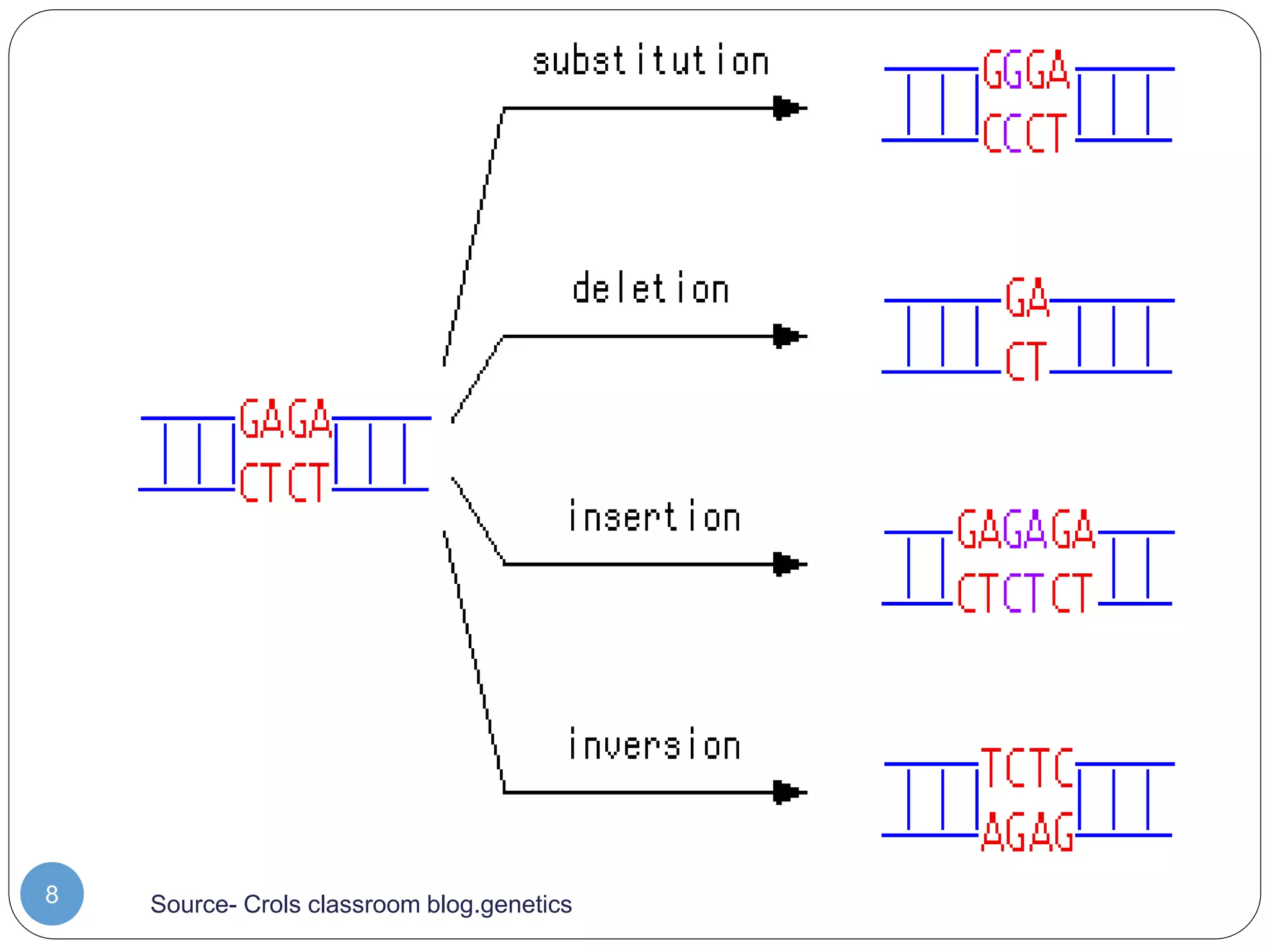
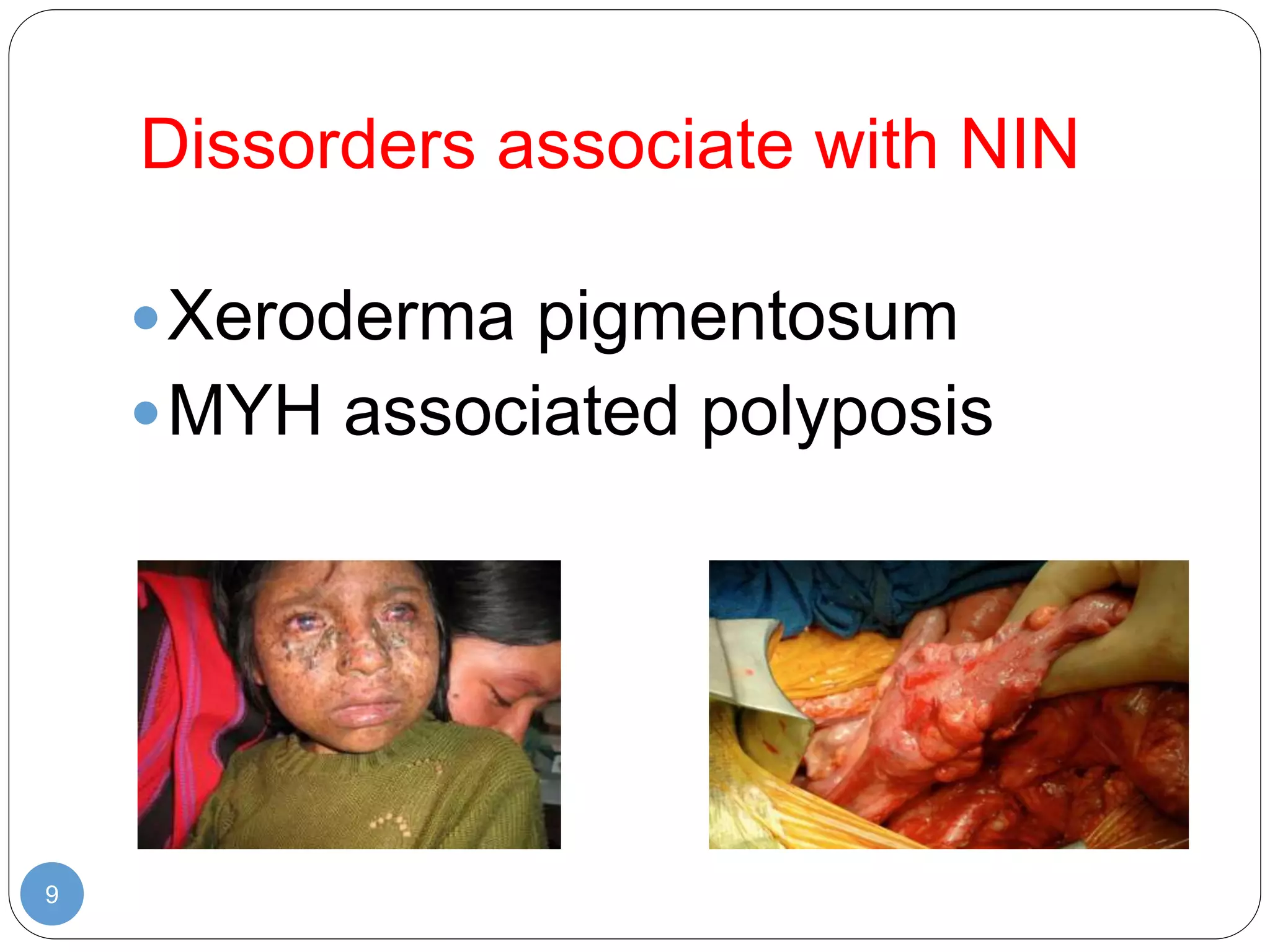
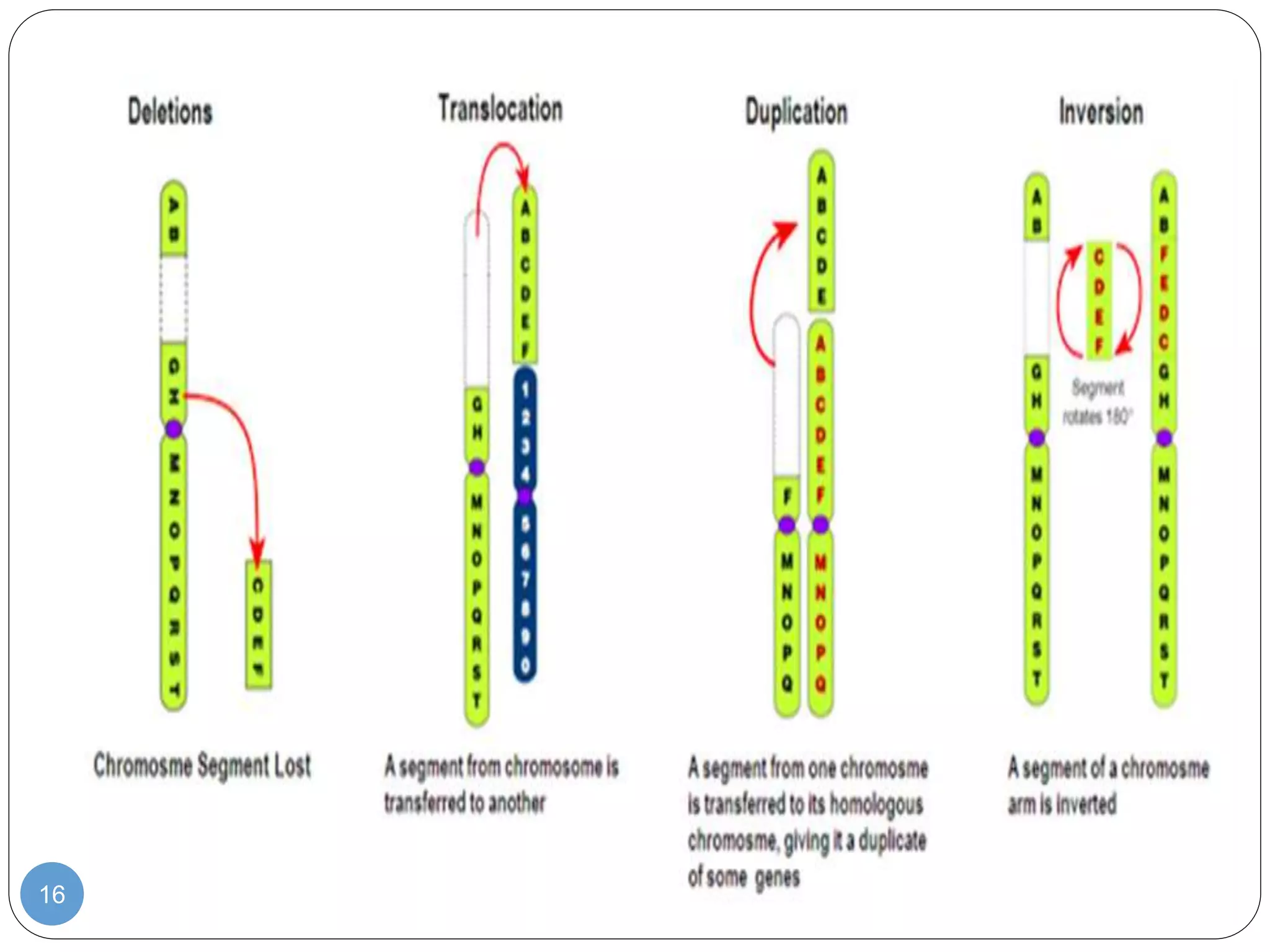
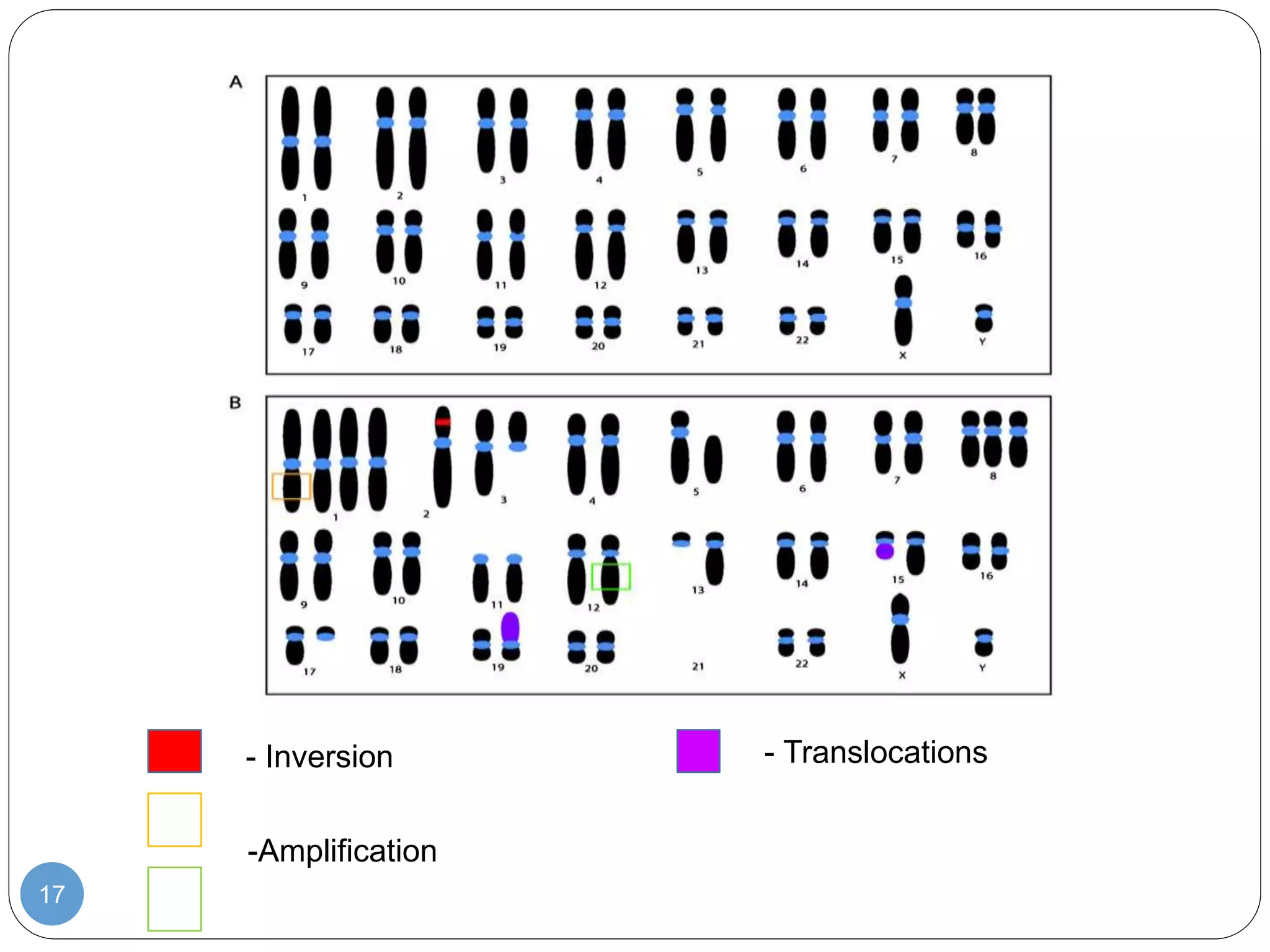
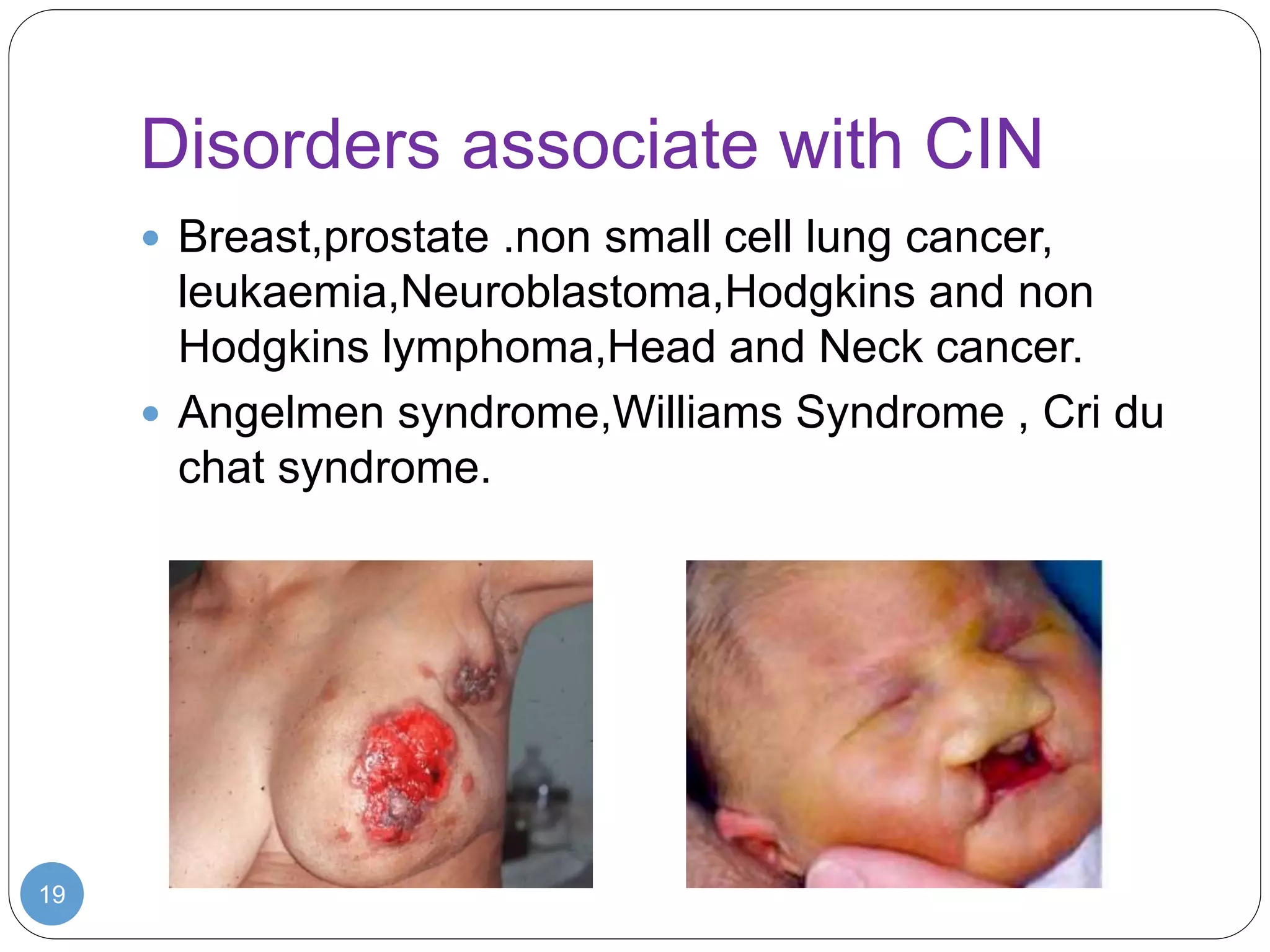
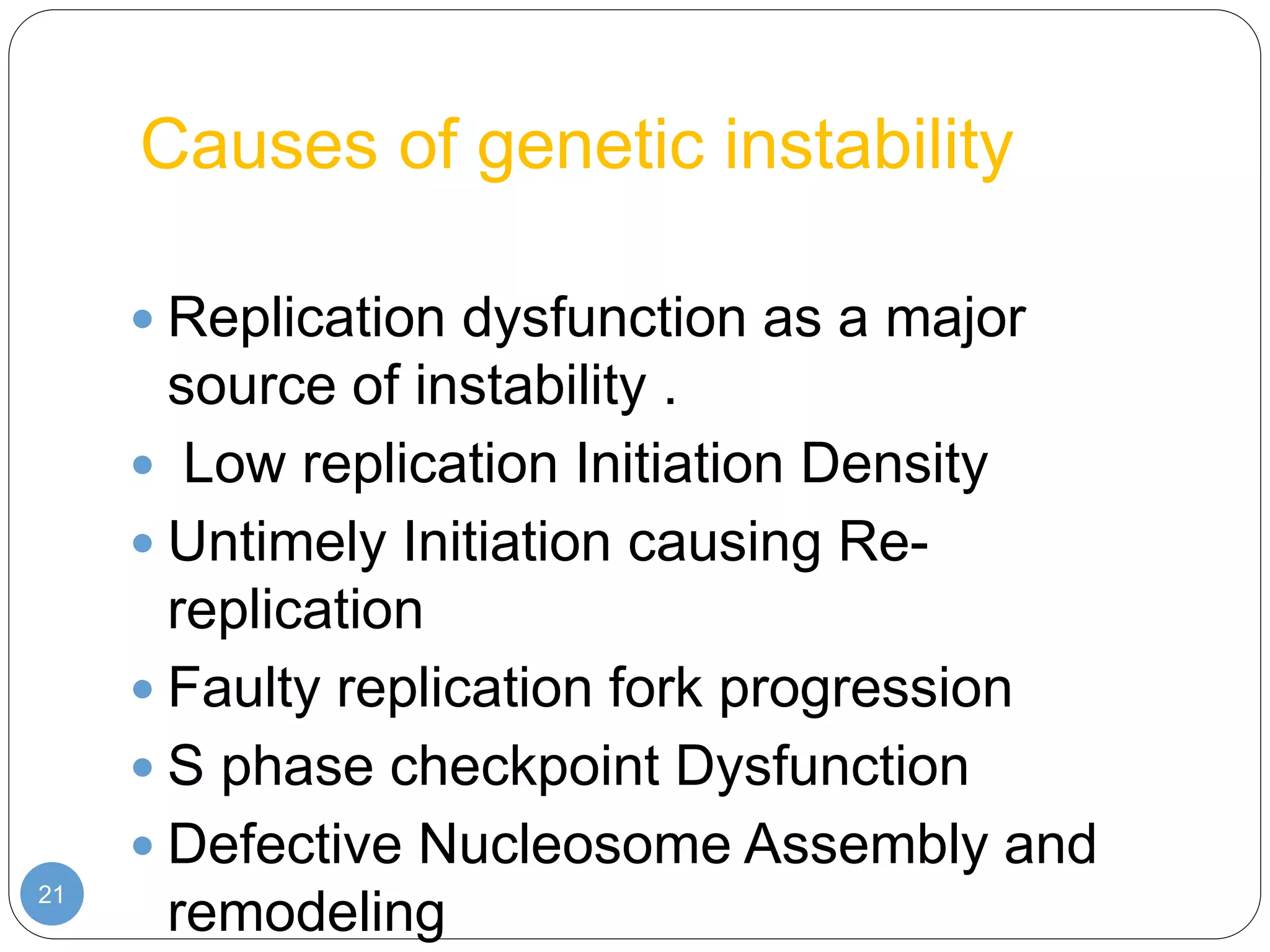
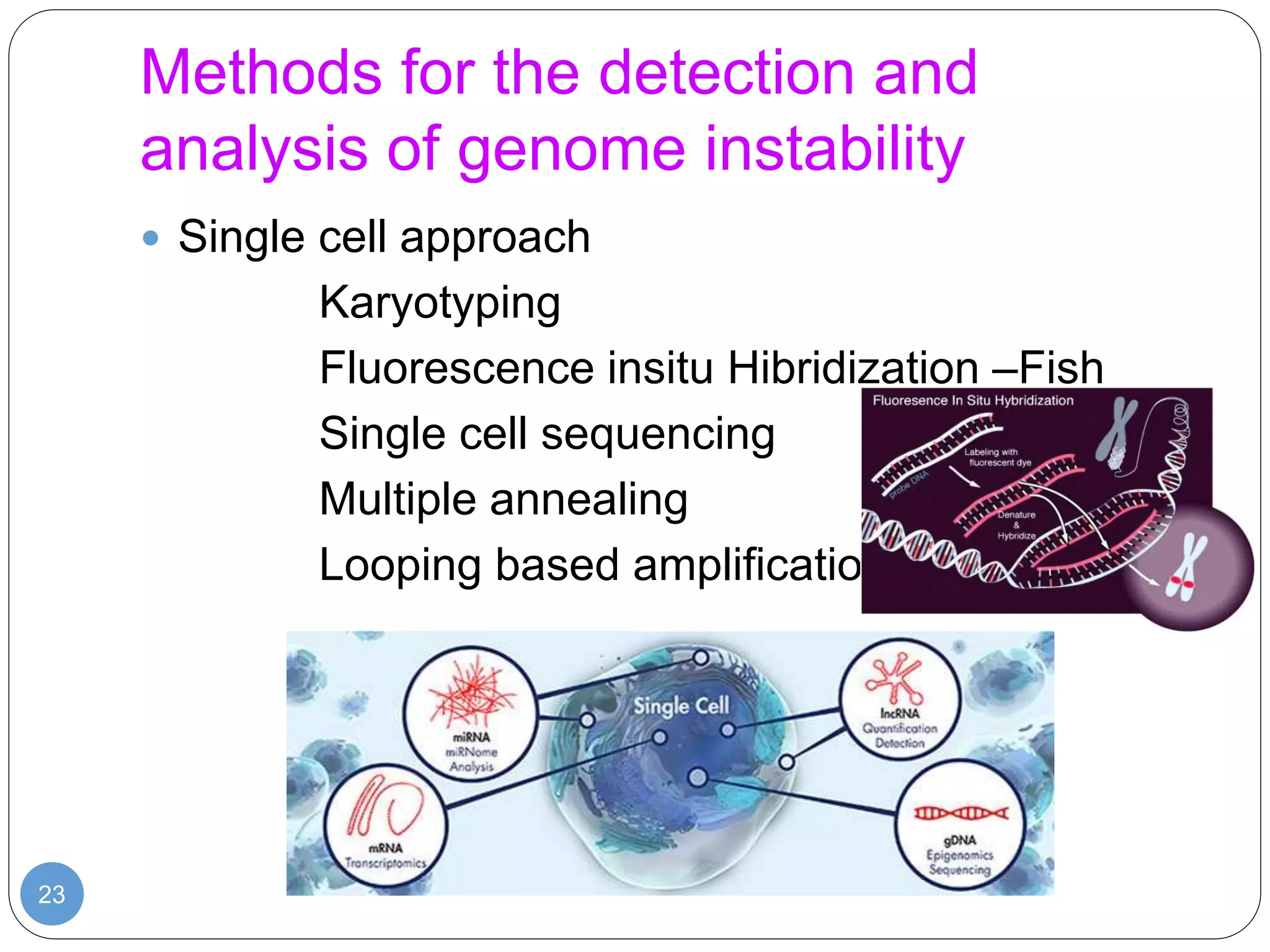
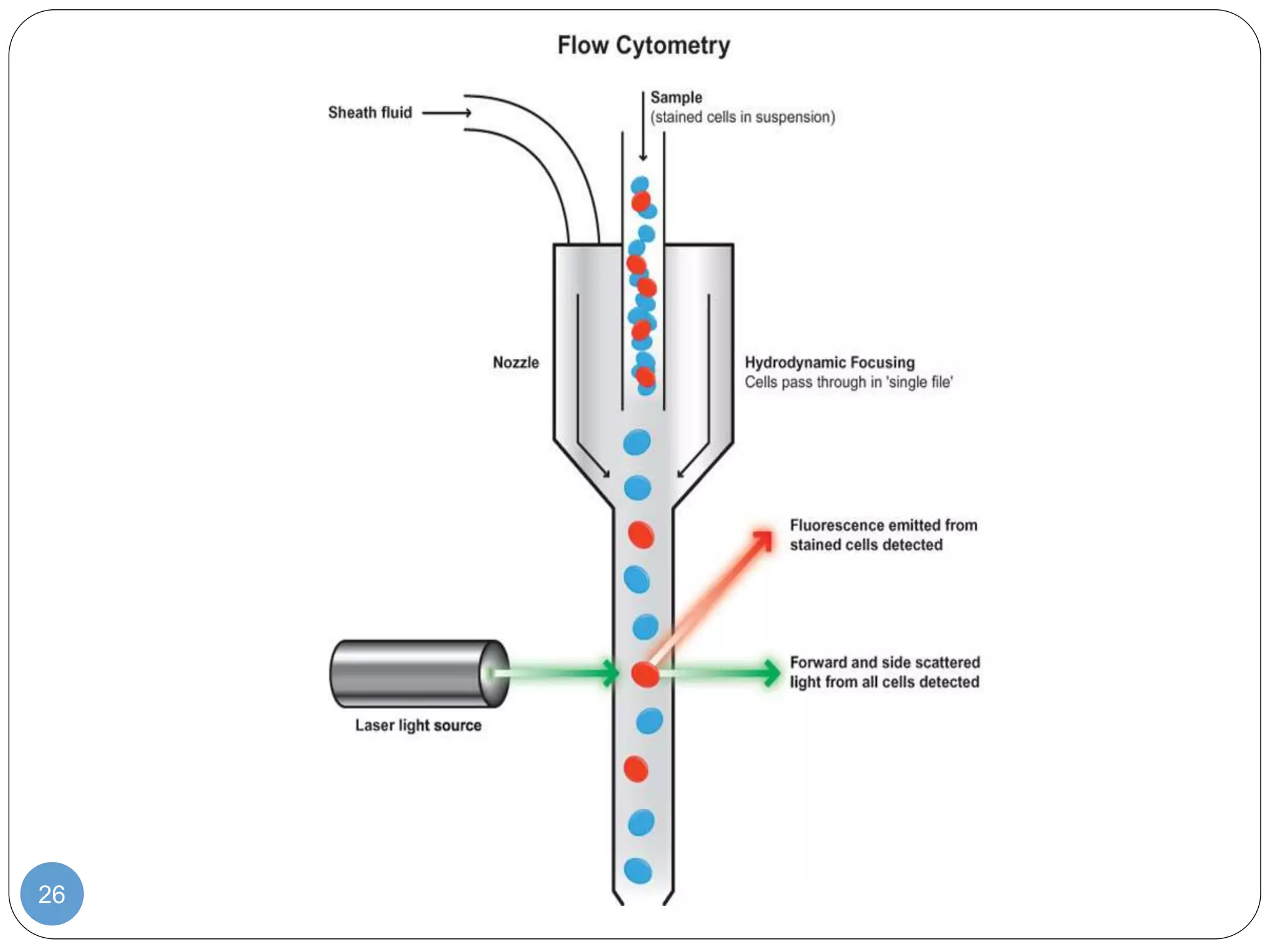
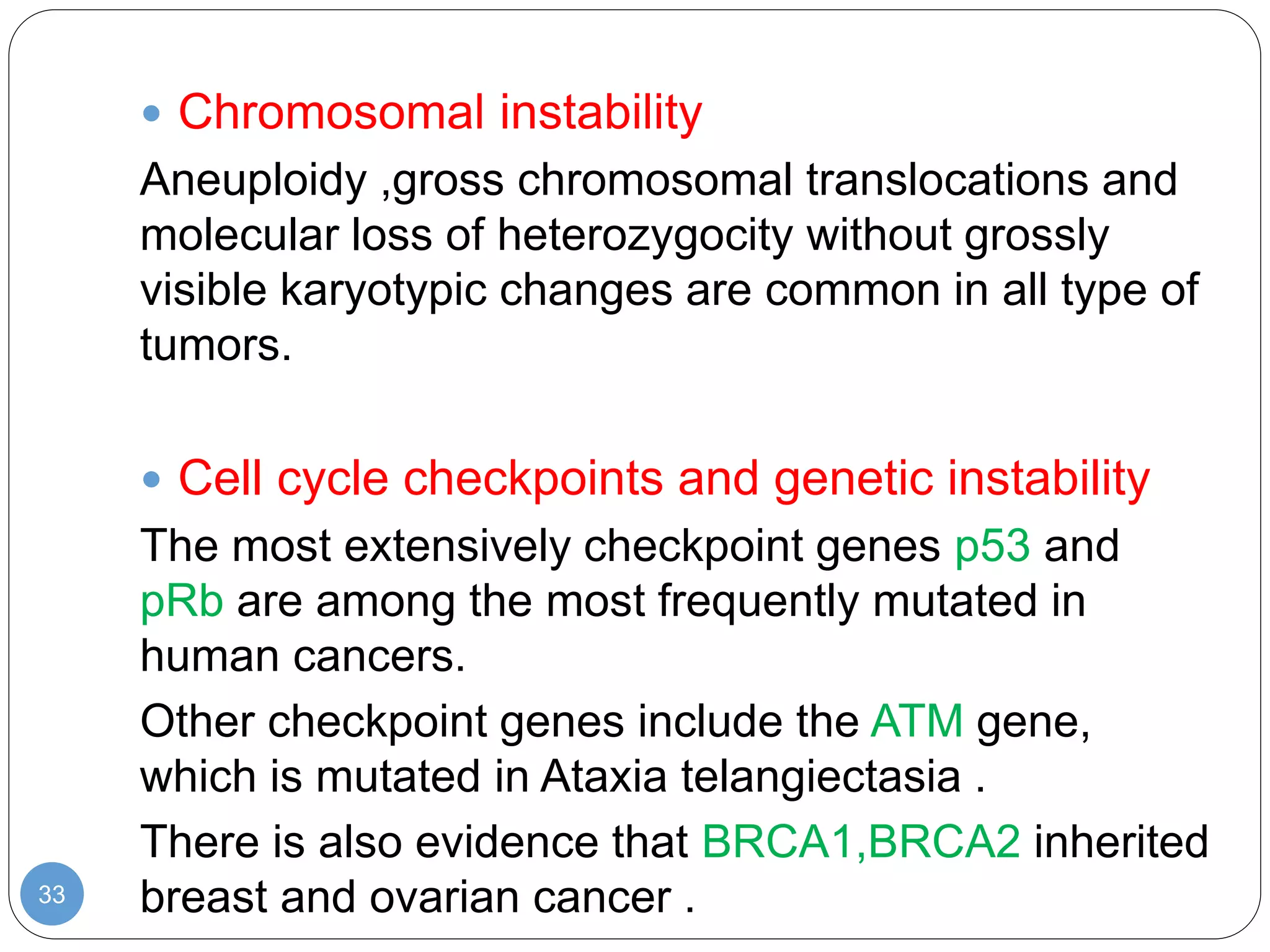
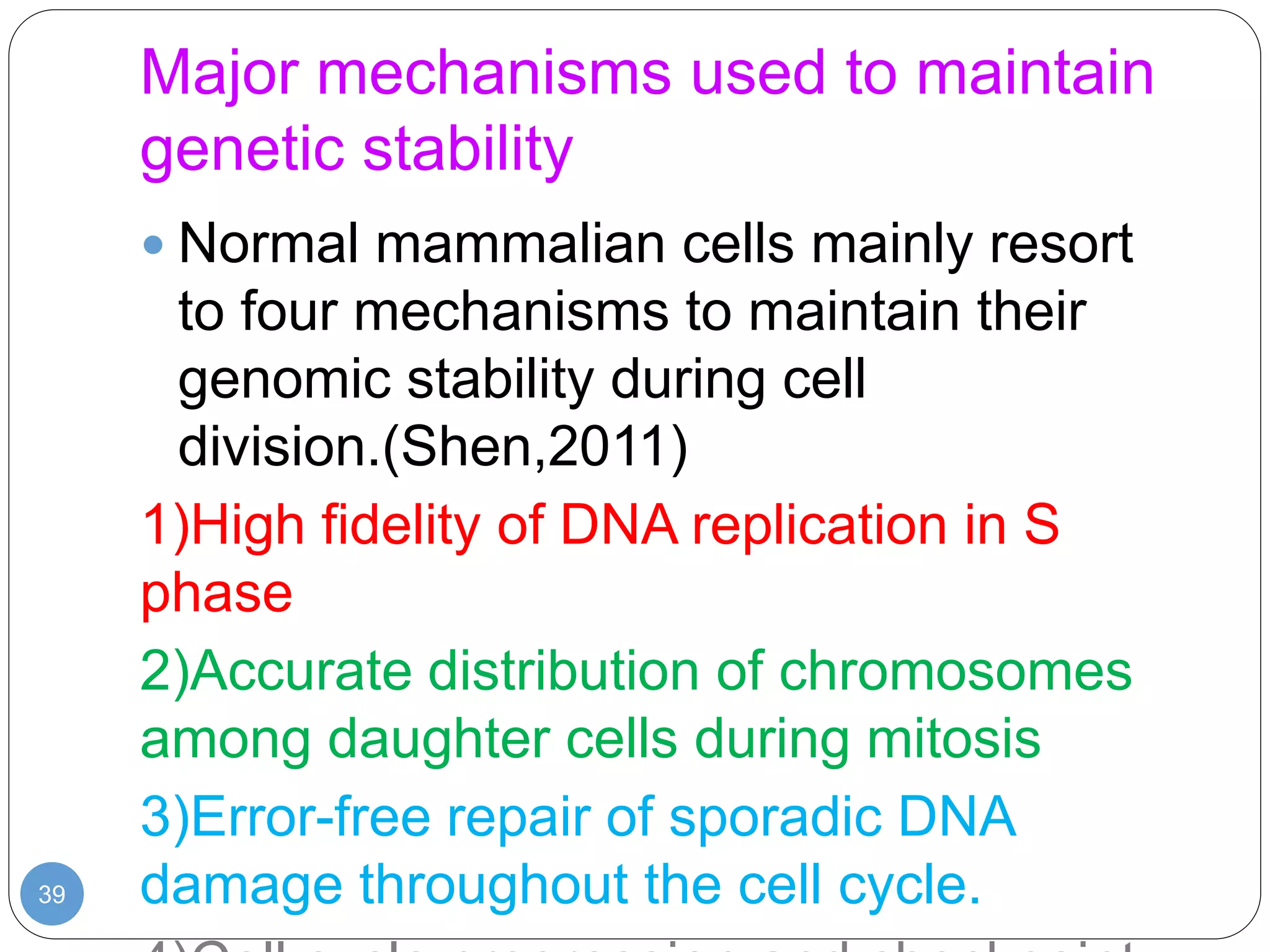
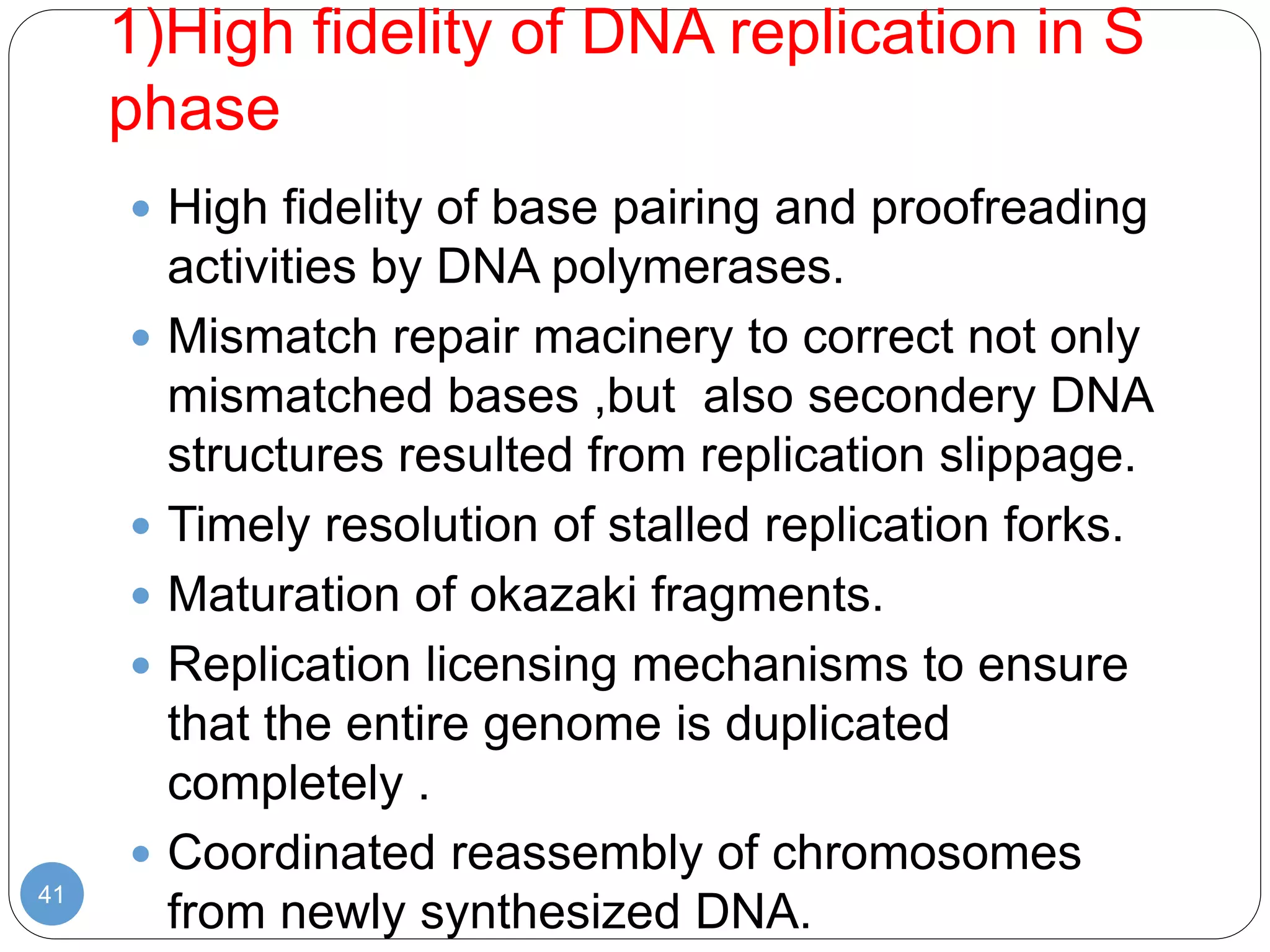
This document discusses genetic instability. It defines genetic instability as an increased rate of genomic alterations ranging from point mutations to chromosome rearrangements. It describes three main types: nucleotide instability, microsatellite instability, and chromosomal instability. Causes of genetic instability include replication errors, defects in DNA repair pathways, and issues during cell division. Methods for detecting instability include karyotyping, FISH, and array technologies. Genetic instability is a hallmark of cancer and helps accelerate tumor genesis by increasing mutations. Cells use mechanisms like DNA proofreading and cell cycle checkpoints to maintain stability.