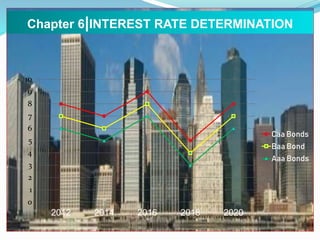
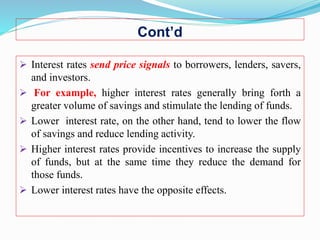
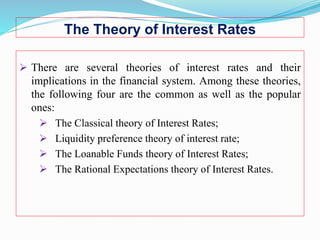
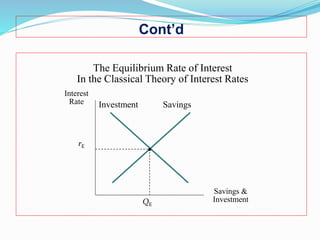
The document discusses several theories of interest rate determination:
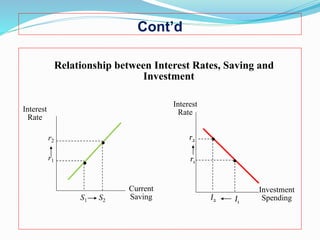
1. The classical theory argues that interest rates are determined by the supply of savings and demand for investment, where the equilibrium rate balances the two.
2. The liquidity preference theory views interest as the price of money, with rates set by demand for and supply of money in the economy.
3. The loanable funds theory sees rates as set by demand for and supply of credit in the economy from savers, borrowers, and foreign actors.