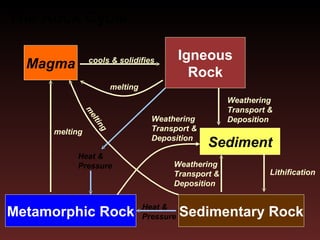
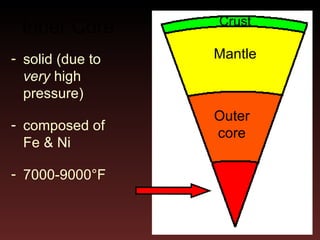
The document summarizes the rock cycle and key components of Earth's structure. It describes how igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks form through processes like cooling of magma, weathering and transport, lithification under pressure, and transformation under heat and pressure. It also outlines Earth's inner core, outer core, mantle and crust layers, their compositions and properties.