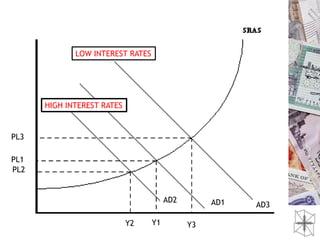
1) Interest rates affect consumption, investment, and net exports which determines aggregate demand. Higher rates decrease borrowing and demand while lower rates increase borrowing and demand.
2) Interest rates can be used to target inflation levels. Higher rates lead to lower inflation while lower rates lead to higher inflation.
3) Changing interest rates also impacts unemployment levels. Raising rates decreases output and employment while lowering rates increases output and employment.