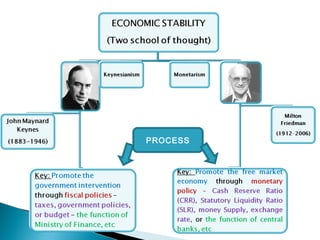
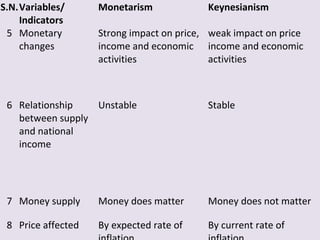
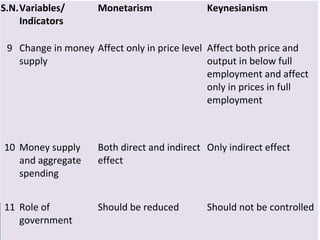
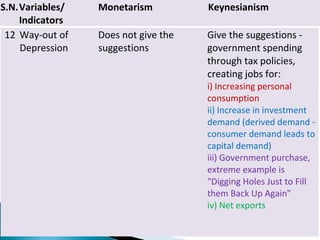
The document compares the monetary and Keynesian approaches to economic stability. The monetary (or monetarist) approach is based on the role of money in stabilizing aggregate demand, and believes that limiting government intervention and controlling the money supply are key. The Keynesian approach focuses on the role of government spending in stabilizing aggregate demand, and does not restrict government intervention. It believes fiscal policy tools like tax rates and government spending are most important for achieving economic stability, especially during downturns when suggested solutions include increasing various types of spending.