This document provides an overview of key concepts related to the financial system including:
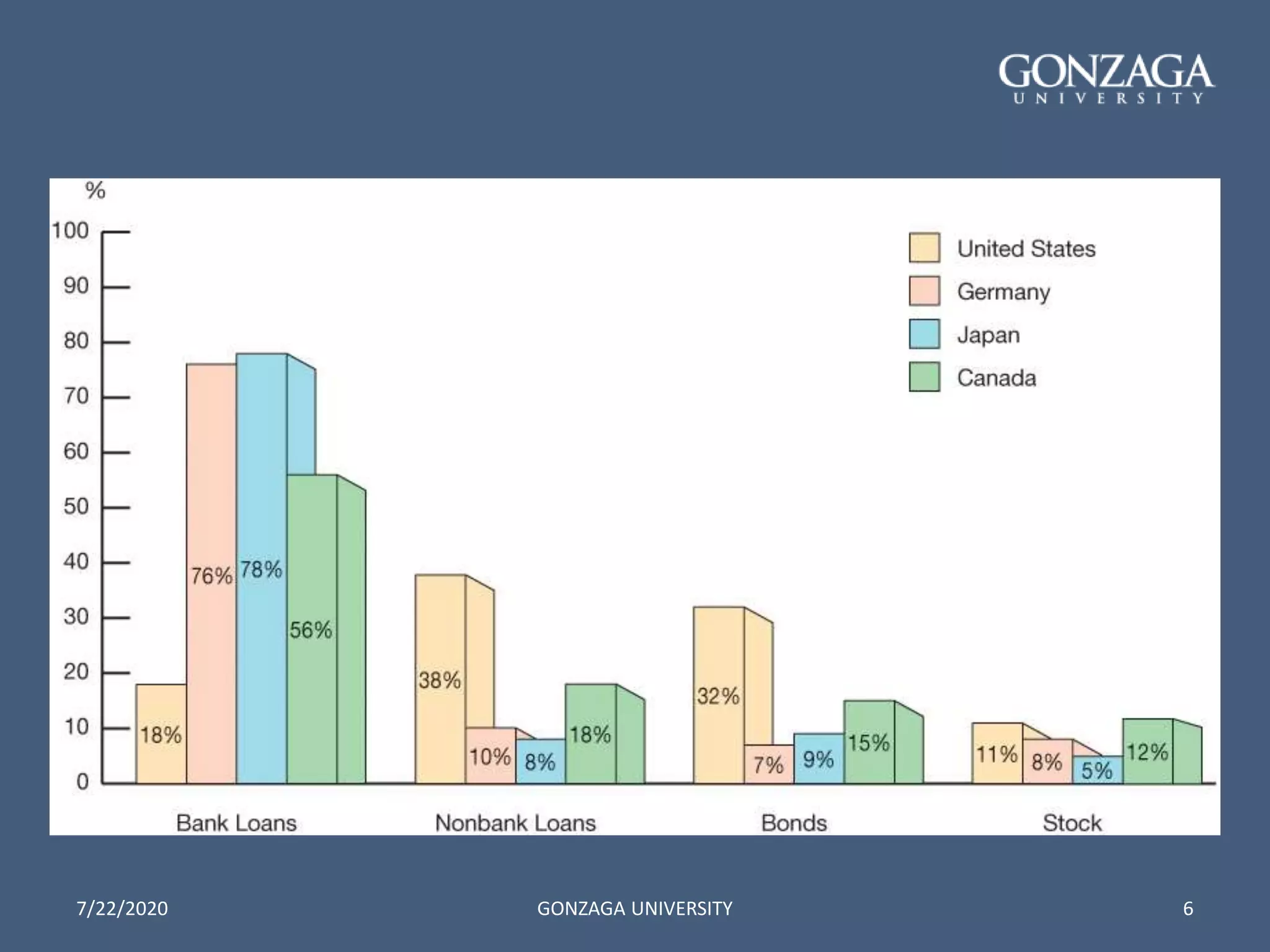
- 8 basic facts about the global financial system such as the predominant role of banks and importance of debt over equity.
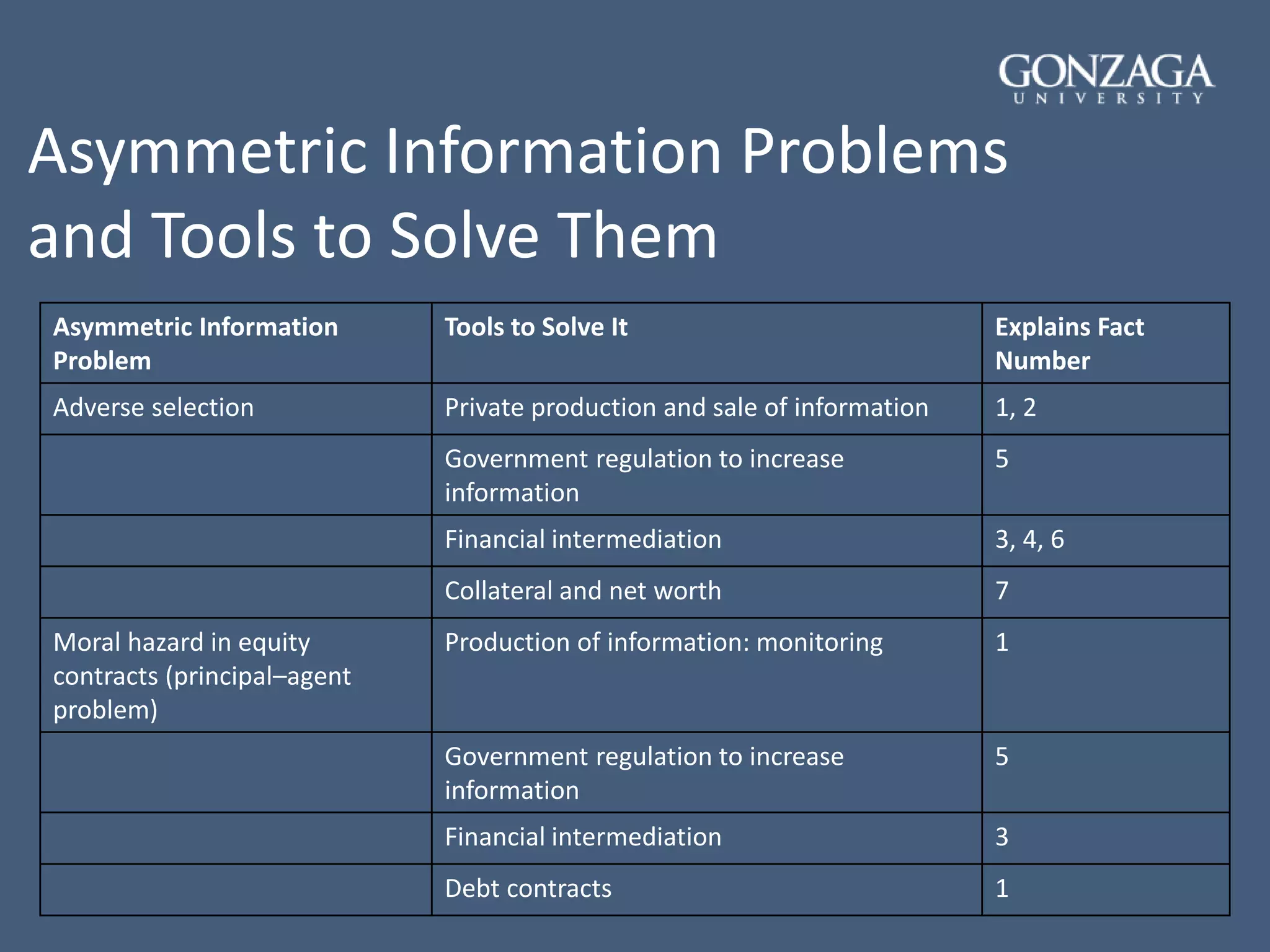
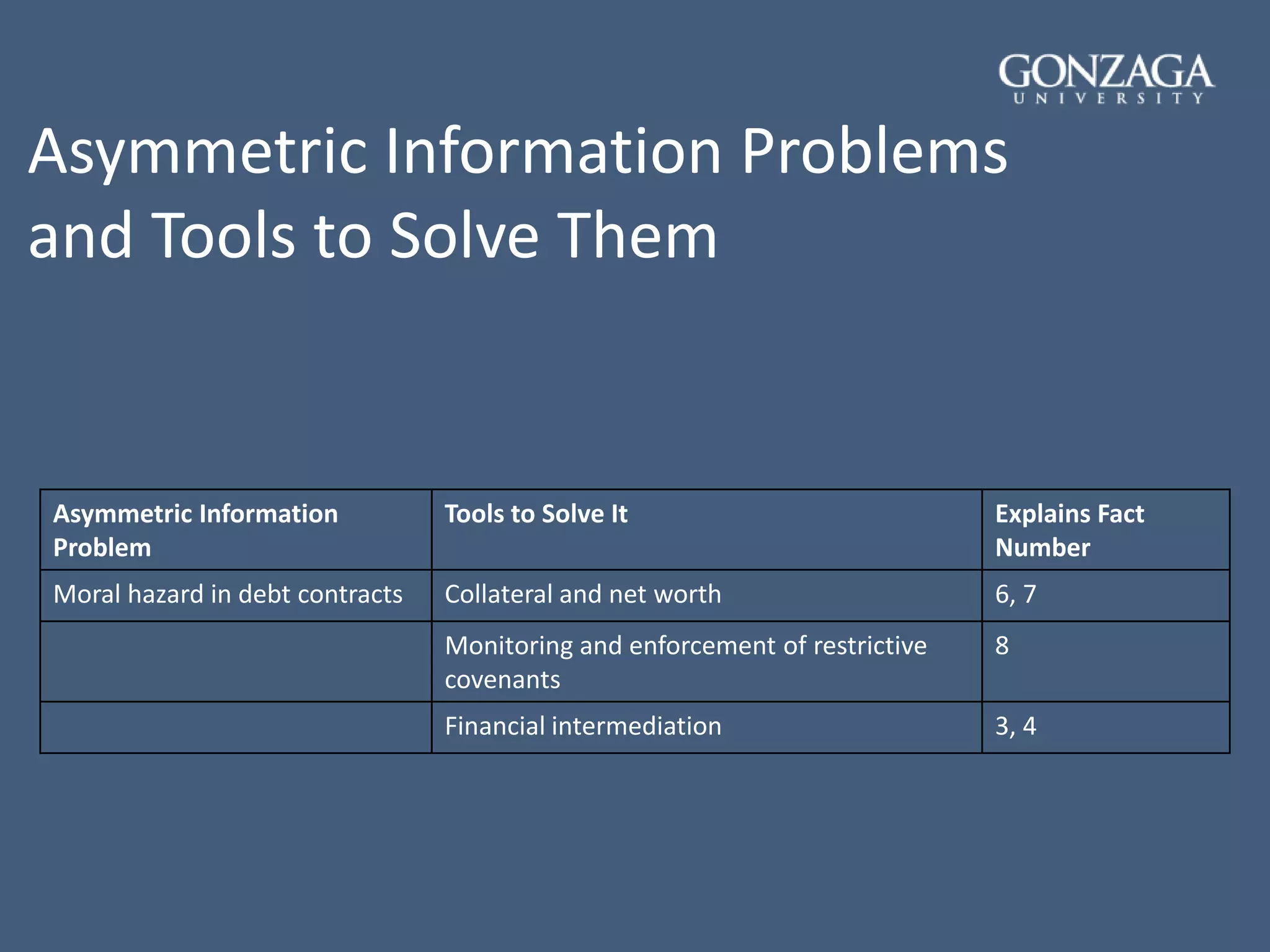
- How transaction costs, asymmetric information, adverse selection, and moral hazard shape the structure and functioning of the financial system.
- Tools used to address problems of adverse selection and moral hazard like monitoring, regulation, intermediation, collateral, and contract design.
- Examples of how conflicts of interest and crises emerge from these issues and their economic impacts.