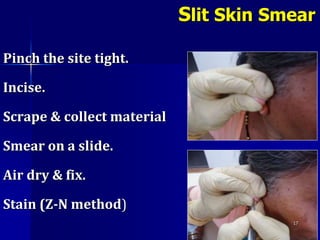
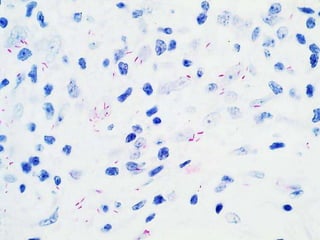
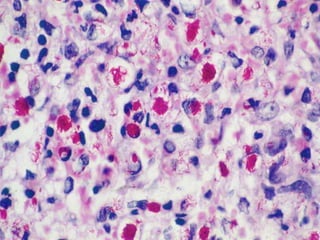
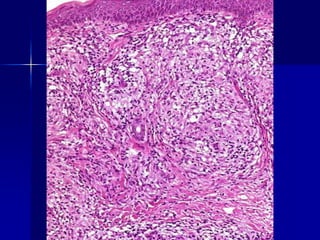
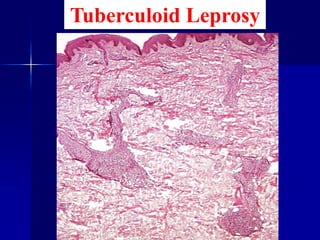
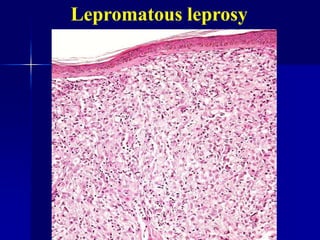
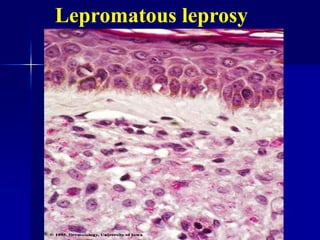
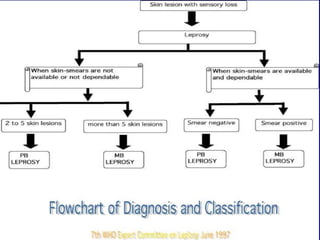
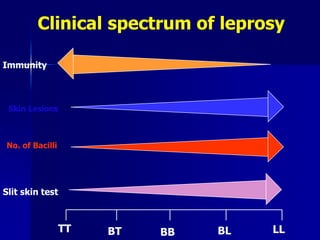
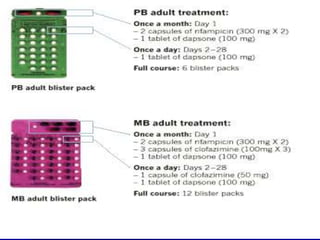
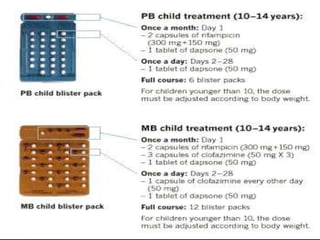
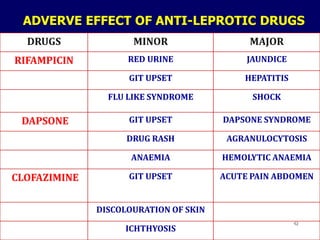
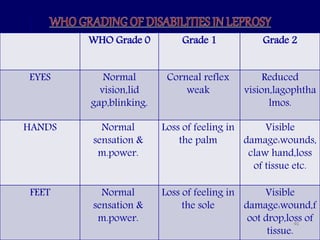
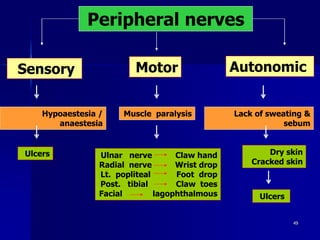
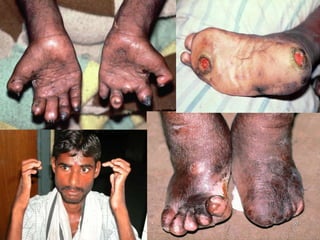
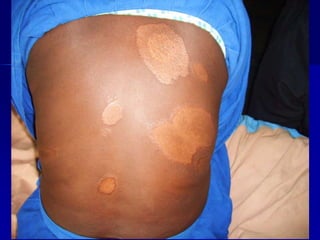
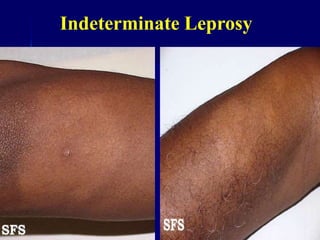
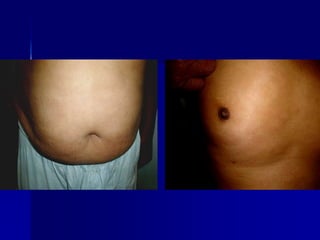
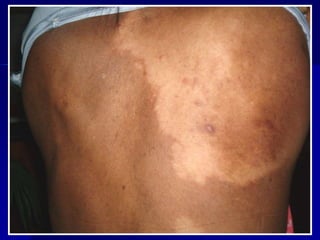
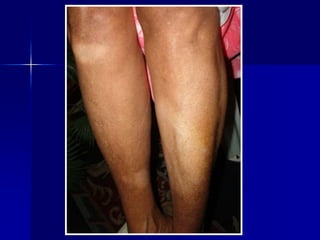
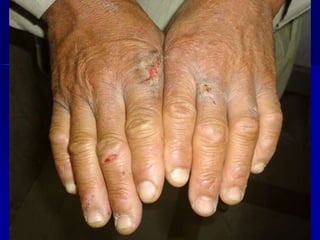
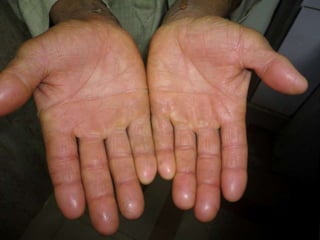
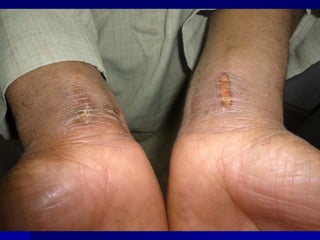
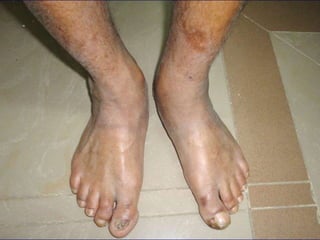
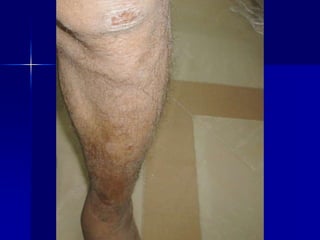
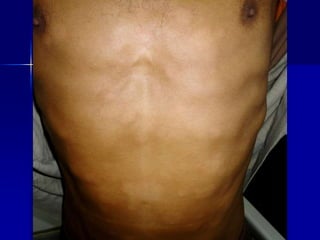
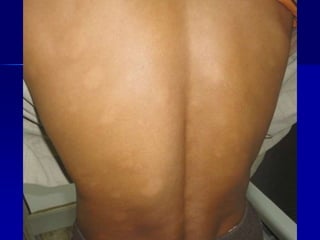
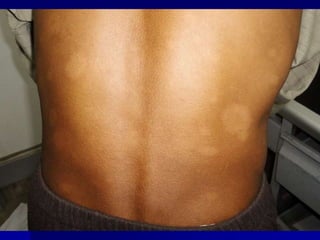
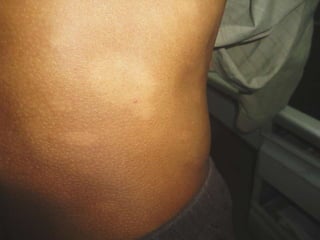
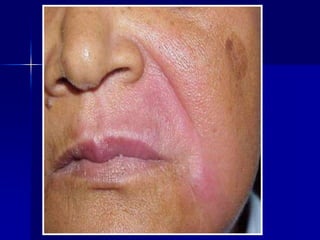
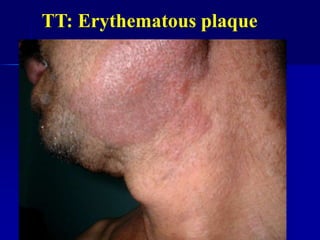
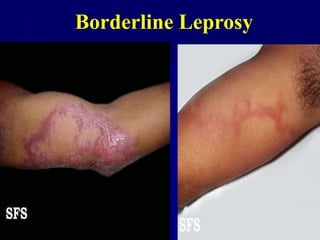
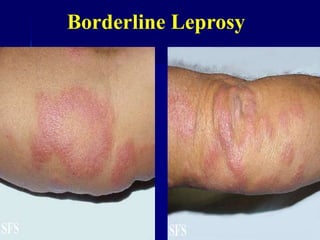
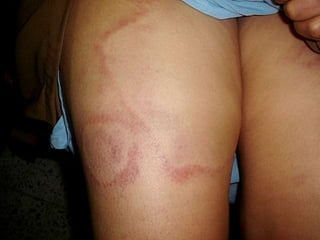
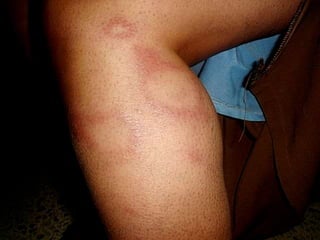
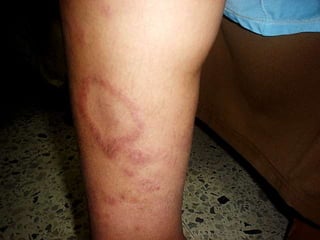
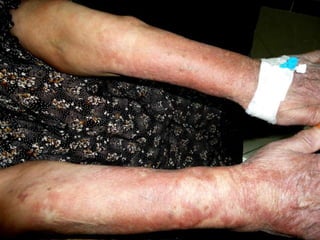
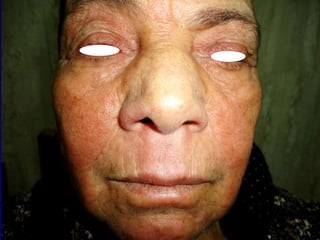
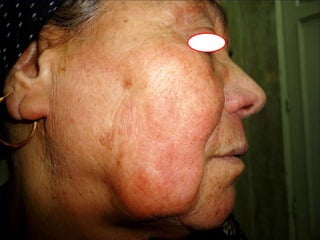
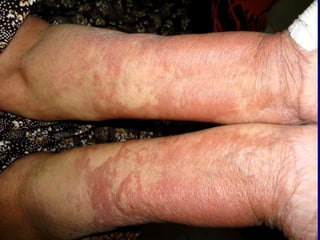
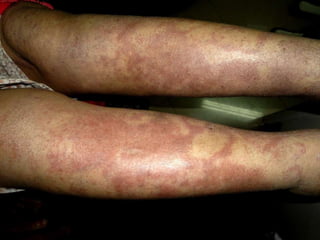
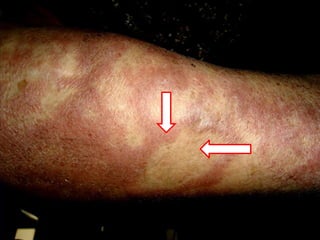
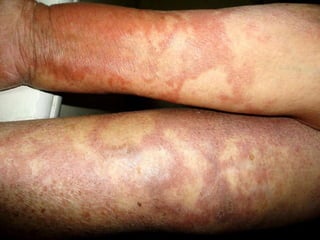
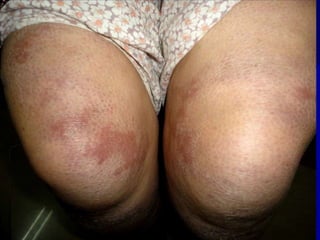
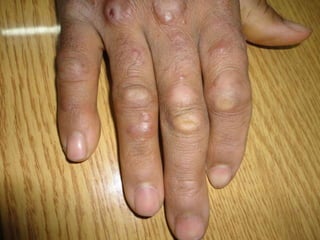
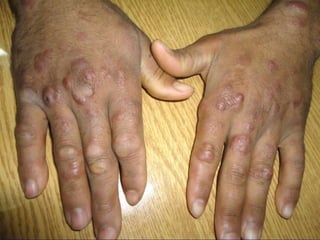
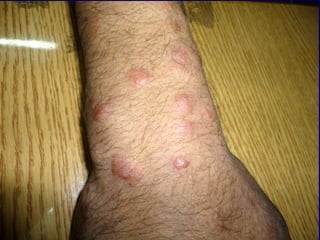
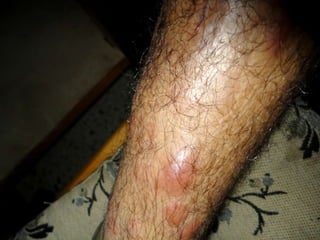
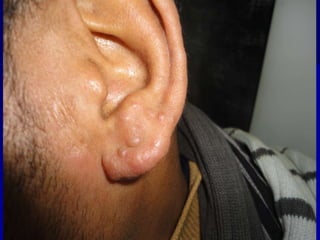
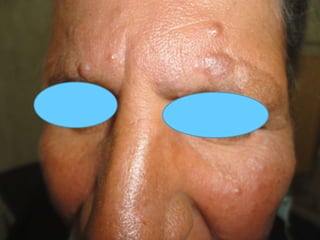
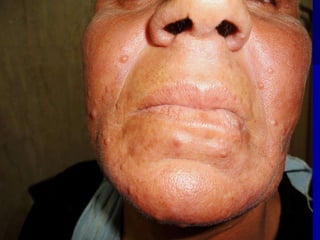
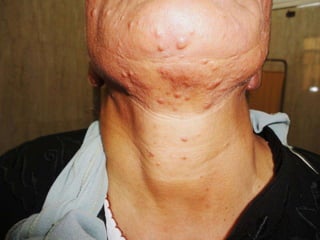
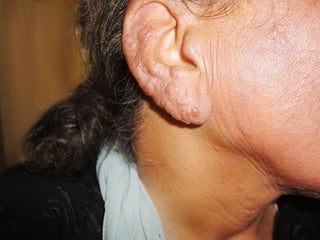
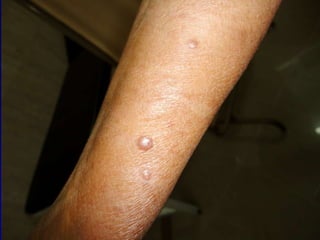
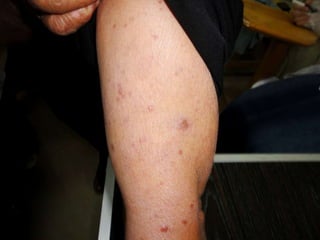
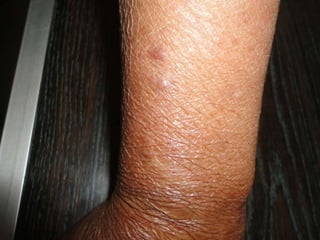
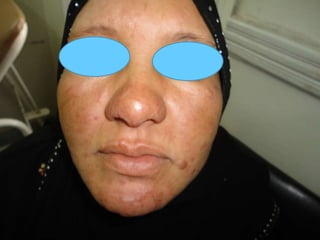
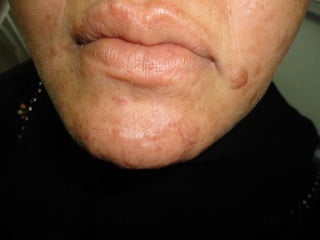
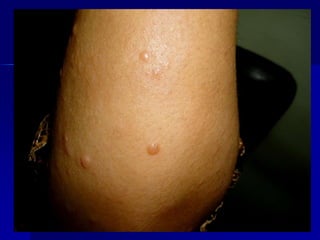
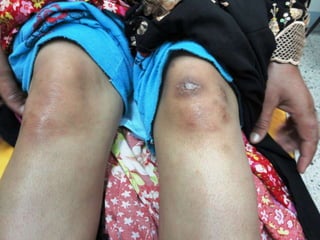
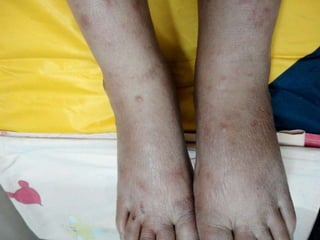
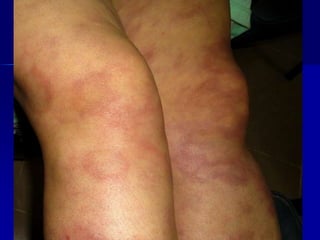
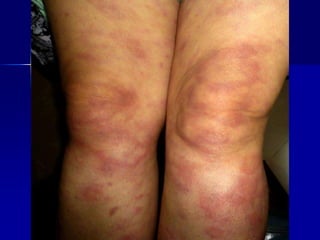
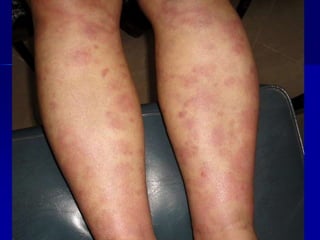
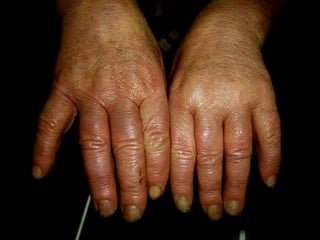
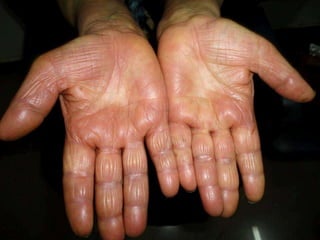
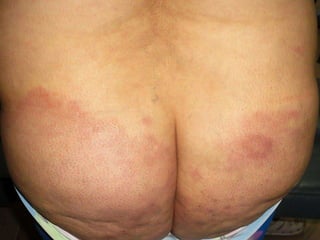
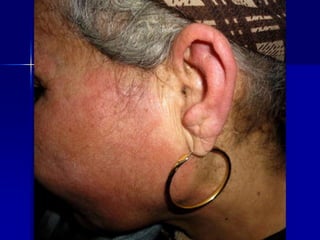
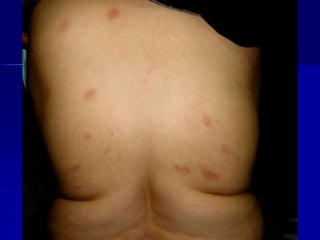
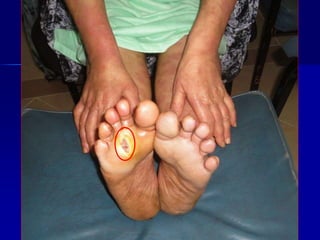
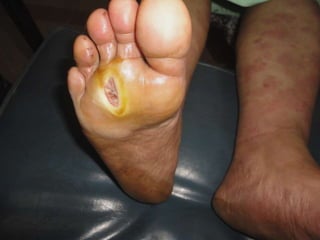
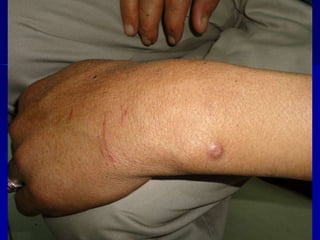
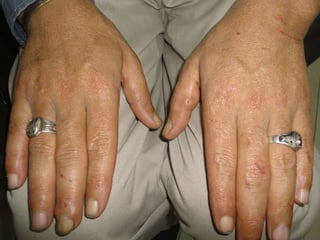
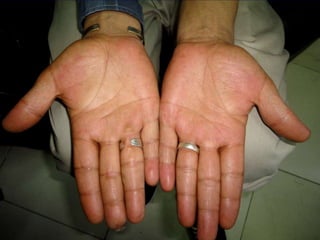
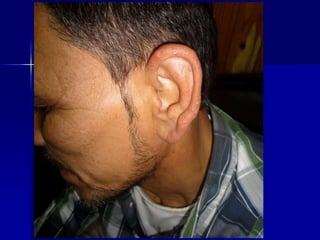
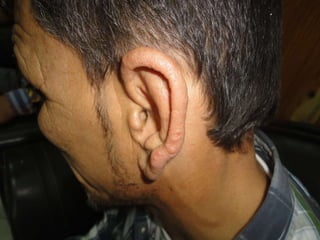
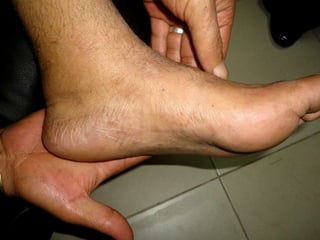
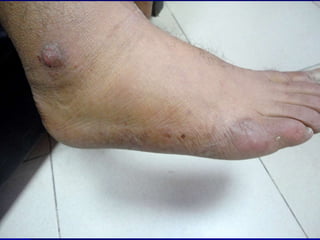
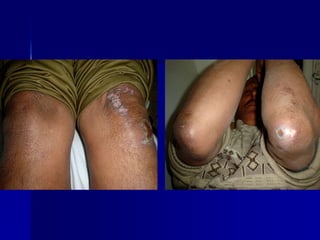
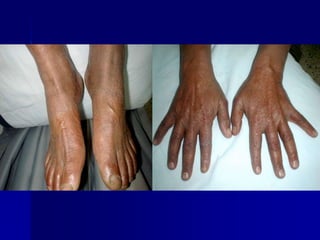
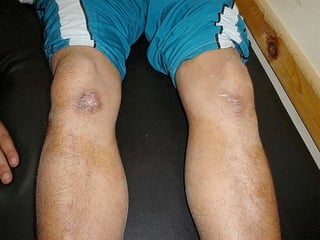
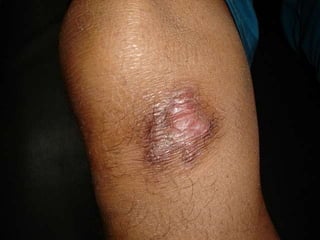
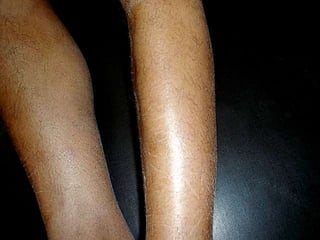
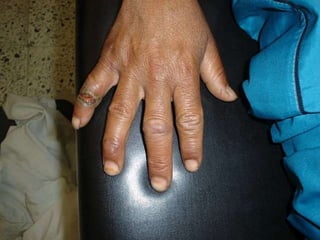
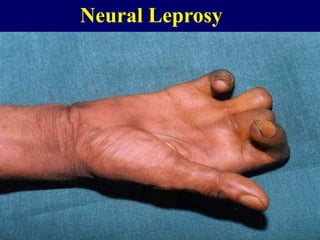
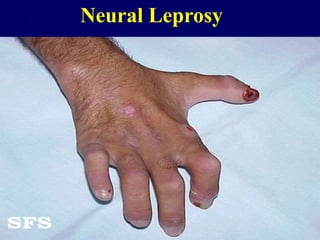
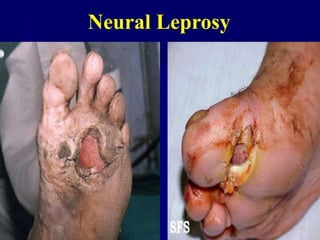
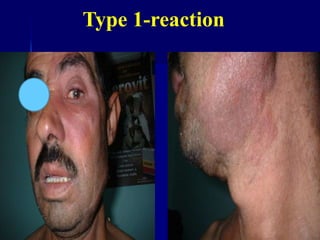
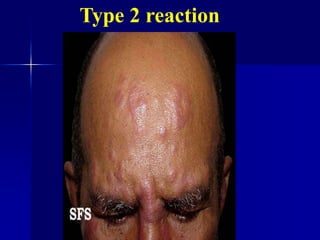
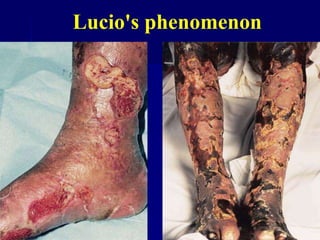
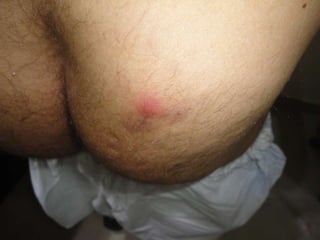
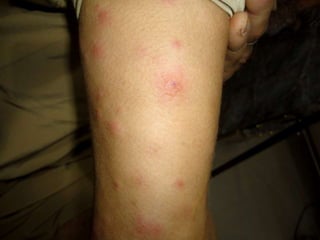
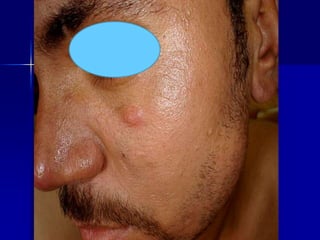
Leprosy is a chronic infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium leprae, primarily affecting the peripheral nerves, skin, and mucous membranes, with higher prevalence in Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America. Transmission occurs mainly through droplet infection, human contact, and occasionally from other animal carriers; early diagnosis and treatment with multi-drug therapy (MDT) are crucial for preventing complications and disabilities. Clinical classifications are based on bacterial load and host immunity, with leprosy presenting various forms and requiring specific therapeutic regimens.