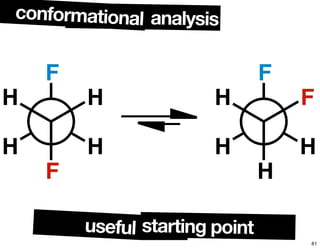
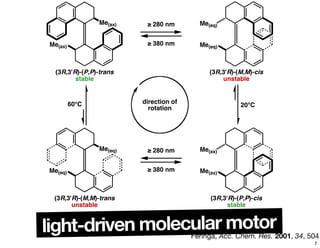
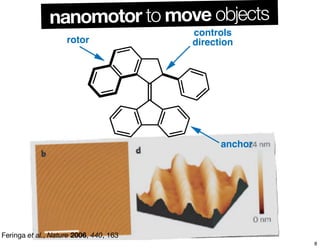
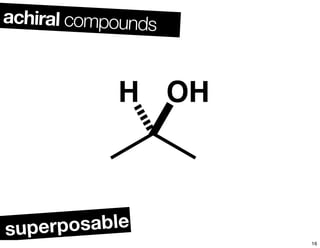
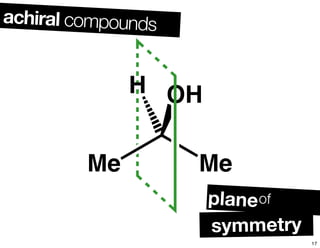
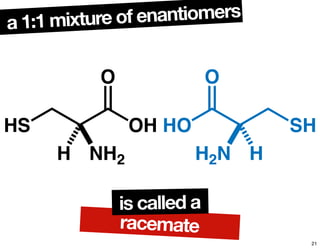
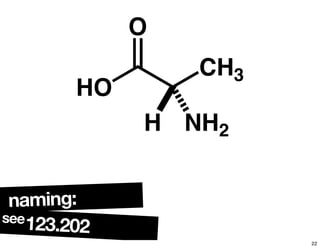
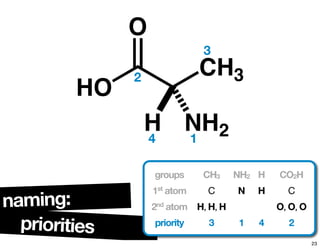
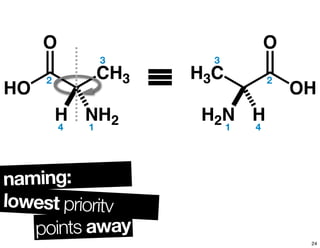
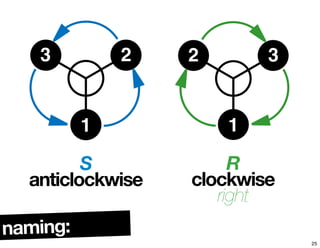
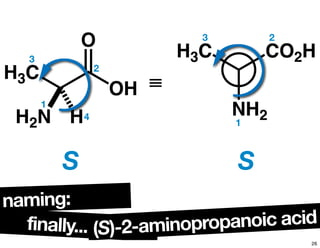
The document discusses various topics related to chirality and stereochemistry including:
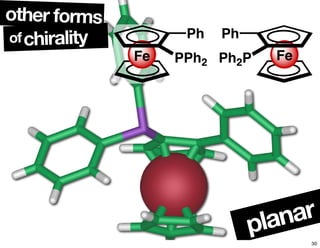
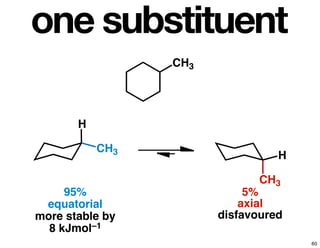
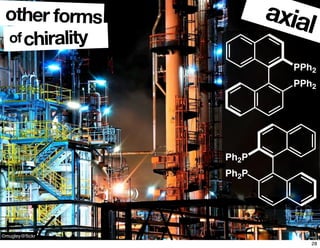
- Different forms that can exhibit chirality beyond just tetrahedral stereocenters.
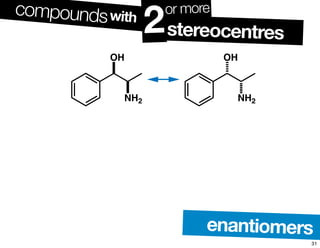
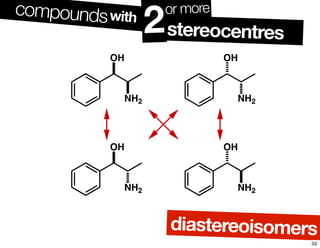
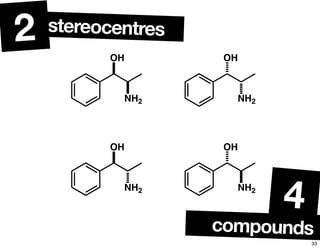
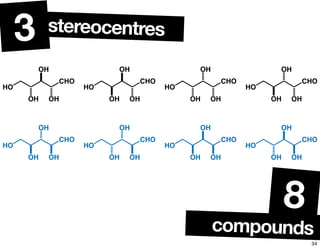
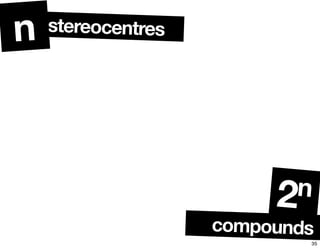
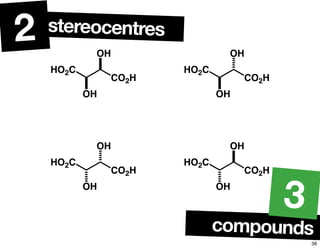
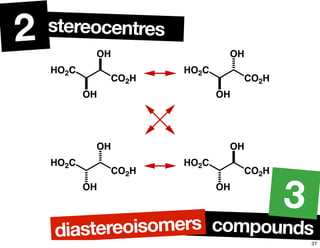
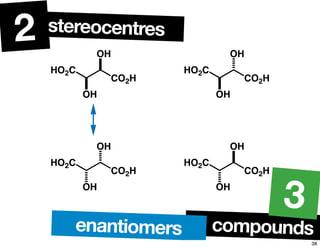
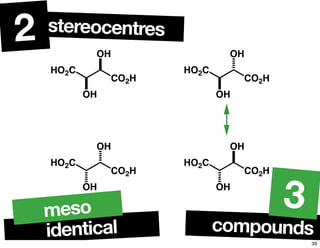
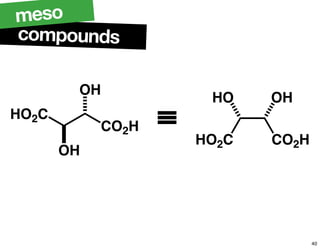
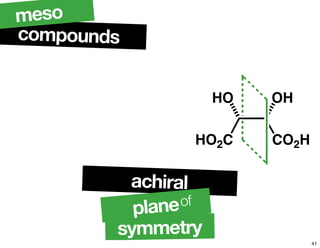
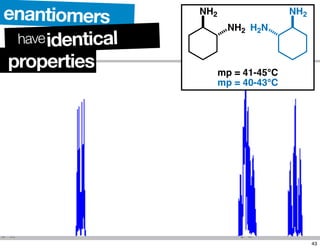
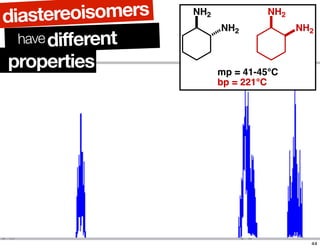
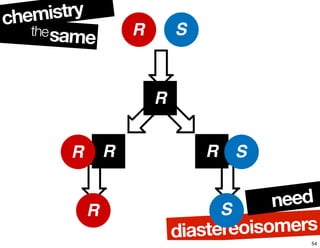
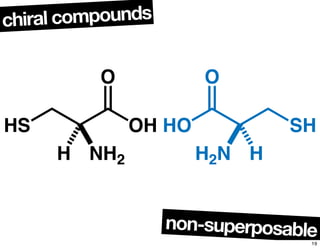
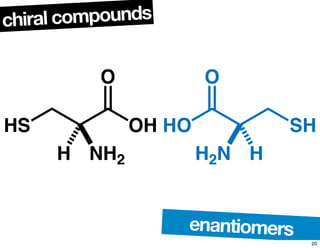
- The relationship between enantiomers, diastereomers, and meso compounds for molecules with multiple stereocenters.
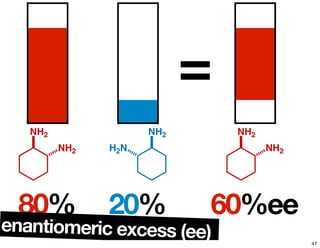
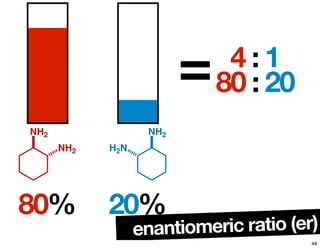
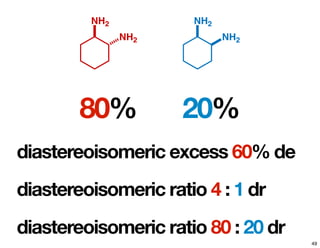
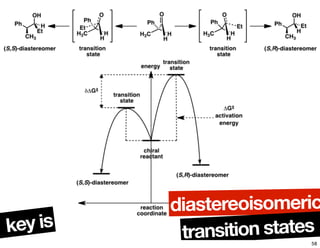
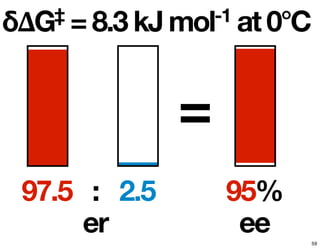
- How purity of chiral compounds is measured in terms of enantiomeric excess and ratio, and diastereomeric excess and ratio.
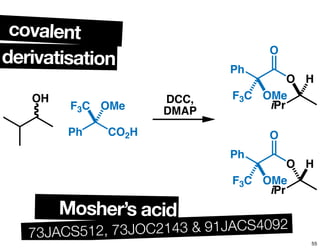
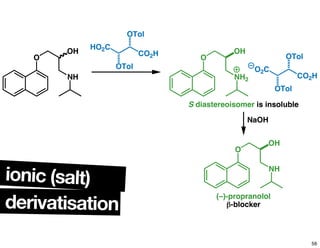
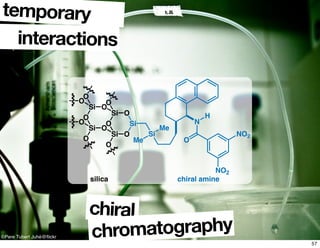
- Common methods for determining enantiomeric excess such as derivatization reactions and chiral chromatography.











![chiralityof
other forms helical
P [8]helicene M [8]helicene
29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1123713a-161117223754/85/Lecture1-123713A-30-320.jpg)